Abstract
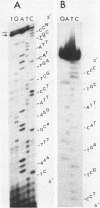
We recently determined that respiratory syncytial virus (strain A2) encodes a fourth unique envelope-associated virion protein that has molecular weight of approximately 24,000, as estimated by gel electrophoresis. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding this novel protein has now been determined from five cDNA clones, including three that contain the complete mRNA sequence. The complete mRNA sequence is 957 nucleotides, exclusive of polyadenylate, and contains two partially overlapping open reading frames. The 5'-proximal open reading frame is favored for utilization by the criteria of the location and sequence of its translational start site. Furthermore, the calculated molecular weight of the encoded protein, 22,153, is in agreement with the previous estimate of 24,000 for the authentic protein identified by hybrid selection and in vitro translation. The sequence of the predicted protein, now designated the 22K protein, contains 194 amino acids, is relatively hydrophilic, and appears to be the most basic of the respiratory syncytial virus proteins. The mRNA also contains a second, internal open reading frame which would encode a protein of 90 amino acids. However, no evidence for this translation product is known. The first nine nucleotides in the mRNA sequence, 5'-GGGGCAAAU, are identical to the conserved sequence identified previously at the 5' termini of seven other respiratory syncytial viral mRNAs; the sequence at the 3' end of the 22K mRNA, 5'. . . AGUUAUUU-polyadenylate, contains the elements of the previously identified 3'-terminal consensus sequence for respiratory syncytial virus mRNAs, AGUUAA(N)1-4-polyadenylate (P. L. Collins, Y. T. Huang, and G. W. Wertz, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81:7683-7687). In addition, we present and describe the intergenic sequence of a dicistronic RNA derived from readthrough of the F and 22K protein genes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cash P., Pringle C. R., Preston C. M. The polypeptides of human respiratory syncytial virus: products of cell-free protein synthesis and post-translational modifications. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcriptional map for Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):682–693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.682-693.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Identification of a tenth mRNA of respiratory syncytial virus and assignment of polypeptides to the 10 viral genes. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):572–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.572-578.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7683–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W., Ball L. A., Hightower L. E. Coding assignments of the five smaller mRNAs of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickens L. E., Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. Transcriptional mapping of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):364–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.364-369.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J. Analysis of proteins synthesized in respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):372–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.372-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Venkatesan S. Amino acid sequence of human respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5941–5951. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie B. F., Gerin J. L. Immunochemical identification of viral and nonviral proteins of the respiratory syncytial virus virion. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):243–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.243-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazier K., Raghow R., Kingsbury D. W. Regulation of Sendai virus transcription: evidence for a single promoter in vivo. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):863–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.863-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Complete sequences of the intergenic and mRNA start signals in the Sendai virus genome: homologies with the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3829–3841. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Conserved polyadenylation signals in two negative-strand RNA virus families. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):518–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Adler S., Lazzarini R. A., Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K., Westphal H. Intervening polyadenylate sequences in RNA transcripts of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A. Polycistronic vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Respiratory syncytial virus mRNA coding assignments. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.667-672.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. The genome of respiratory syncytial virus is a negative-stranded RNA that codes for at least seven mRNA species. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):150–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.150-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Determination by peptide mapping of the unique polypeptides in Sendai virions and infected cells. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J., Choppin P. W. Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J. Sequence of interrupted and uninterrupted mRNAs and cloned DNA coding for the two overlapping nonstructural proteins of influenza virus. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. M., Pons M. W. Respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. Polypeptides of respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.427-431.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M., Levine S. Respiratory syncytial virus polypeptides: their location in the virion. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R., Shirodaria P. V., Gimenez H. B., Levine S. Antigen and polypeptide synthesis by temperature-sensitive mutants of respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):173–183. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Venkatesan S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):92–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.92-99.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Shibuta H., Nomoto A., Iwasaki K. Sequence of 3,687 nucleotides from the 3' end of Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of viral NP, P and C proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7317–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueba O. Purification and polypeptides of respiratory syncytial virus. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(4):361–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Elango N., Chanock R. M. Construction and characterization of cDNA clones for four respiratory syncytial viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1280–1284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Morrison T. Structural and functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):71–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.71-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Pringle C. R. Respiratory syncytial virus proteins. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):228–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]