Abstract
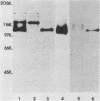
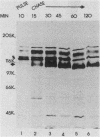
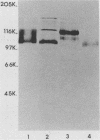
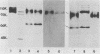
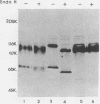
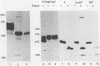
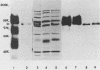
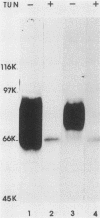
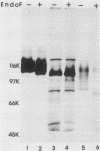
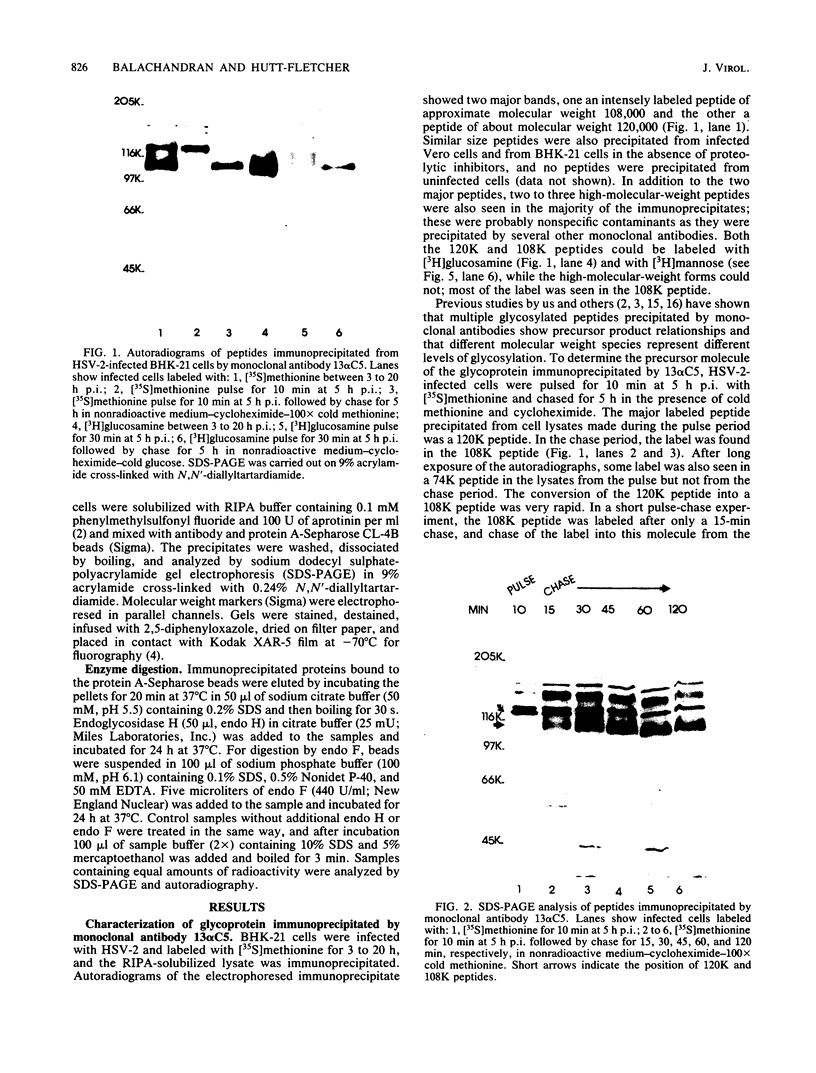
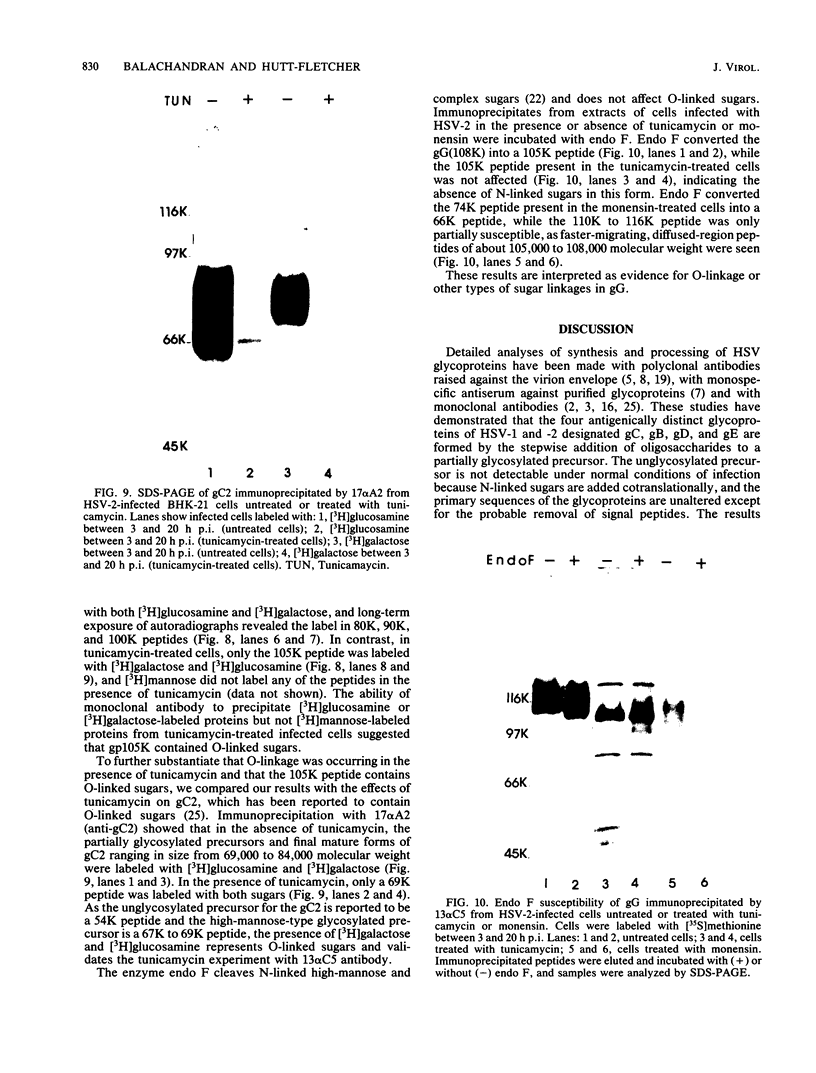
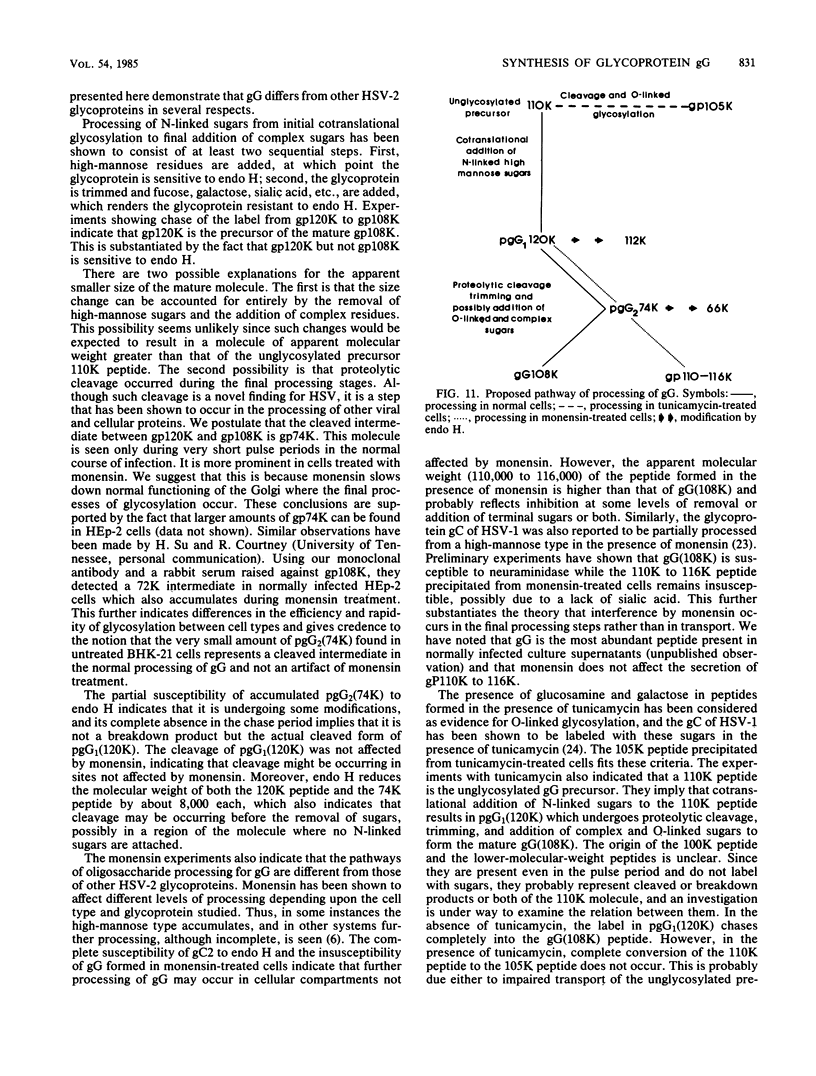
Monoclonal antibody 13 alpha C5-1-A11 immunoprecipitated two major polypeptides of molecular weights 108,000 and 120,000 from extracts of herpes simplex virus type 2-infected BHK-21 cells labeled with [35S]methionine or [3H]glucosamine. In pulse-chase experiments, both labels were chased from the 120,000-molecular-weight peptide (120K peptide) into the 108K molecule. Endoglycosidase H (endo H) reduced the 120K peptide to a 112K peptide but did not affect the 108K peptide. Similar profiles were obtained with monoclonal antibody AP-1 which reacts with a 92K glycoprotein, gG, which maps to the short unique region of the genome. Cross-absorption experiments indicated that both antibodies reacted with the same peptides, suggesting that the 120K peptide is a partially glycosylated high-mannose-type precursor of gG (pgG1). Immunoprecipitation from monensin-treated cells indicated that pgG1(120K) may undergo peptide cleavage to form a 74K high-mannose-type peptide (pgG2) and that this 74K peptide may be further processed into an endo H-resistant 110K to 116K peptide. In the presence of tunicamycin, gG(108K) was replaced by 110K and 105K peptides which were resistant to both endo H and endoglycosidase F. The 105K peptide was the only molecule labeled by [3H]galactose or [3H]glucosamine in the presence of tunicamycin, and none of the peptides were labeled with [3H]mannose, indicating the probable presence of O-linked sugars in the 105K peptide. Our results imply that cotranslational glycosylation of the unglycosylated precursor 110K peptide results in the high-mannose-type pgG1(120K), which probably