Abstract
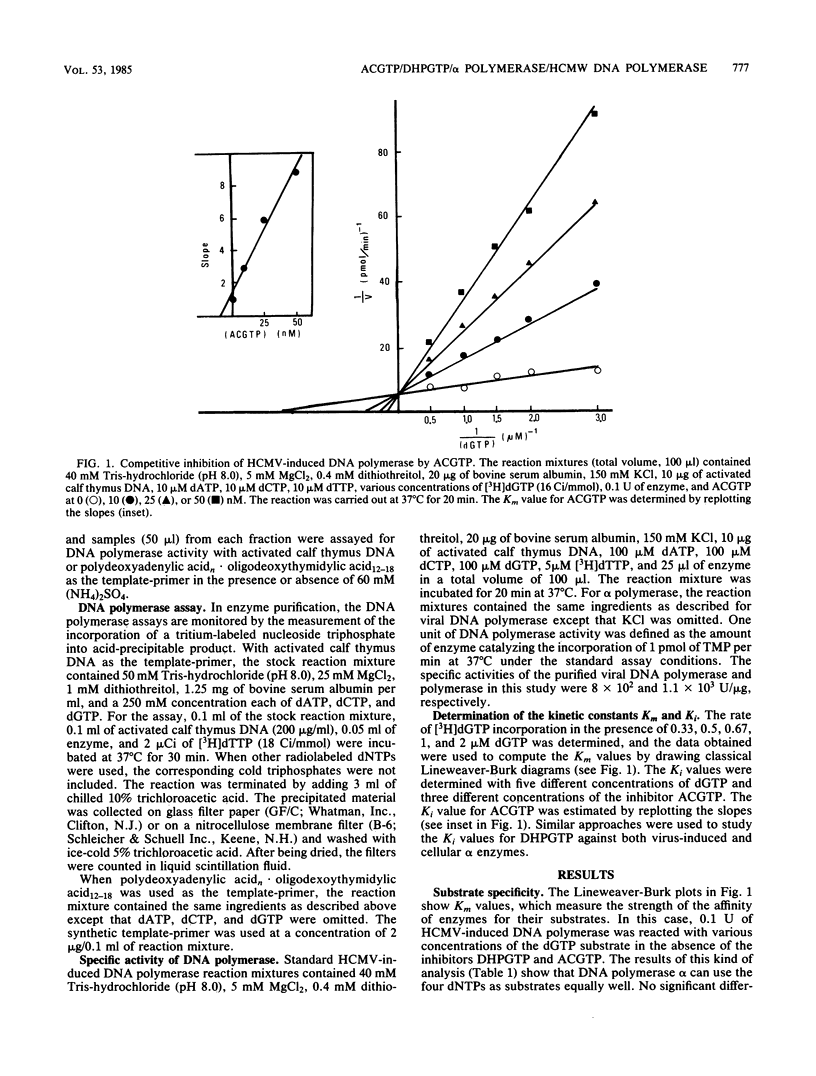
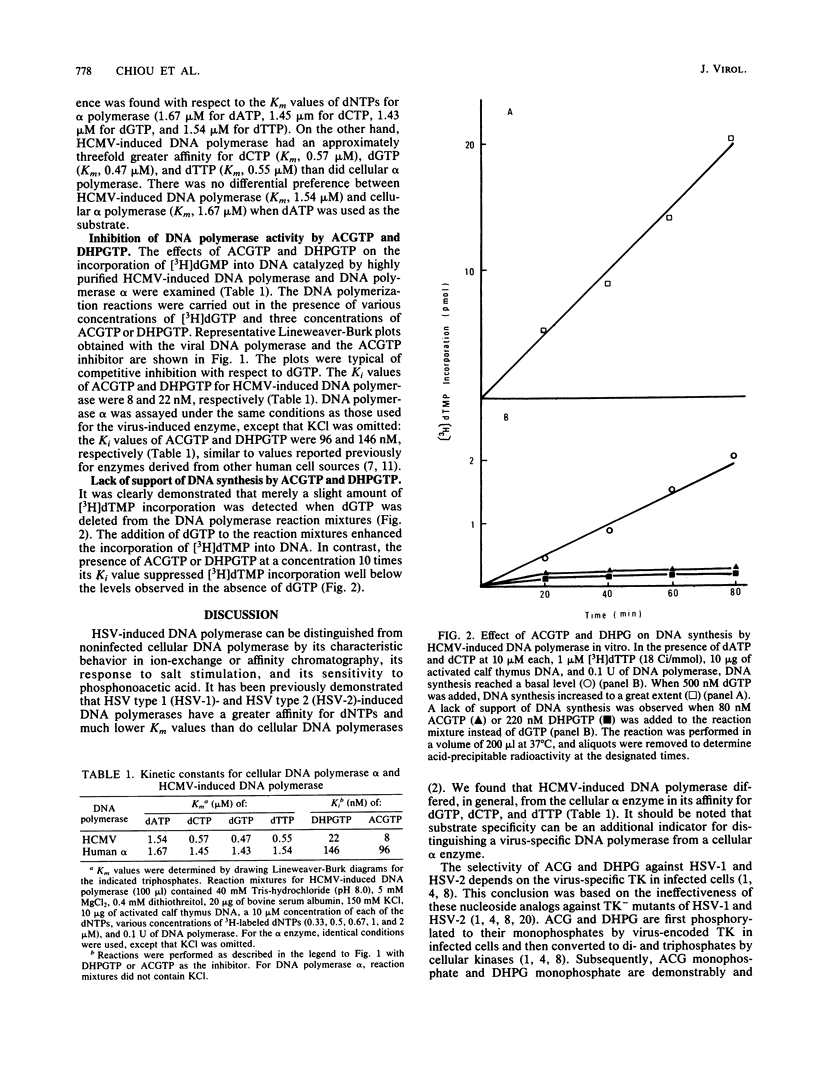
The triphosphates of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine were examined for their inhibitory effect on highly purified cellular DNA polymerase alpha and human cytomegalovirus (Towne strain)-induced DNA polymerase. These two nucleoside triphosphates competitively inhibited the incorporation of dGMP into DNA catalyzed by the DNA polymerases. The virus-induced DNA polymerase had greater binding affinity for the triphosphate of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine (Ki, 8 nM) than for the triphosphate of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine (Ki, 22 nM), although the nucleoside of the latter compound was strikingly more effective against human cytomegalovirus replication in cell cultures than the nucleoside of the former. The Ki values of these two nucleoside triphosphates for alpha polymerase were 96 and 146 nM, respectively, and were 7- to 12-fold higher than those for the virus-induced enzyme. These data indicated that virus-induced DNA polymerase was more sensitive to inhibition by these two nucleoside triphosphates than was the cellular alpha enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton W. T., Karkas J. D., Field A. K., Tolman R. L. Activation by thymidine kinase and potent antiherpetic activity of 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine (2'NDG). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1716–1721. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Grill S. P., Dutschman G. E., Nakayama K., Bastow K. F. Metabolism of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine, a new anti-herpes virus compound, in herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12460–12464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P. Unique spectrum of activity of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]-guanine against herpesviruses in vitro and its mode of action against herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacino J. M., Lopez C. Efficacy and selectivity of some nucleoside analogs as anti-human cytomegalovirus agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):505–508. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Zaia J. A., Levin M. J. Growth inhibition by acycloguanosine of herpesviruses isolated from human infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 May;15(5):642–645. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.5.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Inhibition of purified human and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. Effects on primer-template function. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11447–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes J. E., Huang E. S. Stimulation of cellular thymidine kinases by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.13-21.