Abstract
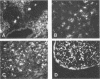
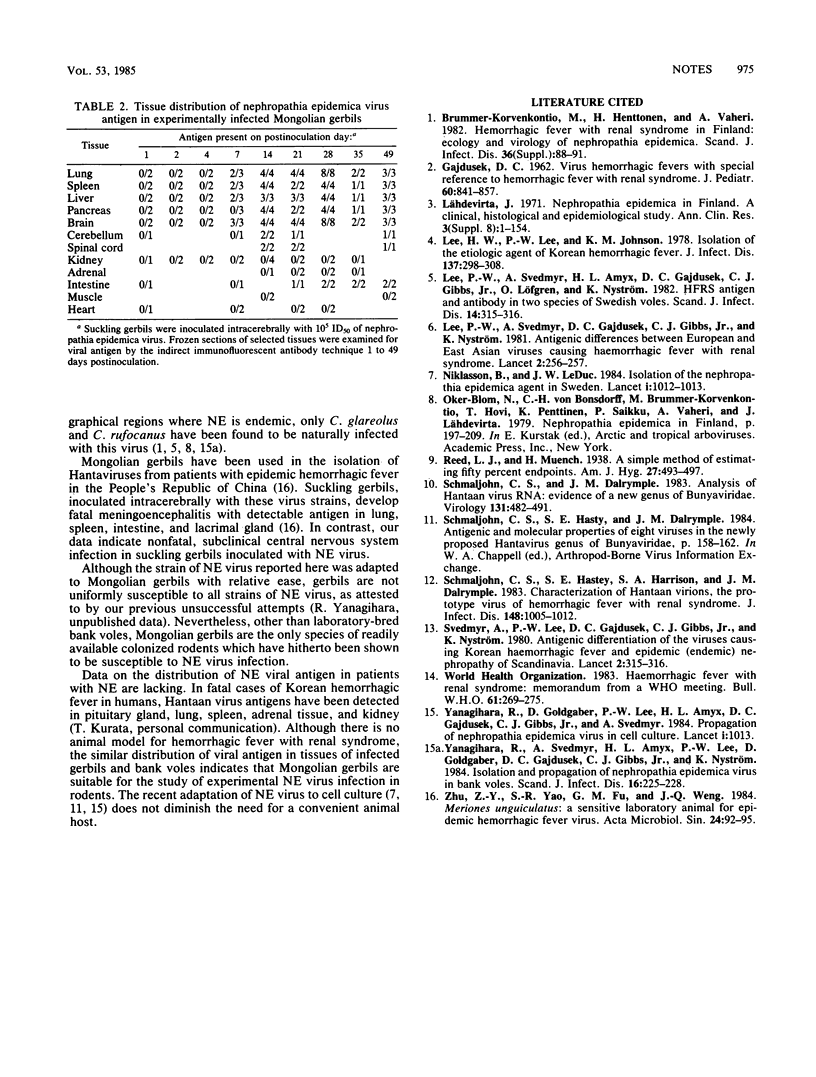
Nephropathia epidemica virus, the etiological agent of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Scandinavia, was serially propagated in Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). Intracerebrally inoculated suckling gerbils developed subclinical infections, with viral antigen found in lung, brain, liver and spleen. The distribution of viral antigen was similar to that seen in experimentally infected bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus), the principal wild rodent reservoir of nephropathia epidemica virus. This model provides a readily available animal host for the study of experimental nephropathia epidemica virus infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Henttonen H., Vaheri A. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Finland: ecology and virology of nephropathia epidemica. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;36:88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Virus hemorrhagic fevers. Special reference to hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (epidemic hemorrhagic fever). J Pediatr. 1962 Jun;60:841–857. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Johnson K. M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):298–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Svedmyr A., Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Löfgren O., Nyström K. HFRS antigen and antibody in two species of Swedish voles. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(4):315–316. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-4.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Svedmyr A., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Antigenic difference between European and East Asian viruses causing haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Aug 1;2(8240):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica in Finland. A clinical histological and epidemiological study. Ann Clin Res. 1971;3:1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niklasson B., Le Duc J. Isolation of the nephropathia epidemica agent in Sweden. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):1012–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Dalrymple J. M. Analysis of Hantaan virus RNA: evidence for a new genus of bunyaviridae. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):482–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Hasty S. E., Harrison S. A., Dalrymple J. M. Characterization of Hantaan virions, the prototype virus of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1005–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A., Lee P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Antigenic differentiation of the viruses causing Korean haemorrhagic fever and epidemic (endemic) nephropathy of Scandinavia. Lancet. 1980 Aug 9;2(8189):315–316. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Goldgaber D., Lee P. W., Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Svedmyr A. Propagation of nephropathia epidemica virus in cell culture. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):1013–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Svedmyr A., Amyx H. L., Lee P., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Isolation and propagation of nephropathia epidemica virus in bank voles. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(3):225–228. doi: 10.3109/00365548409070393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]