Abstract
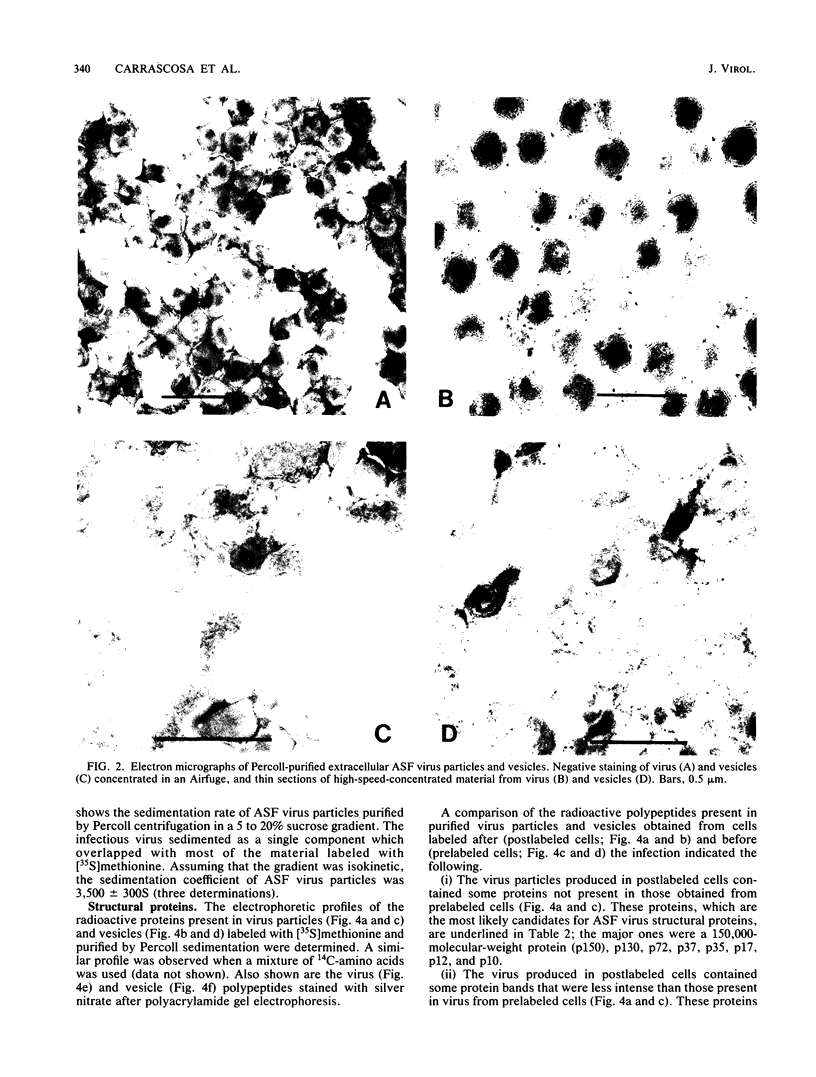
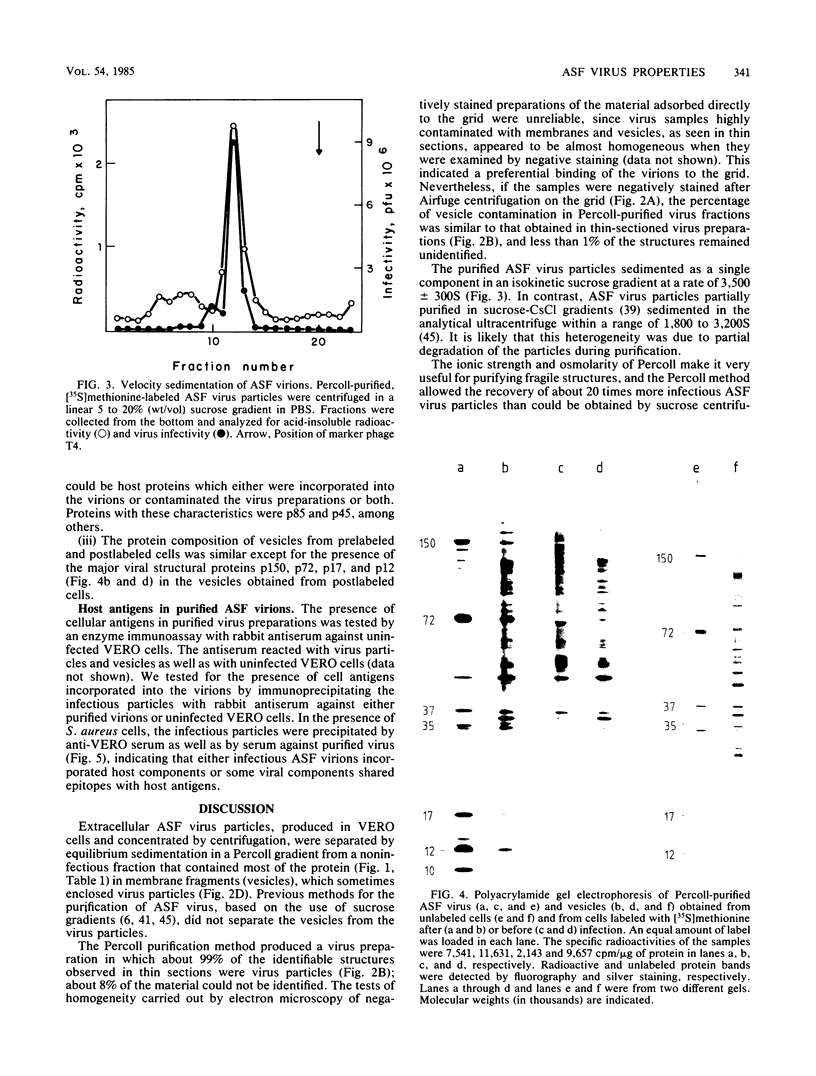
We describe a method for African swine fever (ASF) virus purification based on equilibrium centrifugation in Percoll density gradients of extracellular virions produced in infected VERO cells that yielded about 15 +/- 9% recovery of the starting infectious virus particles. The purified virus preparations were essentially free of a host membrane fraction (vesicles) that could not be separated from the virus by previously described purification methods. The purified virus sedimented as a single component in sucrose velocity gradients with a sedimentation coefficient of 3,500 +/- 300S, showed a DNA-protein ratio of 0.18 +/- 0.02 and a specific infectivity of 2.7 X 10(7) PFU/micrograms of protein, and remained fully infectious after storage at -70 degrees C for at least 7 months. The relative molecular weights of the 34 polypeptides detected in purified virus particles ranged from 10,000 to 150,000. Some of these proteins were probably cellular components that might account for the reactivity of purified virus with antiserum against VERO cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P., Plowright W. The morphological characteristics of African swine fever virus and its resemblance to tipula iridescent virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(3):392–396. doi: 10.1007/BF01241958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Blasco R., Ley V., Beloso A., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Restriction site map of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):258–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bencosme S. A., Tsutsumi V. Fast method for processing biologic material for electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. N., Brown F. Purification and physicochemical characteristics of African swine fever virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):509–518. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Production and titration of African swine fever virus in porcine alveolar macrophages. J Virol Methods. 1982 Jan;3(6):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
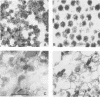
- Carrascosa J. L., Carazo J. M., Carrascosa A. L., García N., Santisteban A., Viñuela E. General morphology and capsid fine structure of African swine fever virus particles. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casal I., Enjuanes L., Viñuela E. Porcine leukocyte cellular subsets sensitive to African swine fever virus in vitro. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):37–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.37-46.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Gelmann E. P., Reitz M. S., Jr Homology of human T-cell leukaemia virus envelope gene with class I HLA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 1;305(5929):60–62. doi: 10.1038/305060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer C. J. Studies to determine neutralizing antibody in sera from animals recovered from African swine fever and laboratory animals inoculated with African virus with adjuvants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):164–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01241270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Carrascosa A. L., Moreno M. A., Viñuela E. Titration of African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):471–477. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Isolation and properties of the DNA of African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):479–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman A. J., Wardley R. C., Wilkinson P. J. The immunological response of pigs and guinea pigs to antigens of African swine fever virus. Arch Virol. 