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank K. B., Chiou J. F., Cheng Y. C. Interaction of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase with 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1566–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Spector T. Acyclovir triphosphate is a suicide inactivator of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9575–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. III. Virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):298–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.298-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Patel P. C., Huang E. S. Effect of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine on viral-specific polypeptide synthesis in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. C., Dvorak C. A., Smee D. F., Matthews T. R., Verheyden J. P. 9-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine: a new potent and selective antiherpes agent. J Med Chem. 1983 May;26(5):759–761. doi: 10.1021/jm00359a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuirt P. V., Shaw J. E., Elion G. B., Furman P. A. Identification of small DNA fragments synthesized in herpes simplex virus-infected cells in the presence of acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):507–509. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Beauchamp L., de Miranda P., Elion G. B., Bauer D. J., Collins P. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):583–585. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Martin J. C., Verheyden J. P., Matthews T. R. Anti-herpesvirus activity of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):676–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Galloway K. S., Kennell W. L., Ogilvie K. K., Radatus B. K. A new nucleoside analog, 9-[[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxyl]methyl]guanine, highly active in vitro against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Furman P. A., Lubbers C. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of cellular alpha and virally induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases by the triphosphate of acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):741–745. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Miller W. H., Miller R. L., Lambe C. U., Furman P. A. Inhibition of cellular alpha DNA polymerase and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by the triphosphate of BW759U. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):191–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocci M. J., Livelli T. J., Perry H. C., Crumpacker C. S., Field A. K. Effects of the nucleoside analog 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine on human cytomegalovirus replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):247–252. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada V., Erban V., Rezácová D., Vonka V. Thymidine-kinase in cytomegalovirus infected cells. Arch Virol. 1976;52(4):333–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01315622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



