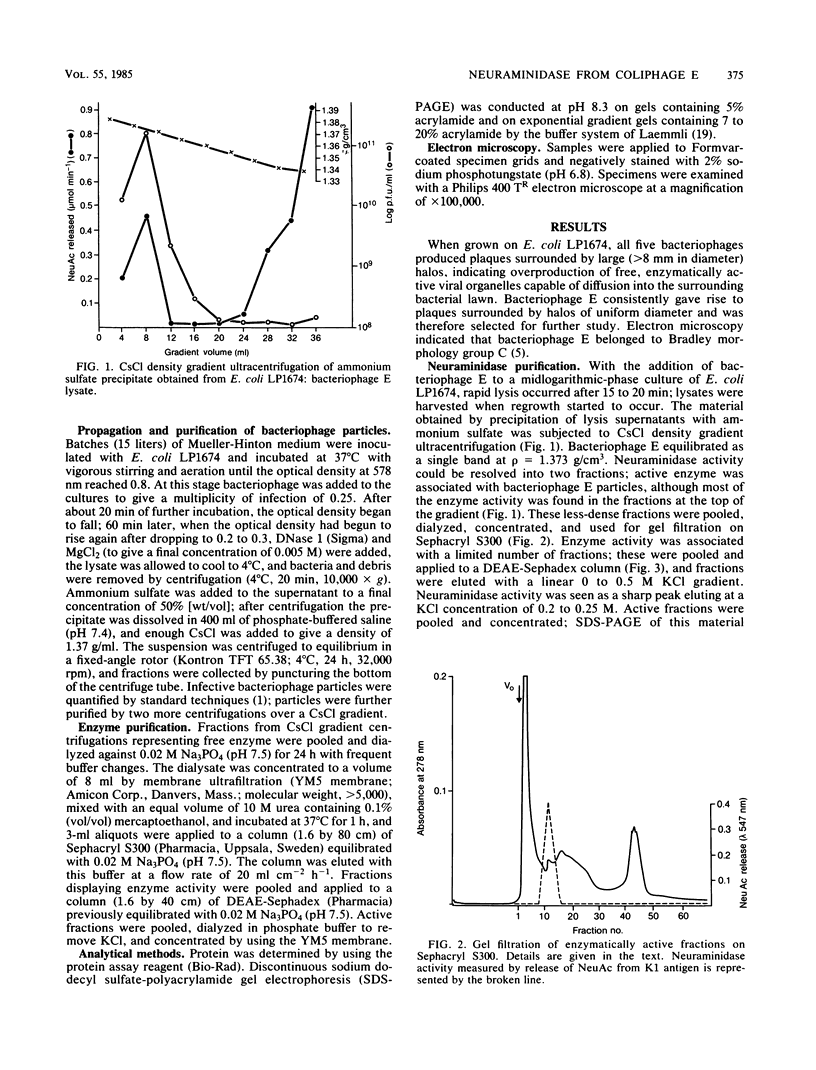
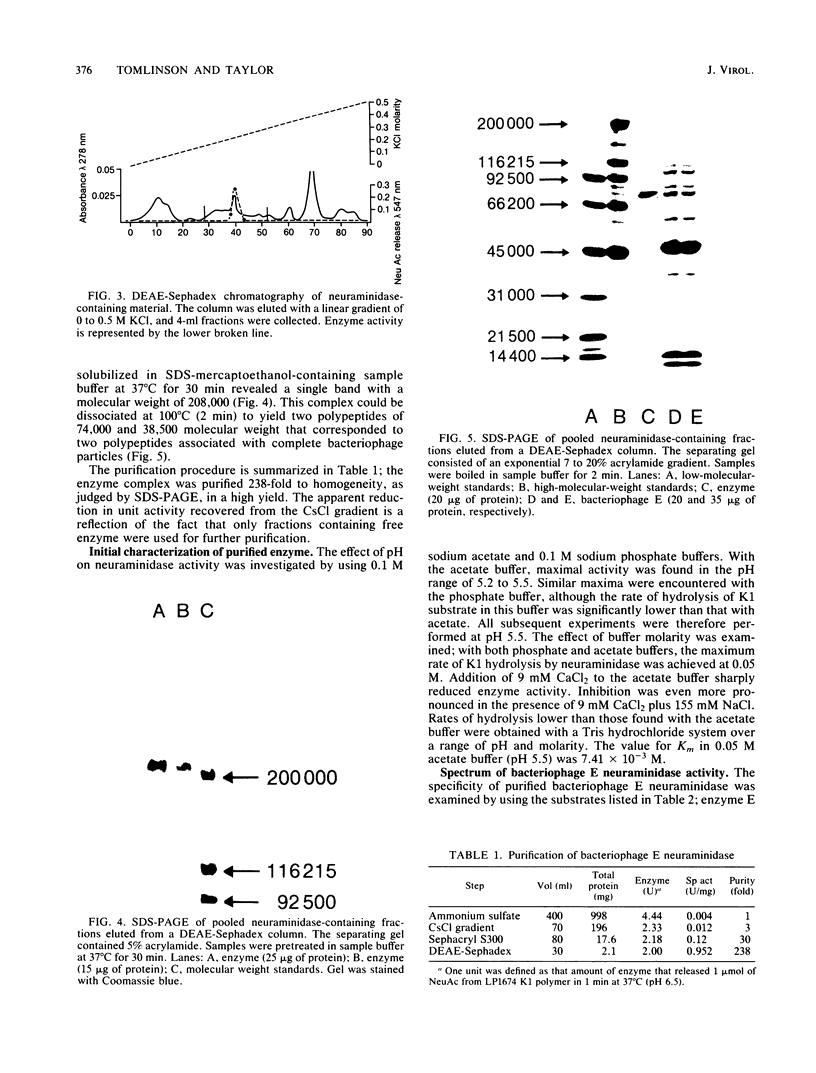
Abstract
Plaque morphology indicated that the five Escherichia coli K1-specific bacteriophages (A to E) described by Gross et al. (R. J. Gross, T. Cheasty, and B. Rowe, J. Clin. Microbiol. 6:548-550, 1977) encode K1 depolymerase activity that is present in both the bound and free forms. The free form of the enzyme from bacteriophage E was purified 238-fold to apparent homogeneity and in a high yield from ammonium sulfate precipitates of cell lysates by a combination of CsCl density gradient ultracentrifugation, gel filtration, and anion-exchange chromatography. The enzyme complex had an apparent molecular weight of 208,000, as judged from its behavior on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and was dissociated by sodium dodecyl sulfate at 100 degrees C to yield two polypeptides with apparent molecular weights of 74,000 and 38,500. Optimum hydrolytic activity was observed at pH 5.5, and activity was strongly inhibited by Ca2+; the Km was 7.41 X 10(-3) M. Rapid hydrolysis of both the O-acetylated and non-O-acetylated forms of the K1 antigen, an alpha 2----8-linked homopolymer of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and of the meningococcus B antigen was observed. Limited hydrolysis of the E. coli K92 antigen, an N-acetylneuraminic acid homopolymer containing alternating alpha 2----8 and alpha 2----9 linkages, occurred, but the enzyme failed to release alpha 2----3-, alpha 2----6-, or alpha 2----9-linked sialic residues from a variety of other substrates.
Full text
PDF

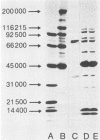
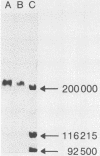
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H., Bayer M. H. Penetration of the polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli (Bi161/42) by bacteriophage K29. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):95–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler W., Fehmel F., Freund-Mölbert E., Knüfermann H., Stirm S. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. IV. Free capsule depolymerase 29. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):976–984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.976-984.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buscher H. P., Casals-Stenzel J., Schaufer R. New sialic acids. Identification of N-glycoloyl-O-acetylneuraminic acids and N-acetyl-O-glycoloylneuraminic acids by improved methods for detection of N-acyl and O-acyl groups and by gas-liquid chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):71–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R. Viral and bacterial neuraminidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;59:35–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65444-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghidoni R., Sonnino S., Tettamanti G., Wiegandt H., Zambotti V. On the structure of two new gangliosides from beef brain. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):511–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Cross-antigenicity and immunogenicity between capsular polysaccharides of group C Neisseria meningitidis and of Escherichia coli K92. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jan;135(1):94–104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Isolation of bacteriophages specific for the K1 polysaccharide antigen of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):548–550. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.548-550.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. C., Howlett G. J., Nestorowicz A., Webster R. G. The equilibrium constant for the interaction between a monoclonal Fab fragment and an influenza virus neuraminidase. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1313–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Bhattacharjee A. K., Bundle D. R., Kenny C. P., Martin A., Smith I. C. Strucutres of the capsular polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis as determined by 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S78–S83. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Boschek B., Thiele H., Stirm S. Endo-N-acetylneuraminidase associated with bacteriophage particles. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):697–704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.697-704.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Egan W., Robbins J. B. Sialic acid-containing polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli strain Bos-12: structure and immunology. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S71–S77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil J. Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1980;37:157–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Sutton A., Schneerson R., Lin W., Egan W., Hoff G. E., Robbins J. B. Form variation in Escherichia coli K1: determined by O-acetylation of the capsular polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):669–685. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Immunochemical investigations on lipopolysaccharides and acidic polysaccharides from serum-sensitive and serum-resistant strains of Escherichia coli isolated from urinary-tract infections. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):405–421. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd The chemistry and biosynthesis of selected bacterial capsular polymers. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurewicz E. C., Ghalambor M. A., Duckworth D. H., Heath E. C. Catalytic and molecular properties of a phage-induced capsular polysaccharide depolymerase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5607–5616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]