Abstract
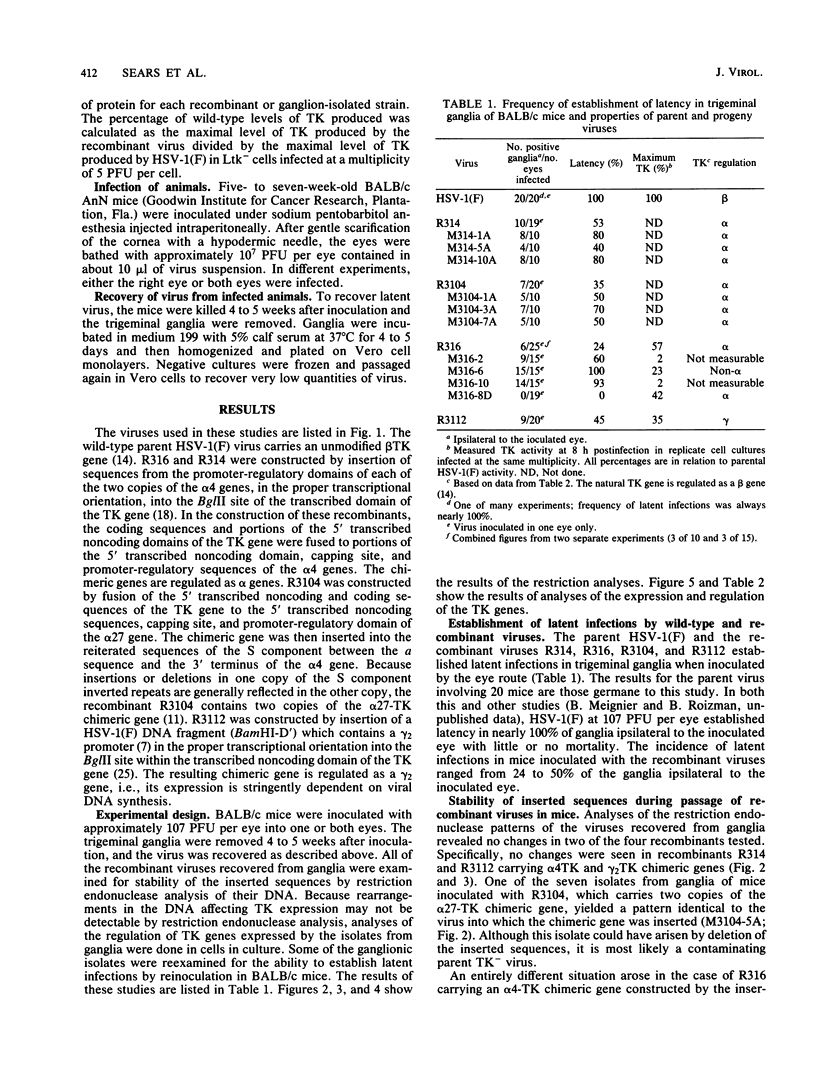
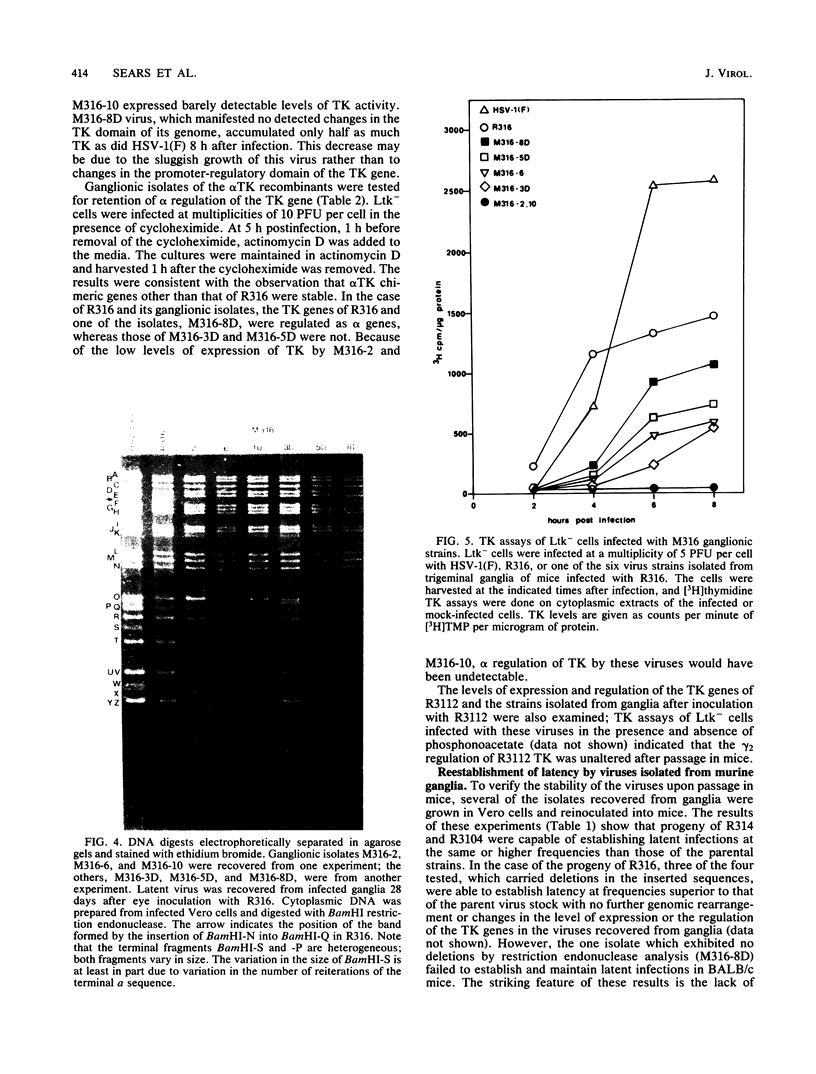
Herpes simplex virus 1 recombinants carrying alpha-, beta-, and late gamma (gamma 2)-regulated thymidine kinase (TK) genes were tested for the ability to establish latency in BALB/c mice inoculated by the eye route. The significant findings were as follows. Representatives of alpha- and gamma 2-regulated TK recombinants all established and maintained latent infections, but the efficiency was somewhat lower than that of wild-type virus. Of the three alpha TK recombinants tested, one (R316) spontaneously deleted portions of the inserted sequences which conferred alpha regulation to the TK gene. The viruses carrying these deletions expressed considerably lower TK activity than did wild-type virus, i.e., 2 to 40% of the levels expressed by the wild-type virus carrying the beta TK gene. However, the ability of these viruses to establish latency was not related to the efficiency of expression of the TK gene. These results indicate the following: (i) conversion of the TK gene into an alpha or gamma 2 gene did not preclude the establishment of latent infections; (ii) there was no correlation between the levels of TK activity expressed in cell culture and the ability to establish latency; and (iii) rearrangement of the genome by insertions or deletions which interrupt gene domains did not automatically result in an inability to establish latent infections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Braun D. K., Pereira L., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha proteins 0, 4, and 27 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.108-118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. K., Pereira L., Norrild B., Roizman B. Application of denatured, electrophoretically separated, and immobilized lysates of herpes simplex virus-infected cells for detection of monoclonal antibodies and for studies of the properties of viral proteins. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.103-112.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Darby G. Pathogenicity in mice of strains of herpes simplex virus which are resistant to acyclovir in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):209–216. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y., Gilden D. H., Shtram Y., Asher Y., Tabor E., Wellish M., Devlin M., Snipper D., Hadar J., Becker Y. A low thymidine kinase-producing mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1 causes latent trigeminal ganglia infections in mice. Arch Virol. 1983;76(1):39–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01315702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. T., Courtney R. J., Dunkel E. C. Detection of an immediate early herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide in trigeminal ganglia from latently infected animals. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):987–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.987-992.