Abstract
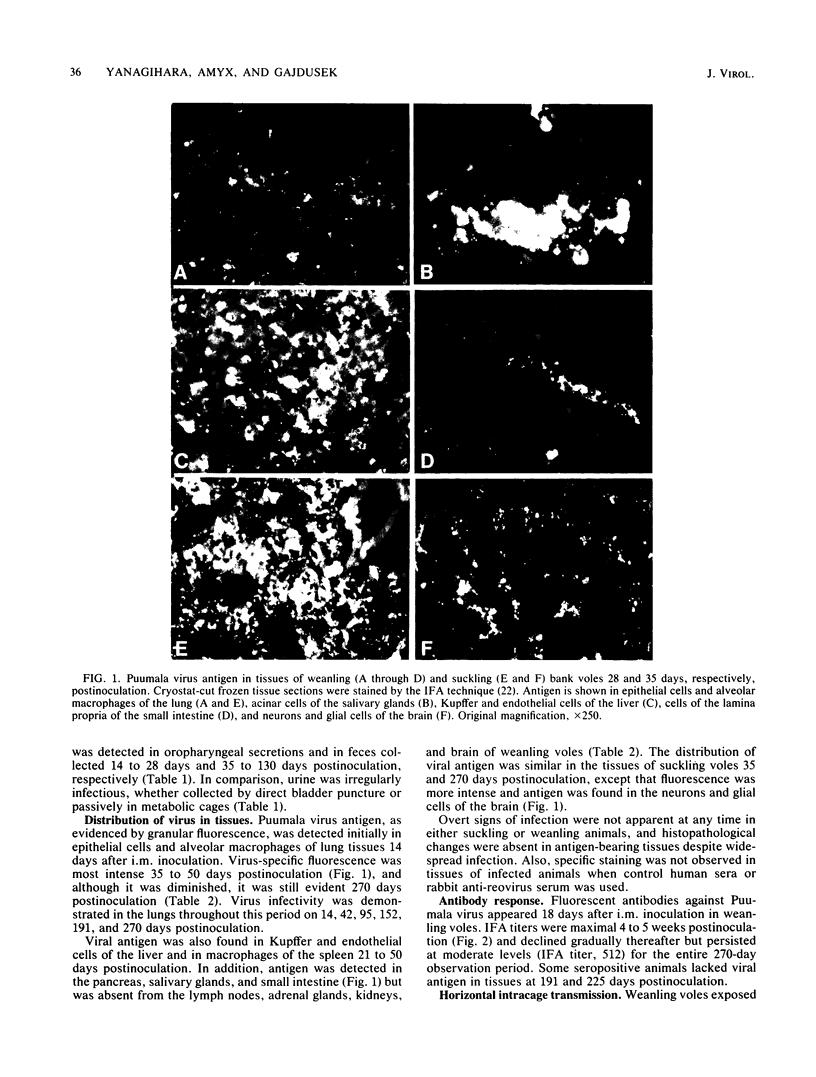
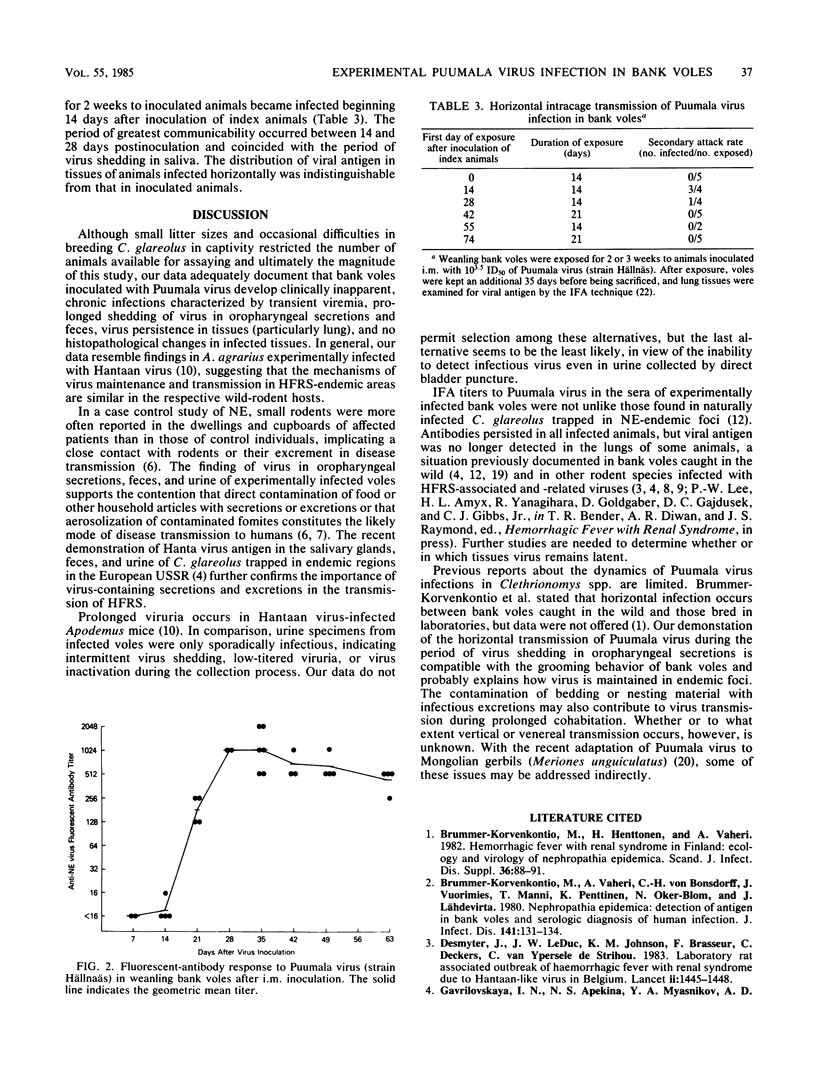
Subclinical chronic infections characterized by transient viremia, prolonged virus shedding in oropharyngeal secretions and feces, and virus persistence in tissues (particularly lung) developed in laboratory-bred weanling bank voles (Clethrionomys glareolus) inoculated intramuscularly with Puumala virus (strain Hällnäs), the etiologic agent of nephropathia epidemica. Viral antigen, as evidence by granular fluorescence, was detected in the lungs, liver, spleen, pancreas, salivary glands, and small intestine. Infectious virus was found in the lungs from 14 to 270 days postinoculation, and feces and urine collected 35 to 130 days postinoculation were regularly and sporadically infectious, respectively. Horizontal transmission coincided with virus shedding in oropharyngeal secretions. Suckling voles also developed asymptomatic persistent infections after intracerebral inoculation, and histopathological changes were absent despite widespread infection. Our data resemble findings in Apodemus agrarius experimentally infected with Hantaan virus, the prototype virus of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, suggesting that the mechanisms of maintenance and transmission of Puumala and Hantaan viruses are similar in their respective wild-rodent hosts.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Henttonen H., Vaheri A. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Finland: ecology and virology of nephropathia epidemica. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;36:88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Vaheri A., Hovi T., von Bonsdorff C. H., Vuorimies J., Manni T., Penttinen K., Oker-Blom N., Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica: detection of antigen in bank voles and serologic diagnosis of human infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):131–134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilovskaya I. N., Apekina N. S., Myasnikov YuA, Bernshtein A. D., Ryltseva E. V., Gorbachkova E. A., Chumakov M. P. Features of circulation of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) virus among small mammals in the European U.S.S.R. Arch Virol. 1983;75(4):313–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01314898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korpela H., Lähdevirta J. The role of small rodents and patterns of living in the epidemiology of nephropathia epidemica. Scand J Infect Dis. 1978;10(4):303–305. doi: 10.3109/inf.1978.10.issue-4.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDuc J. W., Smith G. A., Johnson K. M. Hantaan-like viruses from domestic rats captured in the United States. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Sep;33(5):992–998. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Baek L. J., Johnson K. M. Isolation of Hantaan virus, the etiologic agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever, from wild urban rats. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):638–644. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Baek L. J., Song C. K., Seong I. W. Intraspecific transmission of Hantaan virus, etiologic agent of Korean hemorrhagic fever, in the rodent Apodemus agrarius. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Sep;30(5):1106–1112. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Johnson K. M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):298–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Svedmyr A., Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Löfgren O., Nyström K. HFRS antigen and antibody in two species of Swedish voles. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(4):315–316. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-4.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica in Finland. A clinical histological and epidemiological study. Ann Clin Res. 1971;3:1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouland G. Nephropathia epidemica. 12 kasus fra Grane og Hattfjelldal i Nordland fylke August 1973-Januar 1974. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1975 Mar 10;95(7):426–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström K. Incidence and prevalence of endemic benign (epidemic) nephropathy in AC county, Sweden, in relation to population density and prevalence of small rodents. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1977;609:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Hasty S. E., Dalrymple J. M., LeDuc J. W., Lee H. W., von Bonsdorff C. H., Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Vaheri A., Tsai T. F., Regnery H. L. Antigenic and genetic properties of viruses linked to hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.2858126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traavik T., Sommer A. I., Mehl R., Berdal B. P., Stavem K., Hunderi O. H., Dalrymple J. M. Nephropathia epidemica in Norway: antigen and antibodies in rodent reservoirs and antibodies in selected human populations. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Aug;93(1):139–146. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400061027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C. Propagation of nephropathia epidemica virus in Mongolian gerbils. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):973–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.973-975.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Goldgaber D., Lee P. W., Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Svedmyr A. Propagation of nephropathia epidemica virus in cell culture. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):1013–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara R., Svedmyr A., Amyx H. L., Lee P., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Isolation and propagation of nephropathia epidemica virus in bank voles. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(3):225–228. doi: 10.3109/00365548409070393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]