Abstract
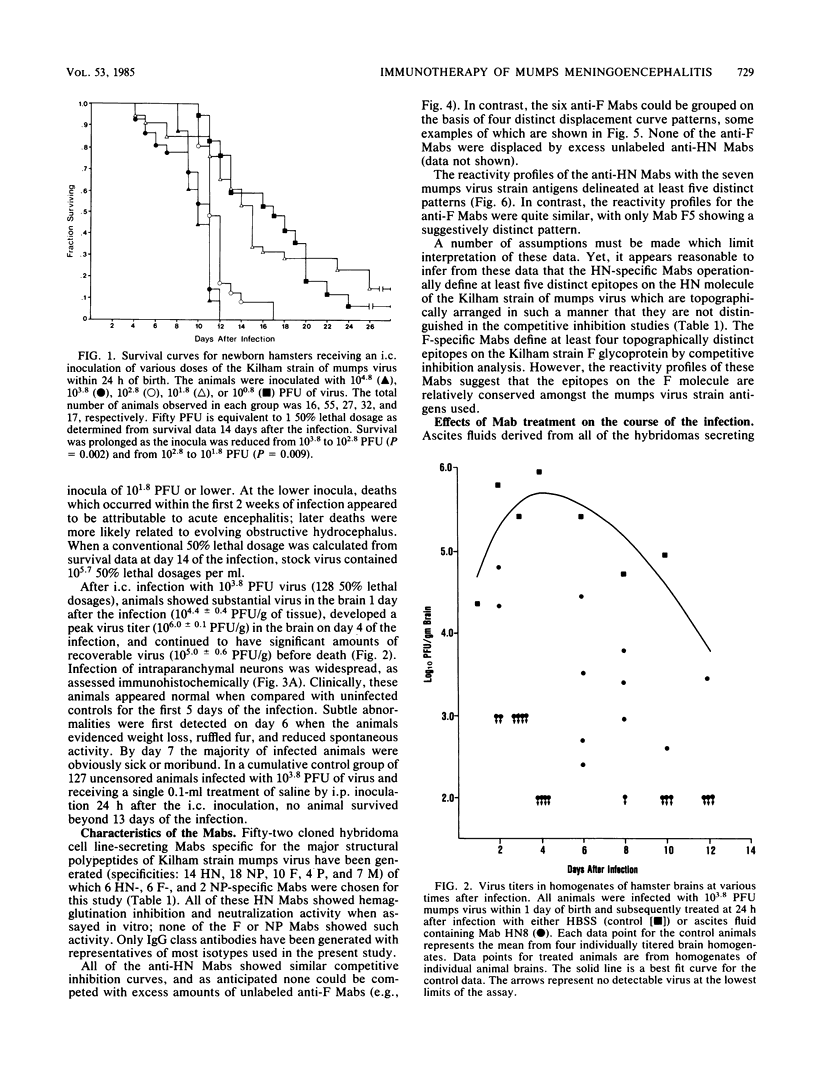
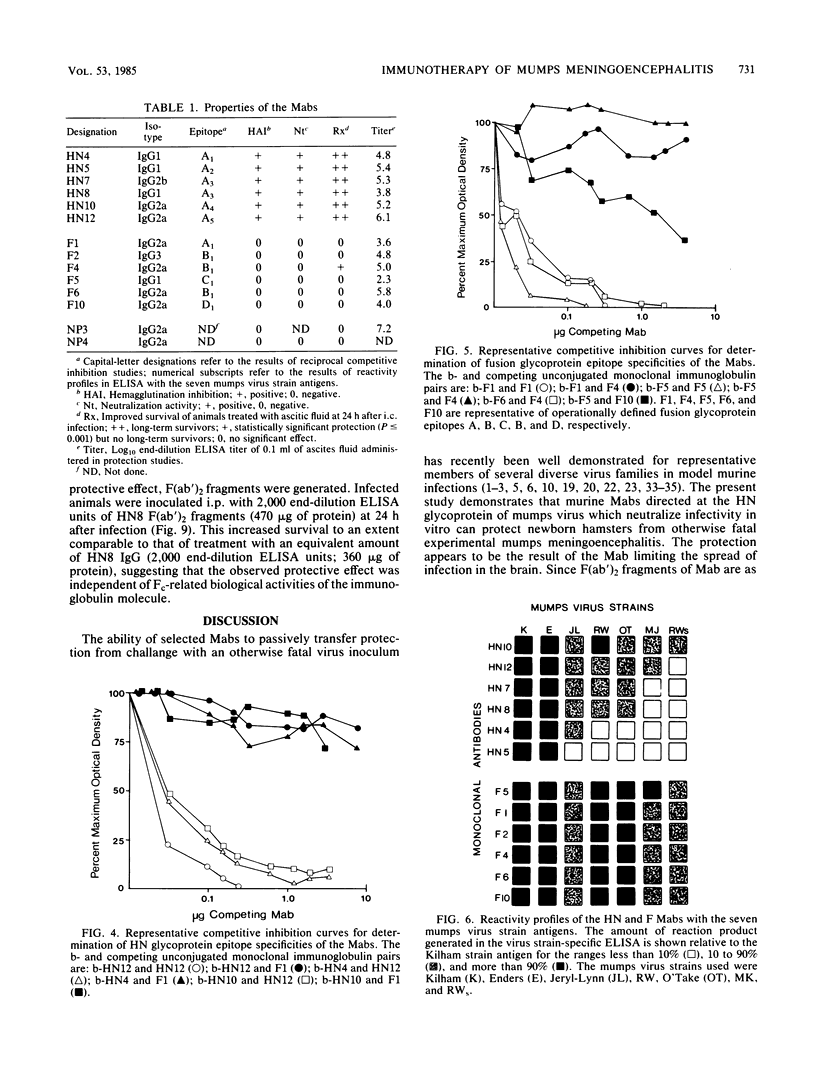
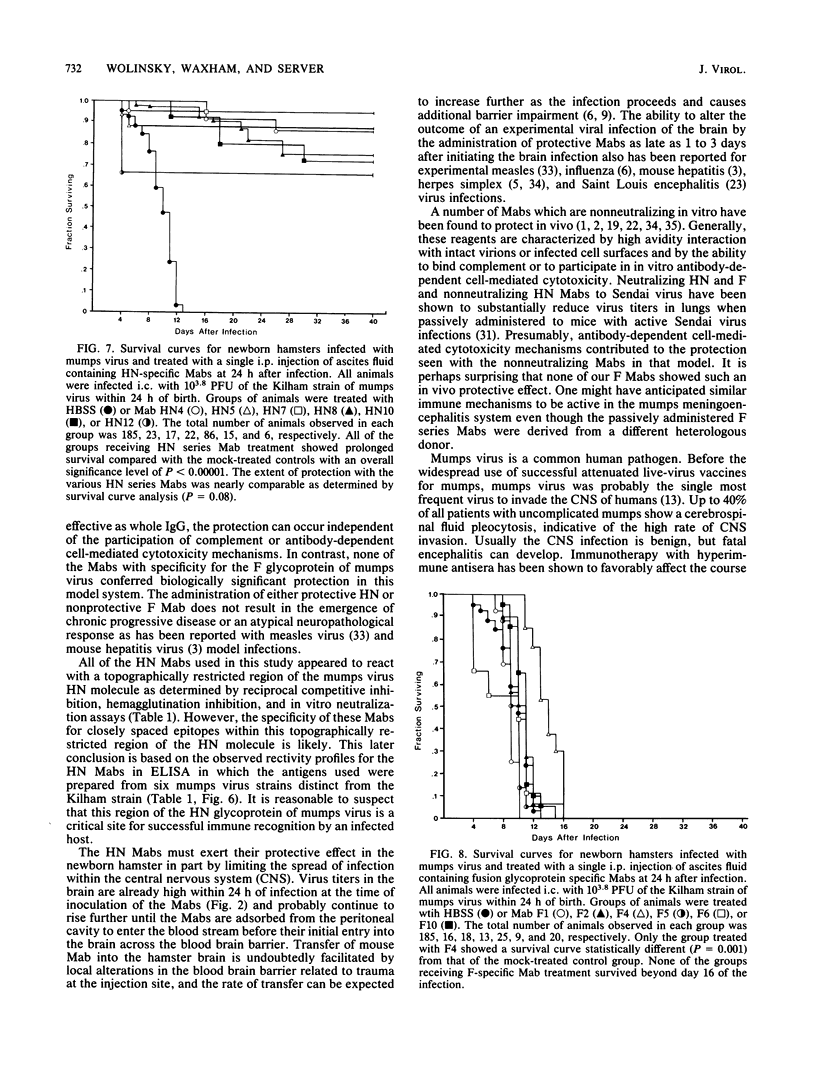
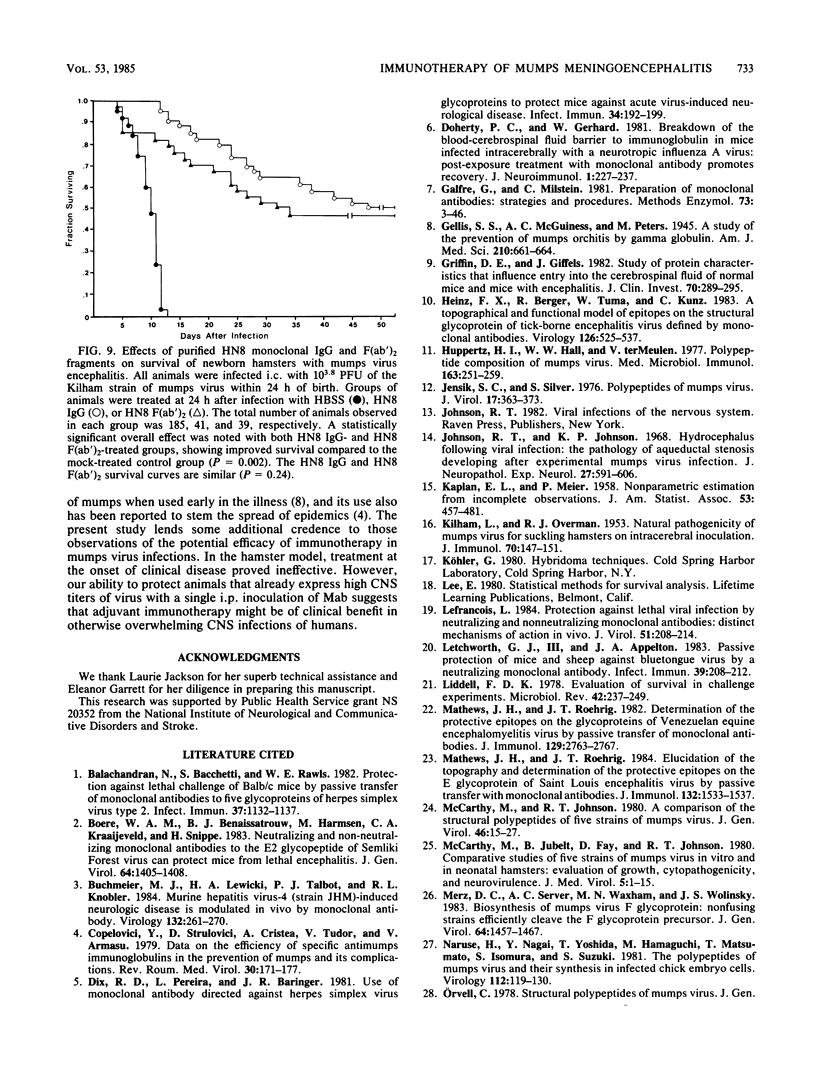
Newborn Syrian hamsters were challanged with an intracerebral inoculum containing 128 50% lethal doses of the Kilham strain of mumps virus and treated 24 h later with a single intraperitoneal injection of mouse monoclonal antibody. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with epitopes on the fusion glycoprotein of mumps virus could not inhibit hemagglutination or neutralize infectivity in vitro and failed to provide biologically important protection against the in vivo infection. In contrast, monoclonal antibodies reactive with epitopes on the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein of mumps virus inhibited hemagglutination and neutralized infectivity in vitro and protected infected animals from the otherwise lethal central nervous system virus infection. Similar protection was provided by both purified immunoglobulin and F(ab')2 fragments. Immuno-cytochemical and virological studies showed diminished virus antigen and virus titers in the brains of successfully treated animals. It appears that a topographically restricted region of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase molecule of the Kilham strain of mumps virus is of critical importance for immune recognition by the infected host.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boere W. A., Benaissa-Trouw B. J., Harmsen M., Kraaijeveld C. A., Snippe H. Neutralizing and non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the E2 glycoprotein of Semliki Forest virus can protect mice from lethal encephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jun;64(Pt 6):1405–1408. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-6-1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copelovici Y., Strulovici D., Cristea A. L., Tudor V., Armaşu V. Data on the efficiency of specific antimumps immunoglobulins in the prevention of mumps and of its complications. Virologie. 1979 Jul-Sep;30(3):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Gerhard W. Breakdown of the blood--cerebrospinal fluid barrier to immunoglobulin in mice injected intracerebrally with a neurotropic influenza A virus. Post-exposure treatment with monoclonal antibody promotes recovery. