Abstract
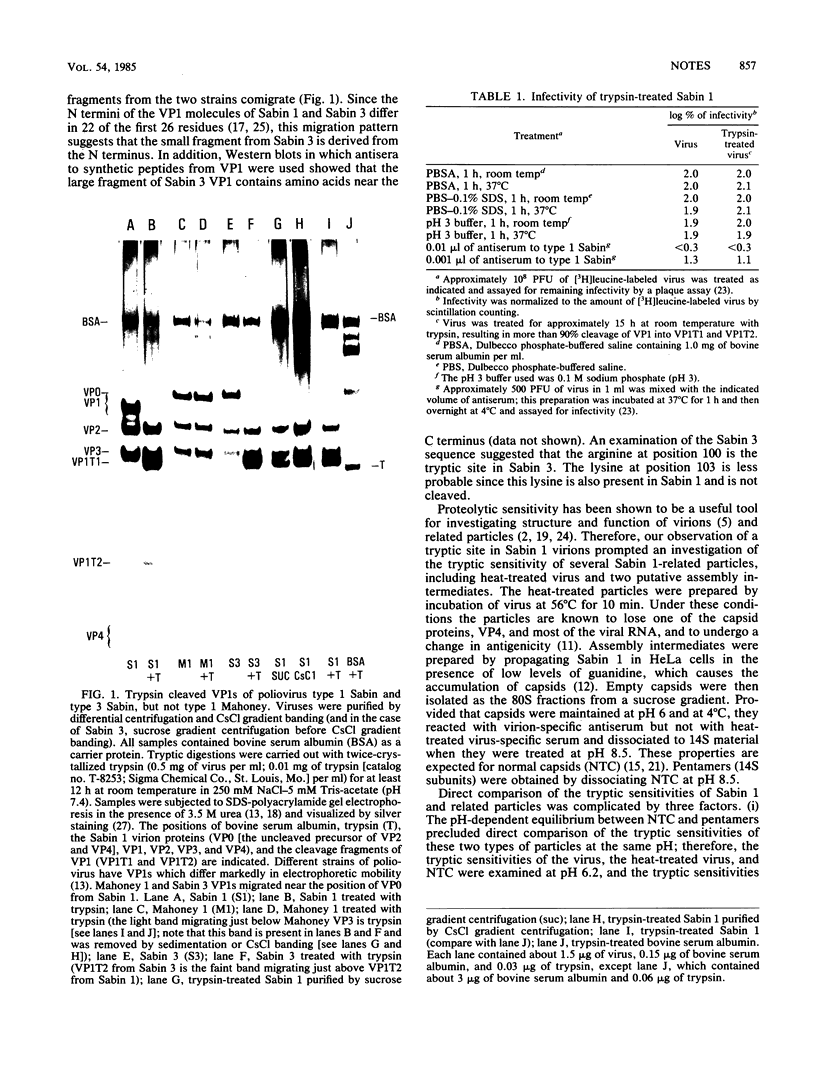
Treatment of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus with trypsin produced two stable fragments of capsid protein VP1 which remained associated with the virions. Trypsinized virus was fully infectious and was neutralized by type-specific antisera. The susceptible site in the Sabin 1 strain was between the lysine at position 99 and the asparagine at position 100. A similar tryptic cleavage occurred in the Leon and Sabin strains of type 3 poliovirus, probably at the arginine at position 100, but not in the type 1 Mahoney strain, which lacks a basic residue at either position 99 or position 100. Tryptic treatment of heat-treated virus and 14S assembly intermediates produced unique stable fragments which were different from those produced in virions. The implications of our results for future characterization of the surface structures of these particles and structural rearrangements in the poliovirus capsid are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edwards J., Mann E., Brown D. T. Conformational changes in Sindbis virus envelope proteins accompanying exposure to low pH. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1090–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1090-1097.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Identification of a new neutralization antigenic site on poliovirus coat protein VP2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):719–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.719-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. S., Harrison S. C. Proteolytic dissection of turnip crinkle virus subunit in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3862–3866. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., HOYER B. H. Early stages of enterovirus infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:101–112. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M. Preliminary studies of crystals of poliovirus type I. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 5;160(4):663–668. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90322-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Gilbert S. F., Grieves J., Anderegg J., Rueckert R. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody against poliovirus and its reaction with related antigens. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Pallansch M. A., Omilianowski D. R., Rueckert R. R. Changes in three of the four coat proteins of oral polio vaccine strain derived from type 1 poliovirus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.256-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu M. E., Pani A., Corrias M. V., Sau M., La Colla P. Poliovirus morphogenesis. I. Identification of 80S dissociable particles and evidence for the artifactual production of procapsids. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.341-347.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Poliovirus empty capsid morphogenesis: evidence for conformational differences between self- and extract-assembled empty capsids. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.792-800.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Vrijsen R., Brioen P., Boeyé A. A pH-dependent antigenic conversion of empty capsids of poliovirus studied with the aid of monoclonal antibodies to N and H antigen. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90393-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Pallansch M. A. Preparation and characterization of encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):315–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohmaier K., Franze R., Adam K. H. Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):295–306. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]