Abstract
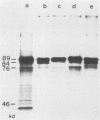
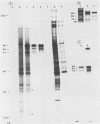
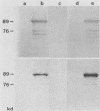
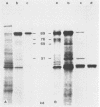
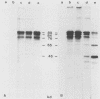
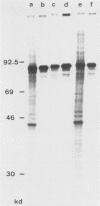
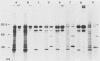
The immediate-early (IE) infected cell proteins induced by the murine cytomegalovirus (Smith strain) were studied. These polypeptides were identified as IE proteins by their synthesis in the presence of actinomycin D after removal from a protein synthesis block mediated by cycloheximide. By using a murine antiserum against murine cytomegalovirus, three abundant polypeptides of 89, 84, and 76 kilodaltons (kd) were immunoprecipitated. The three major proteins are phosphorylated but not glycosylated and share antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies. The 84 and 76-kd polypeptides represent post-translational modification products of the 89-kd protein. Accordingly, in vitro translation of IE infected cell RNA revealed only the 89-kd polypeptide. The viral origin of the RNA species directing the synthesis of the major 89-kd IE polypeptide was verified by hybrid selection of IE RNA with DNA fragments representing the region from 0.769 to 0.815 map units of the murine cytomegalovirus genome. IE polypeptides were found to be located in the nuclei and the cytoplasm of infected cells. Studies on the kinetics of IE polypeptide synthesis revealed negative regulatory effects on IE gene expression correlated with the synthesis of early proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanton R. A., Tevethia M. J. Immunoprecipitation of virus-specific immediate-early and early polypeptides from cells lytically infected with human cytomegalovirus strain AD 169. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):262–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90631-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler J. K., Hudson J. B. Proteins of murine cytomegalovirus: identification of structural and nonstructural antigens in infected cells. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):22–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G. M., Knust E., Koszinowski U. H. Molecular cloning and physical mapping of murine cytomegalovirus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):421–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.421-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling A., Keil G., Nowak B., Fleckenstein B., Berthelot N., Sheldrick P. Genome structure and virion polypeptides of the primate herpesviruses Herpesvirus aotus types 1 and 3: comparison with human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):715–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.715-726.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Siegmann B. Expression of early viral gene products in adenovirus type 12-infected and -transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):99–113. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Immediate-early proteins of human cytomegalovirus strains AD 169, Davis, and Towne differ in electrophoretic mobility. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Protein counterparts of human and simian cytomegaloviruses. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):391–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., McDougall J., Hackman R., Meyers J. D., Thomas E. D., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to cytomegalovirus: rapid identification of clinical isolates and preliminary use in diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.273-281.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Chin G., Hayward G. S. Characterization of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes. I. Nonpermissive rodent cells overproduce the IE94K protein form CMV (Colburn). Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Gibson W. A cycloheximide-enhanced protein in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):362–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil G. M., Ebeling-Keil A., Koszinowski U. H. Temporal regulation of murine cytomegalovirus transcription and mapping of viral RNA synthesized at immediate early times after infection. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):784–795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.784-795.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil G., Fleckenstein B., Bodemer W. Structural proteins of Herpesvirus saimiri. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):463–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.463-470.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. R., Mercer J. A., Spector D. H. Transcription in mouse embryo cells permissively infected by murine cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90550-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Marks J. R., Spector D. H. Molecular cloning and restriction endonuclease mapping of the murine cytomegalovirus genome (Smith Strain). Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):94–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson S., Horodniceanu F., Kress M., Tardy-Panit M. Human cytomegalovirus-induced immediate early antigens: analysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis after immunoprecipitation. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):259–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.259-267.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Keil G. M., Koszinowski U. H. The cytolytic T lymphocyte response to the murine cytomegalovirus. I. Distinct maturation stages of cytolytic T lymphocytes constitute the cellular immune response during acute infection of mice with the murine cytomegalovirus. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):482–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Keil G. M., Koszinowski U. H. The cytolytic T lymphocyte response to the murine cytomegalovirus. II. Detection of virus replication stage-specific antigens by separate populations of in vivo active cytolytic T lymphocyte precursors. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):56–61. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Significance of herpesvirus immediate early gene expression in cellular immunity to cytomegalovirus infection. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):369–371. doi: 10.1038/312369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Sequence of protein synthesis in cells infected by human cytomegalovirus: early and late virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):686–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.686-701.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]