Abstract
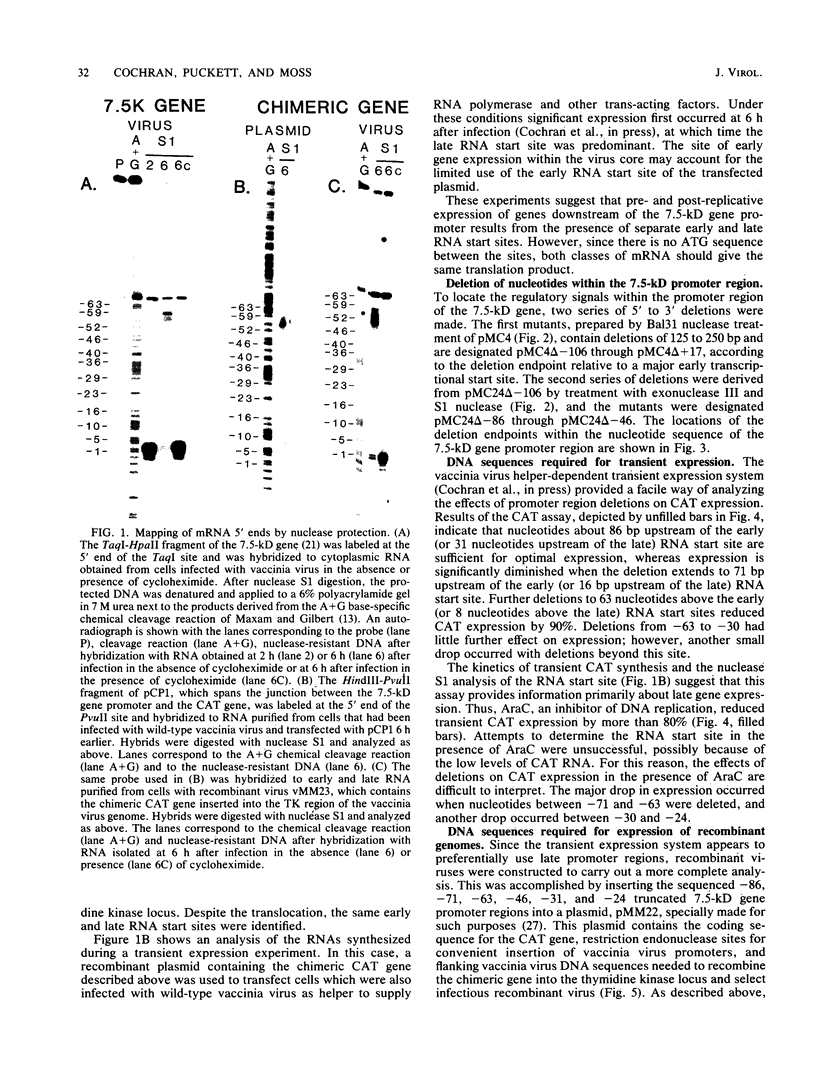
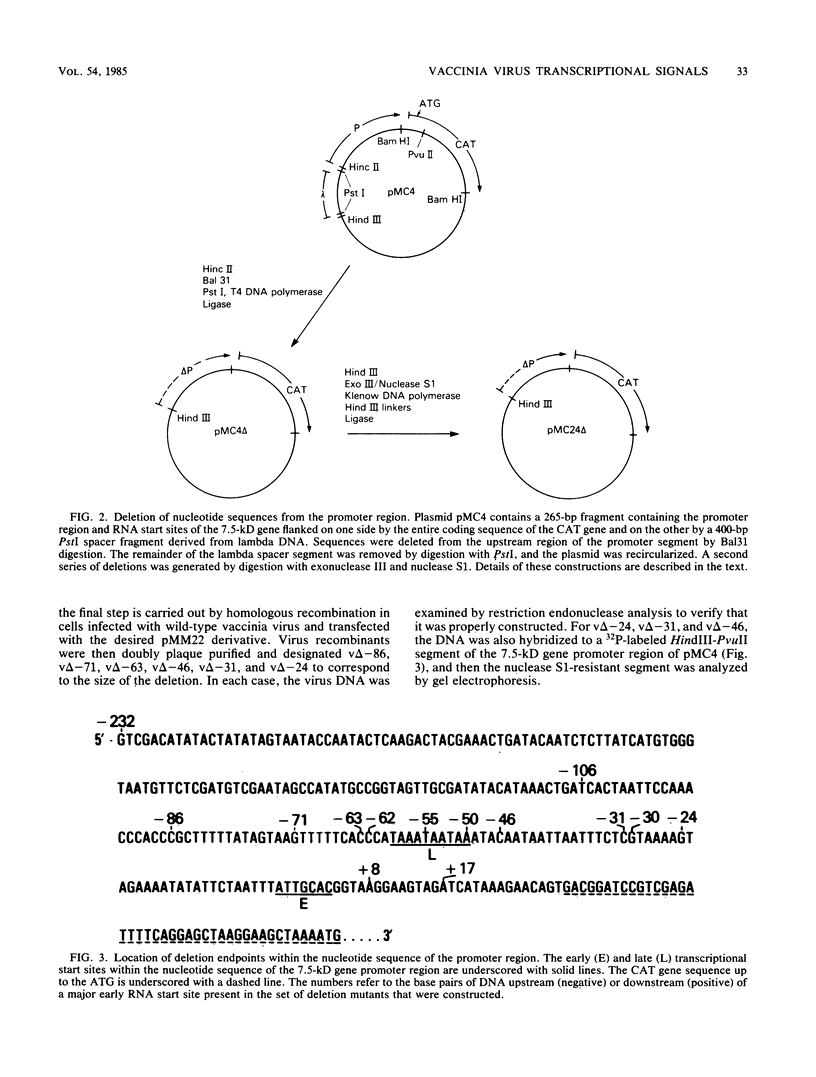
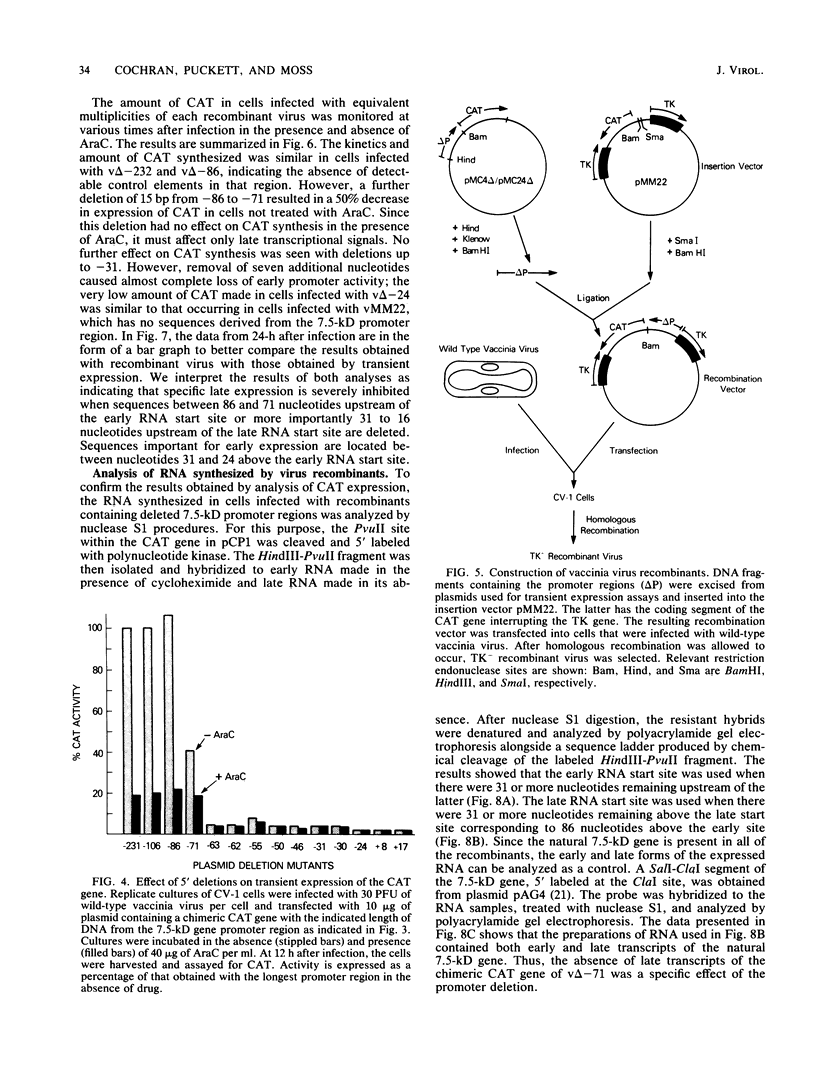
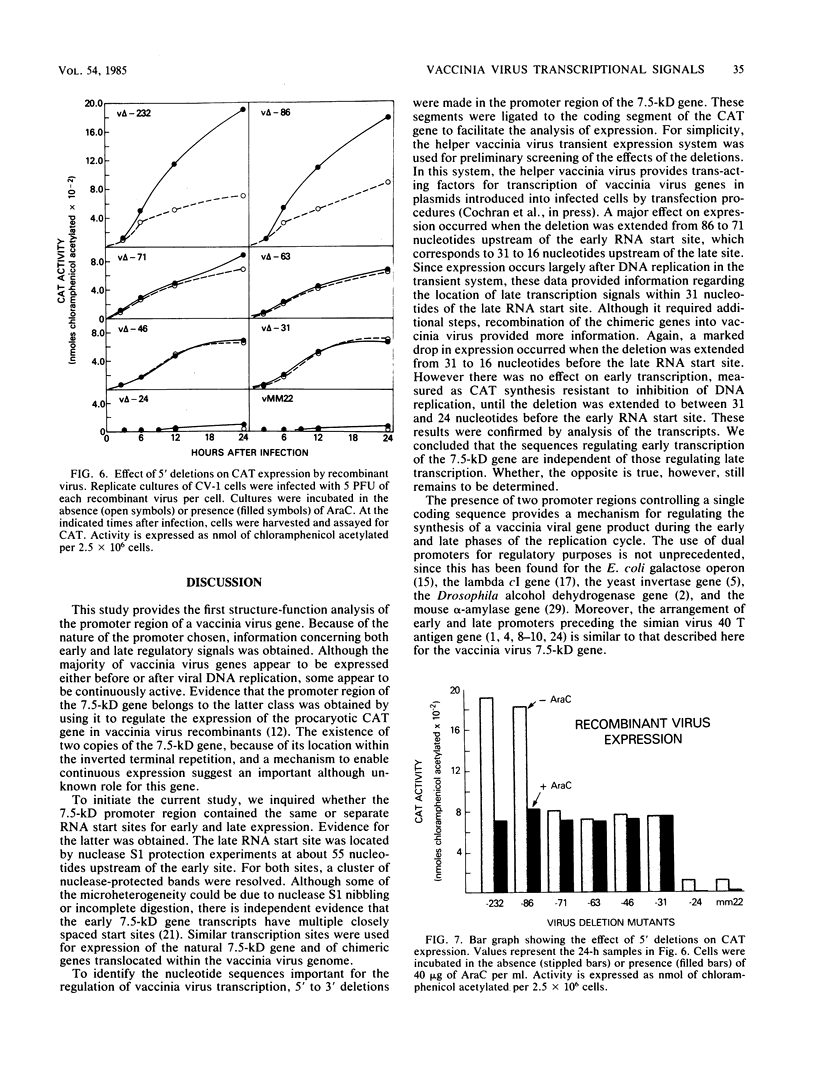
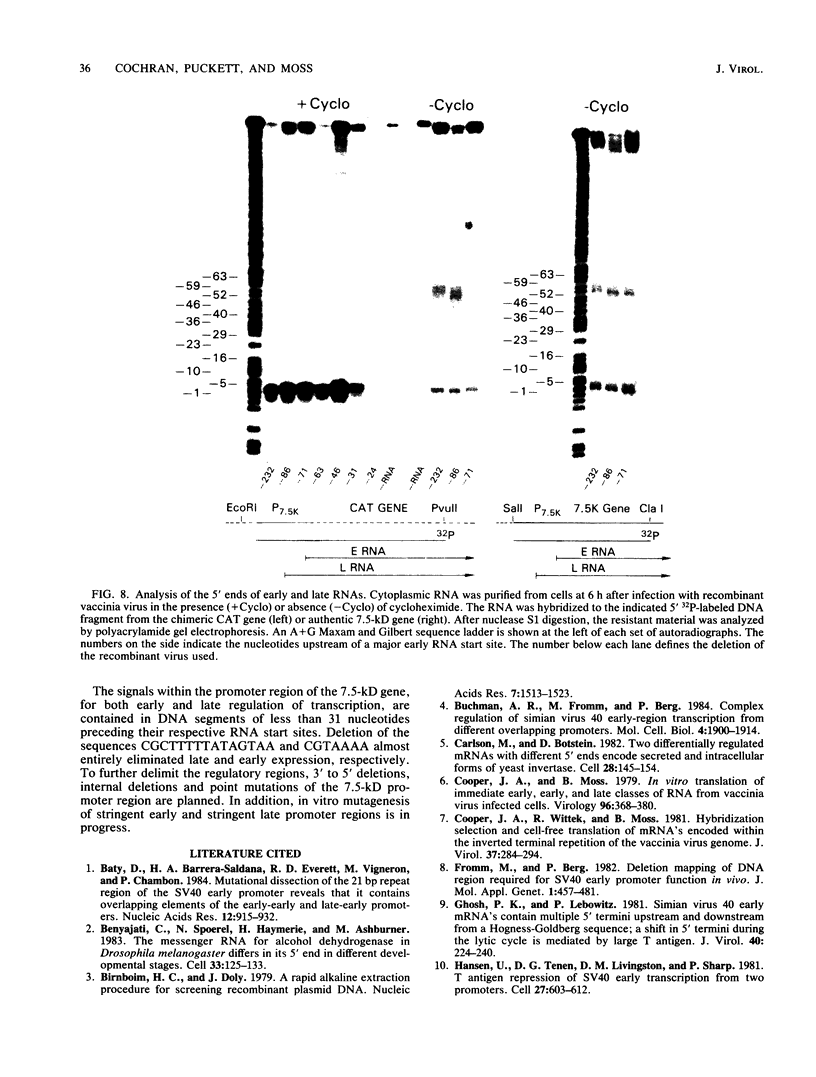
A vaccinia virus gene that is expressed throughout the reproductive cycle was found to have two sets of RNA start sites approximately 55 nucleotides apart. The site nearest to the coding segment is used early in infection and the one further upstream is used after DNA replication. A series of 5' to 3' deletions were made in the promoter region, and the truncated DNA segments were then ligated to the coding portion of the procaryotic chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene to measure expression. The effects of these mutations on chloramphenicol acetyltransferase synthesis were determined in a vaccinia virus helper-dependent transient expression system and by forming infectious vaccinia virus recombinants that contain the chimeric genes. Deletions extending up to 31 nucleotides before the late RNA start site had no effect on either early or late expression. Removal of an additional 15 nucleotides produced a dramatic decrease in late expression but had no effect on early expression. The latter was not diminished until the deletion was extended from 31 to 24 nucleotides before the early RNA start site. These results were confirmed by transcriptional analyses. We concluded that this vaccinia virus gene has two promoters and that the regulatory signals for each are located within 31 nucleotides of their sites of transcription.