Abstract
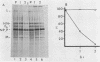
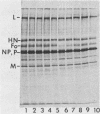
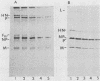
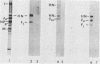
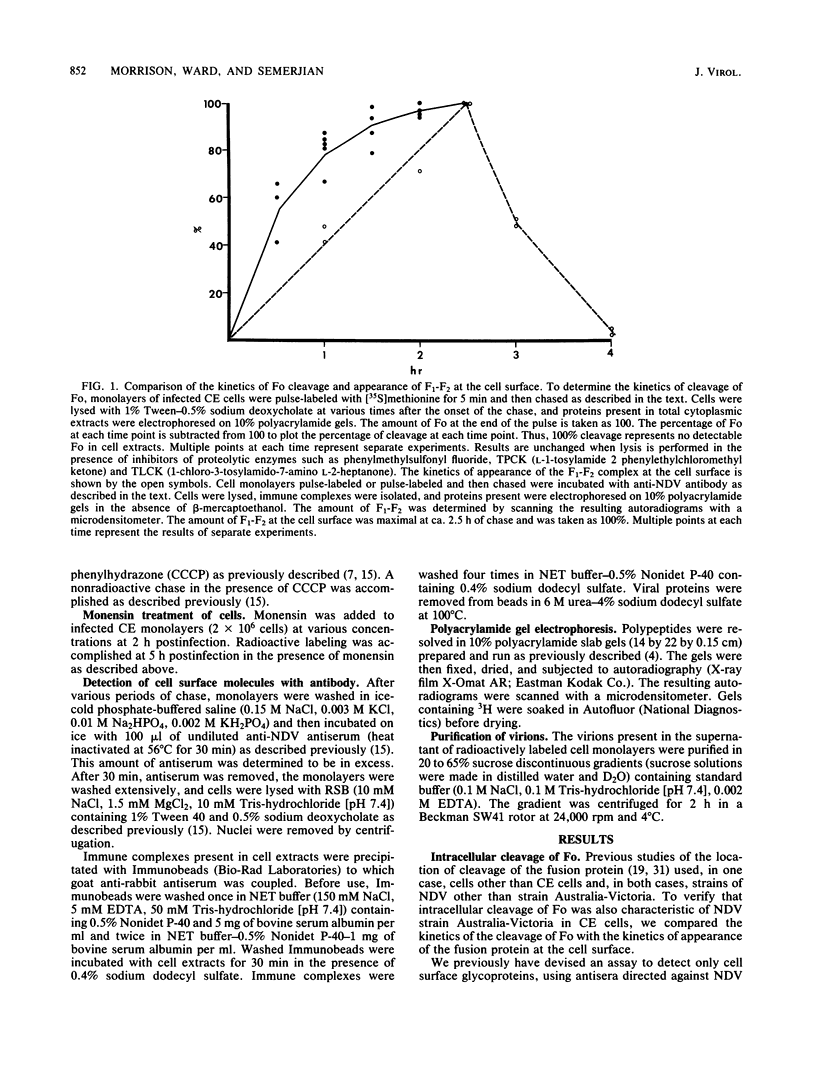
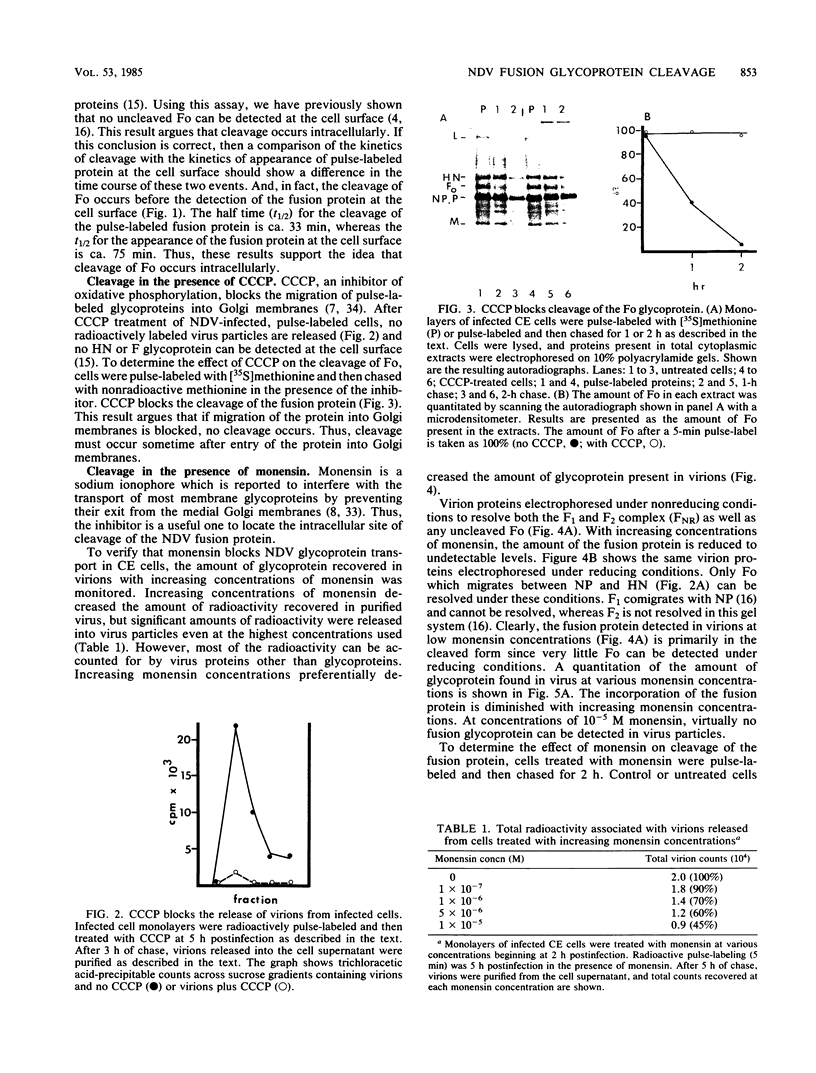
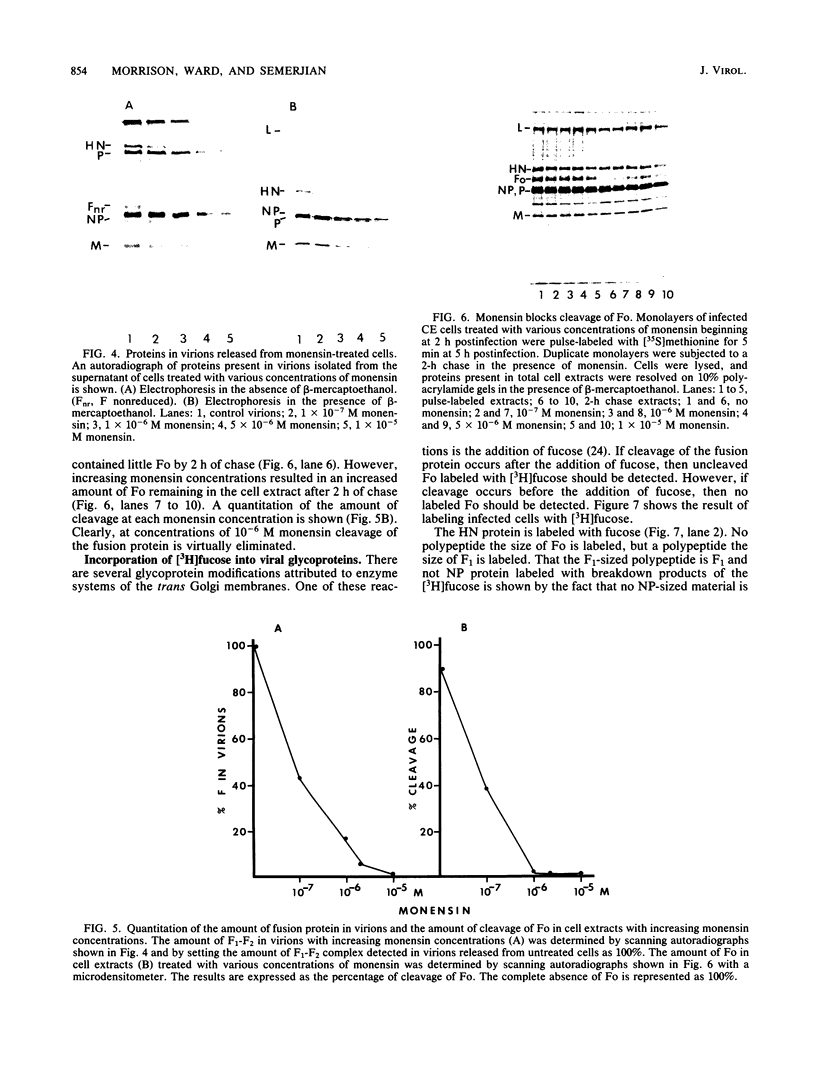
The fusion glycoprotein (Fo) of Newcastle disease virus is cleaved at an intracellular site (Nagai et al., Virology 69:523-538, 1976) into F1 and F2. This result was confirmed by comparing the transit time of the fusion protein to the cell surface with the time course of cleavage of Fo. The time required for cleavage of half of the pulse-labeled Fo protein is ca. 40 min faster than the half time of the transit of the fusion protein to the cell surface. To determine the cell compartment in which cleavage occurs, use was made of inhibitors which block glycoprotein migration at specific points and posttranslational modifications known to occur in specific cell membranes. Cleavage of Fo is inhibited by carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone; thus, cleavage does not occur in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Monensin blocks the incorporation of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins into virions and blocks the cleavage of the fusion glycoprotein. However, Fo cannot be radioactively labeled with [3H] fucose, whereas F1 is readily labeled. These results argue that cleavage occurs in the trans Golgi membranes or in a cell compartment occupied by glycoproteins quite soon after their transit through the trans Golgi membranes. The implications of the results presented for the transit times of the fusion protein between subcellular organelles are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratt M. A., Gallaher W. R. Preliminary analysis of the requirements for fusion from within and fusion from without by Newcastle disease virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):536–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Fatty acid modification of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):342–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.342-347.