1982;74(2-3):91–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01314703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS W. R., COX B. F., HEUSCHELE W. P., STONE S. S. PROPAGATION AND MODIFICATION OF AFRICAN SWINE FEVER VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Jan;26:141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Paul W. E. Limitation of VSV infection by the host's response to VSV-associated cellular antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1736–1741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth R., Pertoft H. Removal of percoll from microsomal vesicles by gel filtration on sephacryl-S-1000 superfine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingeborn B., Pertoft H. Equine abortion (herpes) virus: purification and concentration of enveloped and deenveloped virus and envelope material by density gradient centrifugation in colloidal silica. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):618–623. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznar J., Salas M. L., Viñuela E. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larenaudie B., Haag J., Carnero R. La purification du virus de la peste porcine africaine par le fluorocarbone. Bull Off Int Epizoot. 1965 May-Jun;63(5):711–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letchworth G. J., Whyard T. C. Characterization of African swine fever virus antigenic proteins by immunoprecipitation. Arch Virol. 1984;80(4):265–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01311218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little L. M., Lanman G., Huang A. S. Immunoprecipitating human antigens associated with vesicular stomatitis virus grown in HeLa cells. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Specific incorporation of host cell surface proteins into budding vesicular stomatitis virus particles. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A., HAY D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A. Propagation, modification, and hemadsorption of African swine fever virus in cell cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1962 Mar;23:241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes J. F., Vigário J. D., Terrinha A. M. Ultrastructural study of African swine fever virus replication in cultures of swine bone marrow cells. Arch Virol. 1975;49(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02175596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan I. C., Shimizu M., Hess W. R. Replication of African swine fever virus in cell cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Sep;41(9):1357–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertoft H. Density gradient centrifugation of a herpesvirus (IBRV) in colloidal silica. Virology. 1970 Jun;41(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Pan I. C., Gravell M. Protein kinase activity in African swine fever virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(2):156–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01250227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. S., Hess W. R. Antibody response to inactivated preparations of African swine fever virus in pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Mar;28(123):475–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. S., Hess W. R. Separation of virus and soluble noninfectious antigens in African swine fever virus by isoelectric precipitation. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E., Marcotegui M. A., Fernández M., Sánchez-Botija C. Proteins specified by African swine fever virus. I. Analysis of viral structural proteins and antigenic properties. Arch Virol. 1980;66(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01314979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautman R., Pan I. C., Hess W. R. Sedimentation coefficient of African swine fever virus. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Nov;41(11):1874–1878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardley R. C., de M Andrade C., Black D. N., de Castro Portugal F. L., Enjuanes L., Hess W. R., Mebus C., Ordas A., Rutili D., Sanchez Vizcaino J. African Swine Fever virus. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1983;76(2):73–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01311692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]