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 reiterated S component sequences (c1) situated between the a sequence and alpha 4 gene are not essential for virus replication. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.509-514.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Al-Saadi S. A., Clements G. B. Reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus from dissociated identified dorsal root ganglion cells in culture. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1629–1635. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., DeStefano E. Pathogenesis of experimental skin infections induced by drug-resistant herpes simplex virus mutants. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):693–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.693-701.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G. The transformation of cell growth and transmogrification of DNA synthesis by simian virus 40. Adv Cancer Res. 1981;34:1–68. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Khan A. Resistance of peripheral autonomic neurons to in vivo productive infection by herpes simplex virus mutants deficient in thymidine kinase activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):571–580. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.571-580.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Sharp J. A., Summers W. C. In vitro and in vivo transcription initiation sites on the TK-encoding BamHI Q fragment of HSV-1 DNA. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Halliburton I. W., Meignier B., Silver S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 mutant deleted in the alpha 22 gene: growth and gene expression in permissive and restrictive cells and establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.338-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Dunstan M. E. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase expression in infection of the trigeminal ganglion. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Miller R. L., Rapp F. Trigeminal ganglion infection by thymidine kinase-negative mutants of herpes simplex virus. Science. 1979 Aug 31;205(4409):915–917. doi: 10.1126/science.224454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Ressel S., Dunstan M. E. Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase expression in trigeminal ganglion infection: correlation of enzyme activity with ganglion virus titer and evidence of in vivo complementation. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):328–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90638-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Yamamoto H., Notkins A. L. Immunological response restricts number of cells in sensory ganglia infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):554–556. doi: 10.1038/264554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]