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is anchored to intracellular membranes near its carboxyl end and is proteolytically cleaved at its amino terminus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):957–963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.957-963.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitting T., Kabat D. Evidence for a glycoprotein "signal" involved in transport between subcellular organelles. Two membrane glycoproteins encoded by murine leukemia virus reach the cell surface at different rates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Rothman J. E. Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in a cell-free extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nishikawa K., Naruse H., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. I. Both L and P proteins are required to constitute an active complex. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein metabolism during the steady state of Newcastle disease virus infection. I. Kinetics of amino acid and protein accumulation. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W., Darlington R. W. Isolation and properties of Newcastle disease virus nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1968 Mar;2(3):248–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.3.248-255.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Mahy B. W., Choppin P. W. The synthesis of sendai virus polypeptides in infected cells. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):116–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff D. H., Lenard J. A membrane glycoprotein that accumulates intracellularly: cellular processing of the large glycoprotein of LaCrosse virus. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):821–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Simpson D. Synthesis, stability, and cleavage of Newcastle disease virus glycoproteins in the absence of glycosylation. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.171-180.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins and glycoproteins of paramyxoviruses: a comparison of simian virus 5, Newcastle disease virus, and Sendai virus. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.47-52.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Ogura H., Klenk H. Studies on the assembly of the envelope of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Yaffe A. Intracellular transport and secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.346-353.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Bratt M. A. UV irradiation analysis of complementation between, and replication of, RNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):965–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.965-973.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Käriäinen L. Incomplete complex oligosaccharides in semliki forest virus envelope proteins arrested within the cell in the presence of monensin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):213–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. The golgi apparatus: two organelles in tandem. Science. 1981 Sep 11;213(4513):1212–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.7268428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson A. C., Fox C. F. Precursor protein for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):579–587. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.579-587.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheefers H., Scheefers-Borchel U., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Distribution of virus structural proteins and protein-protein interactions in plasma membrane of baby hamster kidney cells infected with Sindbis or vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7277–7281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J. T., Garten W., Rott R. The site of cleavage in infected cells and polypeptides of representative paramyxoviruses grown in cultured cells of the chorioallantoic membrane. Arch Virol. 1981;67(1):19–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01314598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]