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Sep;1(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Giffels J. Study of protein characteristics that influence entry into the cerebrospinal fluid of normal mice and mice with encephalitis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):289–295. doi: 10.1172/JCI110616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Berger R., Tuma W., Kunz C. A topological and functional model of epitopes on the structural glycoprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus defined by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):525–537. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz H. I., Hall W. W., ter Meulen V. Polypeptide composition of mumps virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Dec 27;163(4):251–259. doi: 10.1007/BF02125509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensik S. C., Silver S. Polypeptides of mumps virus. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):363–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.363-373.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., Johnson K. P. Hydrocephalus following viral infection: the pathology of aqueductal stenosis developing after experimental mumps virus infection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):591–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILHAM L., OVERMAN J. R. Natural pathogenicity of mumps virus for suckling hamsters on intracerebral inoculation. J Immunol. 1953 Feb;70(2):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L. Protection against lethal viral infection by neutralizing and nonneutralizing monoclonal antibodies: distinct mechanisms of action in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):208–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.208-214.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letchworth G. J., 3rd, Appleton J. A. Passive protection of mice and sheep against bluetongue virus by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):208–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.208-212.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddell F. D. Evaluation of survival in challenge experiments. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):237–249. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.237-249.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T. Determination of the protective epitopes on the glycoproteins of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2763–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Roehrig J. T. Elucidation of the topography and determination of the protective epitopes on the E glycoprotein of Saint Louis encephalitis virus by passive transfer with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1533–1537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Johnson R. T. A comparison of the structural polypeptides of five strains of mumps virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):15–27. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M., Jubelt B., Fay D. B., Johnson R. T. Comparative studies of five strains of mumps virus in vitro and in neonatal hamsters: evaluation of growth, cytopathogenicity, and neurovirulence. J Med Virol. 1980;5(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Server A. C., Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Biosynthesis of mumps virus F glycoprotein: non-fusing strains efficiently cleave the F glycoprotein precursor. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1457–1467. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse H., Nagai Y., Yoshida T., Hamaguchi M., Matsumoto T., Isomura S., Suzuki S. The polypeptides of mumps virus and their synthesis in infected chick embryo cells. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90618-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Grandien M. The effects of monoclonal antibodies on biologic activities of structural proteins of Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C. Immunological properties of purified mumps virus glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):517–526. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C. The reactions of monoclonal antibodies with structural proteins of mumps virus. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2622–2629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P. On the fragmentation of monoclonal IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b from BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2895–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammohan K. W., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Induction of subacute murine measles encephalitis by monoclonal antibody to virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):588–589. doi: 10.1038/290588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies for analysis of antibody-dependent immunity to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.168-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn A. L., Johnson E. D., Dalrymple J. M., Cole G. A. Non-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies can prevent lethal alphavirus encephalitis. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):70–72. doi: 10.1038/297070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Server A. C., Merz D. C., Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Differentiation of mumps virus strains with monoclonal antibody to the HN glycoprotein. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):179–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.179-186.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Immunochemical identification of rubella virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):194–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Baringer J. R., Margolis G., Kilham L. Ultrastructure of mumps virus replication in newborn hamster central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;31(4):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Persistence of neuroadapted mumps virus in brains of newborn hamsters after intraperitoneal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):260–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S. Mumps virus-induced hydrocephalus in hamsters. Ultrastructure of the chronic infection. Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(3):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Waxham M. N., Hess J. L., Townsend J. J., Baringer J. R. Immunochemical features of a case of progressive rubella panencephalitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):359–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



