Abstract
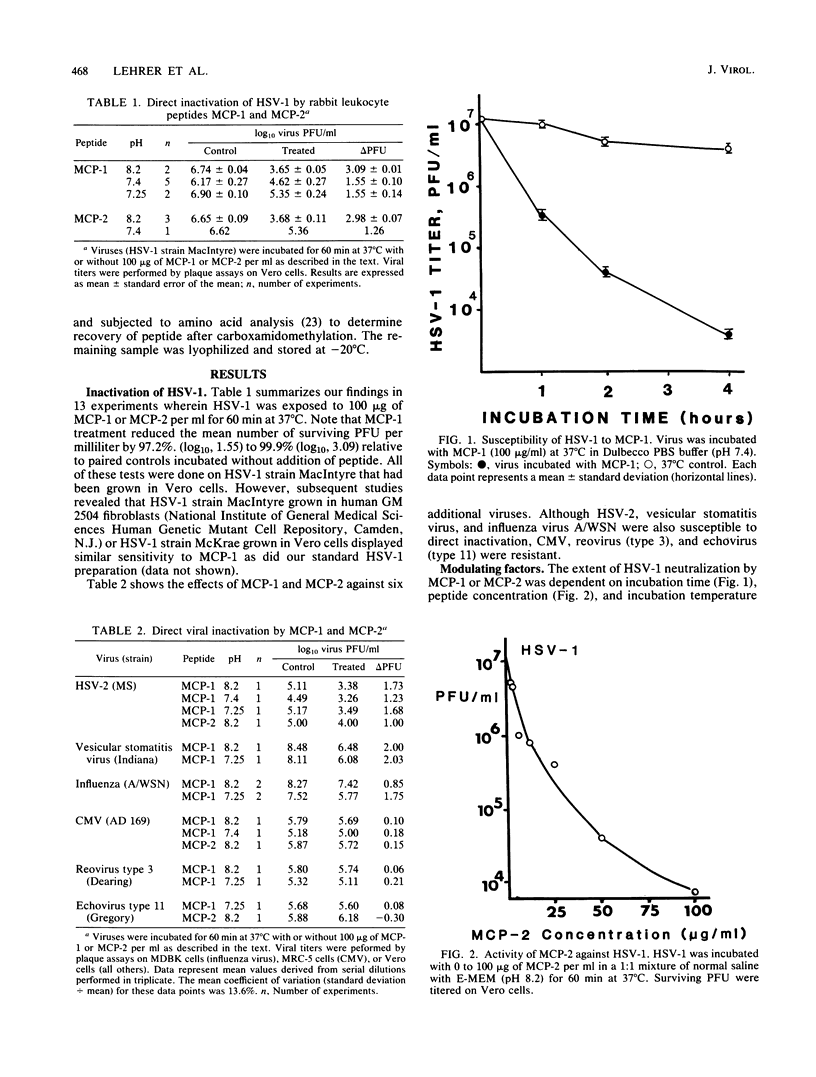
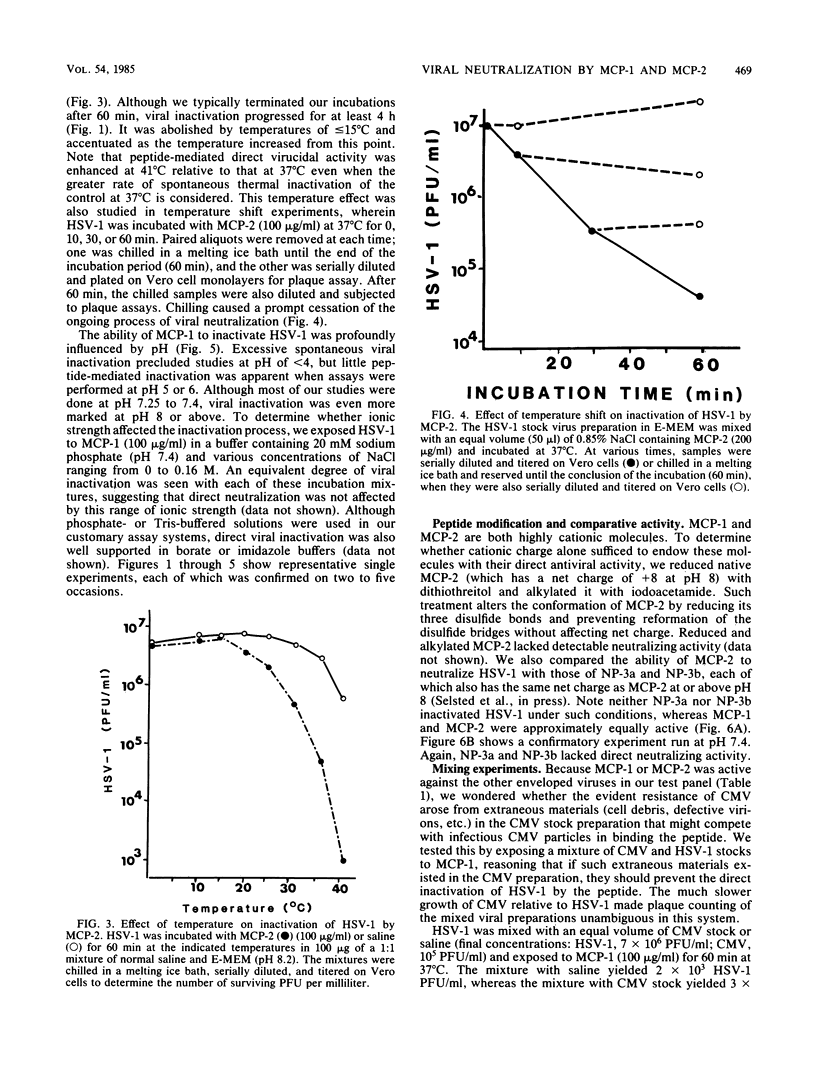
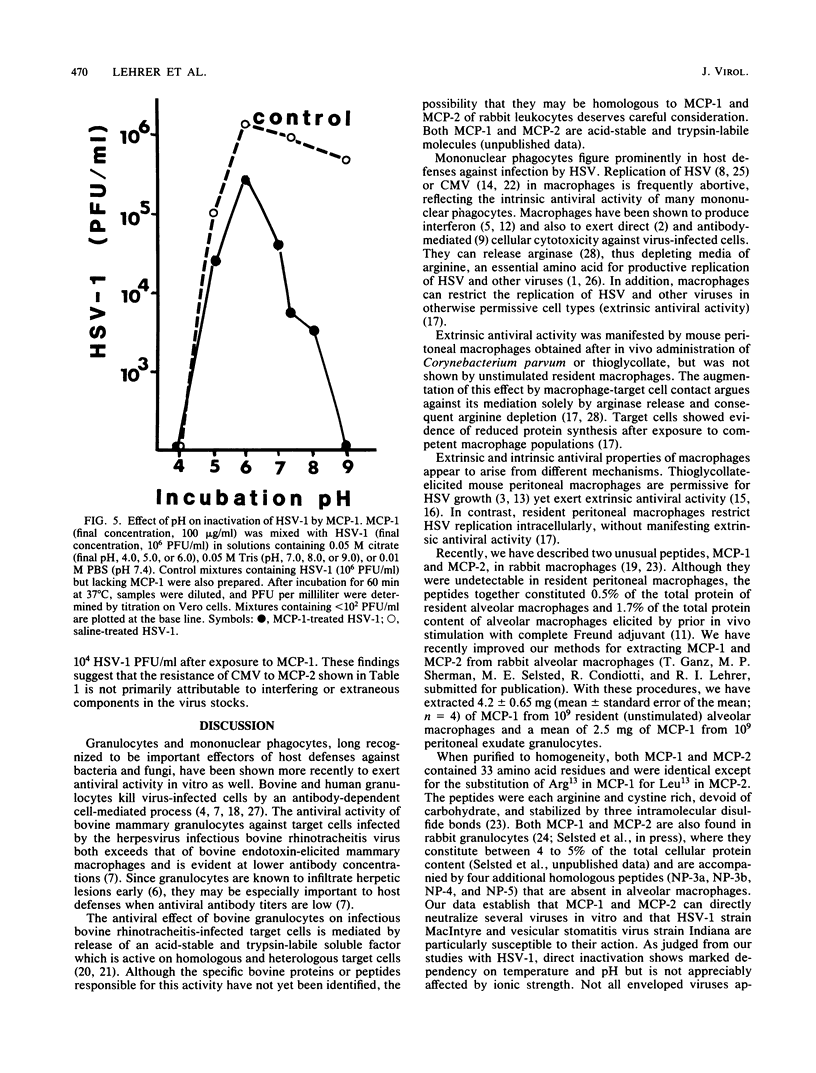
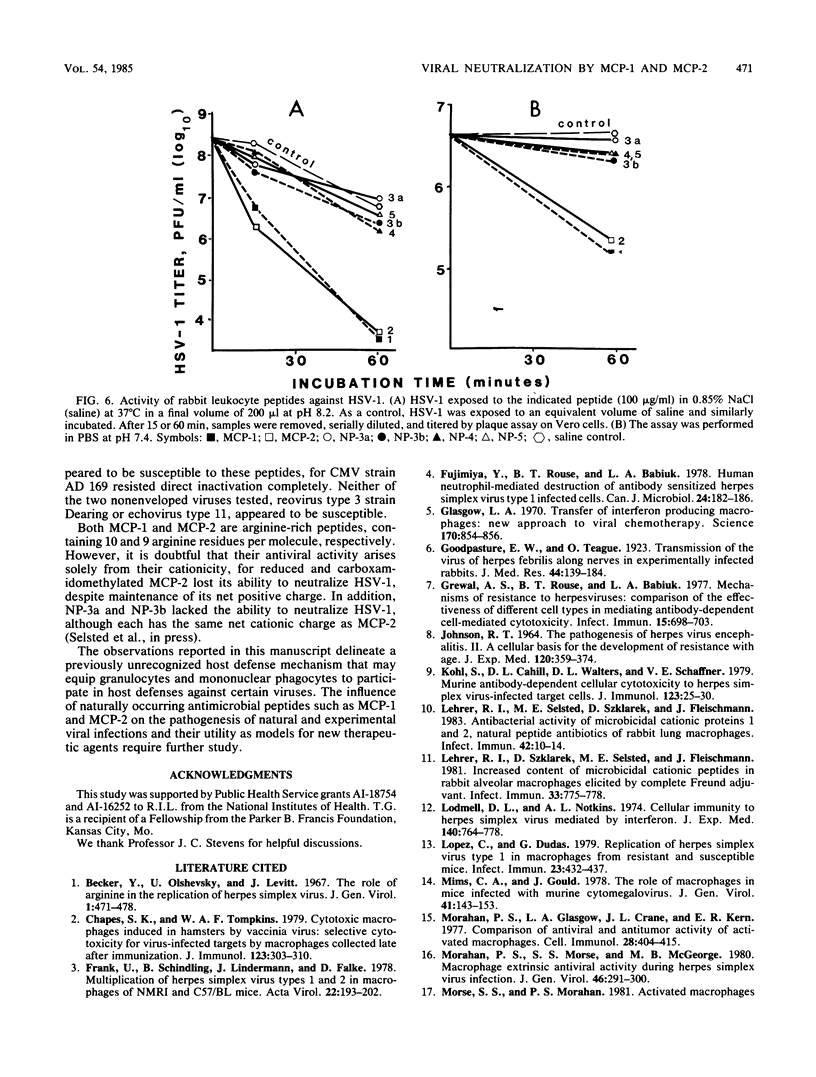
Six homologous peptides were purified to homogeneity from rabbit granulocytes or alveolar macrophages and tested for their ability to inactivate herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Two of the peptides, MCP-1 and MCP-2, showed considerable in vitro neutralizing activity, whereas four structurally homologous peptides (NP-3a, NP-3b, NP-4, and NP-5) were relatively ineffective. Inactivation of HSV-1 by MCP-1 or MCP-2 depended on peptide concentration and on the time, temperature, and pH of the incubation. HSV-2, vesicular stomatitis virus, and influenza virus A/WSN were also susceptible to direct neutralization by MCP-1 or MCP-2, whereas cytomegalovirus, echovirus type 11, and reovirus type 3 were not. We speculate that MCP-1 and MCP-2, peptides that are abundant in rabbit granulocytes and lung macrophages, may contribute to antiviral defenses by mediating the direct inactivation of HSV-1 and selected other viruses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y., Olshevsky U., Levitt J. The role of arginine in the replication of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):471–478. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapes S. K., Tompkins W. A. Cytotoxic macrophages induced in hamsters by vaccinia virus: selective cytotoxicity for virus-infected targets by macrophages collected late after immunization. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank U., Schindling B., Lindermann J., Falke D. Multiplication of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in macrophages of NMRI and C57/BL mice. Acta Virol. 