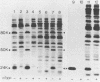
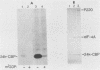
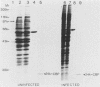
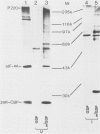
Abstract
In poliovirus-infected HeLa cells, poliovirus RNA is translated at times when cellular mRNA translation is strongly inhibited. It is thought that this translational control mechanism is mediated by inactivation of a cap-binding protein complex (comprising polypeptides of 24 [24-kilodalton cap-binding protein], 50, and approximately 220 kilodaltons). This complex can restore the translation of capped mRNAs in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. We have previously shown that the virally induced defect prevents interaction between cap recognition factors and mRNA. Here, we show that the cap-binding protein complex (and not the 24-kilodalton cap-binding protein) has activity that restores the cap-specific mRNA-protein interaction when added to initiation factors from poliovirus-infected cells. Thus, the activity that restores the cap-specific mRNA-protein interaction and that which restores the translation of capped mRNAs in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells, copurify. The results also indicate, by an alternative assay, that the cap-binding protein complex is the only factor inactivated by poliovirus. We also purified cap-binding proteins from uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. By various criteria, the 24-kilodalton cap-binding protein is not structurally modified as a result of infection. However, the 220-kilodalton polypeptide of the cap-binding protein complex is apparently cleaved by a putative viral (or induced) protease. By in vivo labeling and m7GDP affinity chromatography, we isolated a modified cap-binding protein complex from poliovirus-infected cells, containing proteolytic cleavage fragments of the 220-kilodalton polypeptide.
Full text
PDF




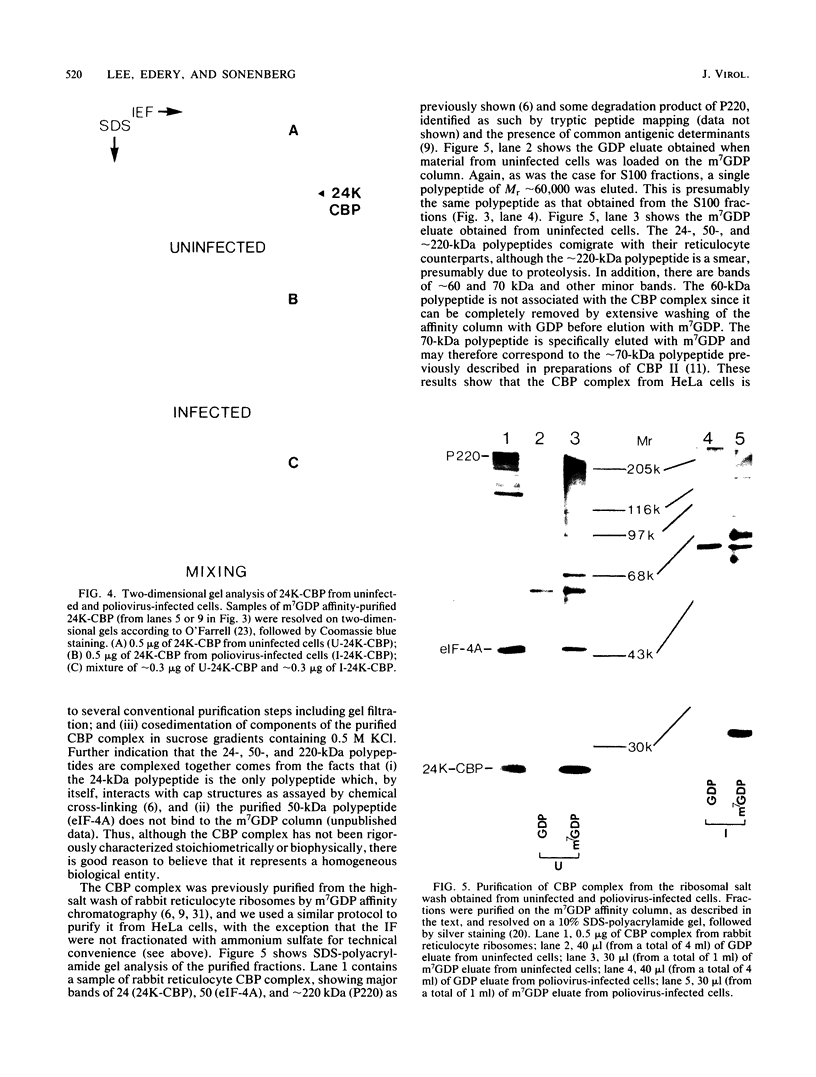




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K. 5'-terminal cap structure in eucaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):175–205. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.175-205.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Transcription in vitro by reovirus-associated ribonucleic acid-dependent polymerase. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.1-11.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Luedi M. L., Meyer L. J., Milburn S. C., Yau P. M., Corbett S., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis initiation factors from human HeLa cells and rabbit reticulocytes are similar: comparison of protein structure, activities, and immunochemical properties. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4202–4206. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Etchison D., Hershey J. W. Protein synthesis eukaryotic initiation factors 4A and 4B are not altered by poliovirus infection of HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7236–7239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Lee K. A., Sonenberg N. Functional characterization of eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein complex: effects on translation of capped and naturally uncapped RNAs. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2456–2462. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus-induced inhibition of host-cell protein synthesis. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):435–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Leis J. P., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A, a protein involved in ATP-dependent binding of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5246–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. L., Etchison D. O., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Localization of cap-binding protein in subcellular fractions of HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E. Presence of the cap-binding protein in initiation factor preparations from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):438–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.438-445.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Etchison D., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Association of cap-binding protein with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 in initiation factor preparations from uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):200–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.200-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E., Brown-Luedi M. L., Hershey J. W. Alterations in initiation factor activity from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10973–10978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Control of protein synthesis in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. I. mRNA discrimination by crude initiation factors. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):510–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.510-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James L. A., Tershak D. R. Protein phosphorylations in poliovirus infected cells. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):28–35. doi: 10.1139/m81-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Sonenberg N. Inactivation of cap-binding proteins accompanies the shut-off of host protein synthesis by poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3447–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Morgan M., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Influence of 5'-terminal m7G and 2'--O-methylated residues on messenger ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5761–5768. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt E., Blaas D., Kuechler E. CAP binding proteins associated with the nucleus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5821–5835. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. ATP/Mg++-dependent cross-linking of cap binding proteins to the 5' end of eukaryotic mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1643–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Rupprecht K. M., Hecht S. M., Shatkin A. J. Eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein: purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose-coupled m7GDP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4345–4349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Rose J. K., Leong K., Bergmann J. E., Gordon J., Baltimore D. Purification of a factor that restores translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA in extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]