undergoes peptide cleavage. This putative cleavage product may then mature into gG (108K) by the trimming of sugars and the addition of complex and probably O-linked sugars; the high-mannose-type pgG2(74K) is probably an intermediate peptide formed in this process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Killington R. A., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Monoclonal antibodies to two glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):438–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.438-446.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Rawls W. E., Bacchetti S. Glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2 as defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):344–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.344-355.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H. Comparative structural analysis of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):428–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.428-435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharides. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(1):21–49. doi: 10.3109/10409238409102805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Buckmaster A., Palfreyman J. W., Hope R. G., Minson A. C. Characterization of the 92,000-dalton glycoprotein induced by herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):547–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.547-554.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Zezulak K. M., Conley A. J., Weinberger M., Snitzer K., Spear P. G. Use of monoclonal antibodies against two 75,000-molecular-weight glycoproteins specified by herpes simplex virus type 2 in glycoprotein identification and gene mapping. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1223-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gA/B: evidence that the infected Vero cell products comap and arise by proteolysis. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):88–97. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.88-97.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth P., Rawls W. E., Duff R., Rapp F., Adam E., Melnick J. L. Antigenic differences between isolates of herpesvirus type 2. Intervirology. 1974;3(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1159/000149738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchánková A., Hirsch I., Kremár M., Vonka V. Determination of herpes simplex virus type-specific antibodies by solid-phase RIA on Helix pomatia lectin-purified antigens. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):964–972. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagh P. V., Bahl O. P. Sugar residues on proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(4):307–377. doi: 10.3109/10409238109113602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Courtney R. J. Glycosylation of herpes simplex virus type 1 gC in the presence of tunicamycin. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.297-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 2 75,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein antigenically related to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):553–562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.553-562.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Mapping of the structural gene for the herpes simplex virus type 2 counterpart of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C and identification of a type 2 mutant which does not express this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.741-747.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Showalter S. D., Bladen S. V., Heilman C. J., Jr, Hampar B. Herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gF and type 1 glycoprotein gC have related antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):185–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.185-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Showalter S. D., Simms D. J., Hampar B. Antibodies to a synthetic oligopeptide that react with herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):430–436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.430-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]