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baty D., Barrera-Saldana H. A., Everett R. D., Vigneron M., Chambon P. Mutational dissection of the 21 bp repeat region of the SV40 early promoter reveals that it contains overlapping elements of the early-early and late-early promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):915–932. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Fromm M., Berg P. Complex regulation of simian virus 40 early-region transcription from different overlapping promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1900–1914. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. In vitro translation of immediate early, early, and late classes of RNA from vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Wittek R., Moss B. Hybridization selection and cell-free translation of mRNA's encoded within the inverted terminal repetition of the vaccinia virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):284–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.284-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P. Simian virus 40 early mRNA's contain multiple 5' termini upstream and downstream from a Hogness-Goldberg sequence; a shift in 5' termini during the lytic cycle is mediated by large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):224–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.224-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. General method for production and selection of infectious vaccinia virus recombinants expressing foreign genes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackett M., Smith G. L., Moss B. Vaccinia virus: a selectable eukaryotic cloning and expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso R. E., Di Lauro R., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Dual control for transcription of the galactose operon by cyclic AMP and its receptor protein at two interspersed promoters. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puckett C., Moss B. Selective transcription of vaccinia virus genes in template dependent soluble extracts of infected cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Mackett M., Moss B. Infectious vaccinia virus recombinants that express hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):490–495. doi: 10.1038/302490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Murphy B. R., Moss B. Construction and characterization of an infectious vaccinia virus recombinant that expresses the influenza hemagglutinin gene and induces resistance to influenza virus infection in hamsters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7155–7159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamanoi F., Stillman B. W. Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication in vitro requires a specific DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6446–6450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Gershowitz A., Moss B. Complete nucleotide sequences of two adjacent early vaccinia virus genes located within the inverted terminal repetition. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):637–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.637-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Moss B. In vitro transcription of the inverted terminal repetition of the vaccinia virus genome: correspondence of initiation and cap sites. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.738-747.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Chambon P. Transcription from the SV40 early-early and late-early overlapping promoters in the absence of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1605–1611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene and the nature of spontaneous frameshift mutations. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.530-537.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Regulation of expression and nucleotide sequence of a late vaccinia virus gene. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):662–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.662-669.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Hammarskjöld M. L. Isolation of DNA from agarose gels using DEAE-paper. Application to restriction site mapping of adenovirus type 16 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):253–264. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. A single mouse alpha-amylase gene specifies two different tissue-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):451–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]