1978 May;22(3):193–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimiya Y., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Human neutrophil--mediated destruction of antibody sensitized herpes simplex virus type I infected cells. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Feb;24(2):182–186. doi: 10.1139/m78-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Transfer of interferon-producing macrophages: new approach to viral chemotherapy. Science. 1970 Nov 20;170(3960):854–856. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3960.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewal A. S., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Mechanisms of resistant of herpesviruses: comparison of the effectiveness of different cell types in mediating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.698-703.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. THE PATHOGENESIS OF HERPES VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS. II. A CELLULAR BASIS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE WITH AGE. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:359–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Cahall D. L., Walters D. L., Schaffner V. E. Murine antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected target cells. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Fleischmann J. Antibacterial activity of microbicidal cationic proteins 1 and 2, natural peptide antibiotics of rabbit lung macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):10–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.10-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Szklarek D., Selsted M. E., Fleischmann J. Increased content of microbicidal cationic peptides in rabbit alveolar macrophages elicited by complete Freund adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):775–778. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.775-778.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Notkins A. L. Cellular immunity to herpes simplex virus mediated by interferon. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):764–778. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Dudas G. Replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 in macrophages from resistant and susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):432–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.432-437.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A., Gould J. The role of macrophages in mice infected with murine cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Glasgow L. A., Crane J. L., Jr, Kern E. R. Comparison of antiviral and antitumor activity of activated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1977 Feb;28(2):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Morse S. S., McGeorge M. G. Macrophage extrinsic antiviral activity during herpes simplex virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Delafield J., Martinez R. J., Lehrer R. I. Microbicidal cationic proteins in rabbit alveolar macrophages: a potential host defense mechanism. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.180-192.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophils in antiviral immunity: inhibition of virus replication by a mediator produced by bovine neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):223–232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wardley R. C., Babiuk L. A., Mukkur T. K. The role of neutrophils in antiviral defense--in vitro studies on the mechanism of antiviral inhibition. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1957–1961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Osborn J. E. Role of macrophages in resistance to murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1383–1390. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1383-1390.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of MCP-1 and MCP-2, natural peptide antibiotics of rabbit lung macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14485–14489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. Purification and antibacterial activity of antimicrobial peptides of rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):150–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.150-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Restriction of herpes simplex virus by macrophages. An analysis of the cell-virus interaction. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):19–38. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANKERSLEY R. W., Jr AMINO ACID REQUIREMENTS OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS IN HUMAN CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:609–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.609-613.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardley R. C., Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Antibody dependent cytotoxicity mediated by neutrophils: a possible mechanism of antiviral defense. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 May;19(5):323–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildy P., Gell P. G., Rhodes J., Newton A. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus multiplication by activated macrophages: a role for arginase? Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):40–45. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.40-45.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


