Abstract
DNA packaging of Salmonella phage P22 starts at a defined site on a concatemer of P22 genomes. The molecular ends formed at the packaging initiation site (pac) map within a region of ca. 120 base pairs and may contain any of the four nucleotides at their 5' end. The determination of the positions of the cuts within the sequence demonstrates a characteristic distribution of cut sites which apparently cannot be attributed to the sequence organization of the involved regions. Symmetric elements of the sequence might serve as signals for a recognition event(s) at pac in a separate process preceding the cutting reaction. The region of packaging initiation is located within the sequence coding for gene 3. The 3 protein is responsible for the site specificity of this process. We find no significant homology to Nu1 protein, which appears to have an analogous or similar function in the DNA maturation of Escherichia coli phage lambda.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. B., Hayden M., Casjens S. On the sequential packaging of bacteriophage P22 DNA. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):673–677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.673-677.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Gold M. Enzymatic breakage of the cohesive end site of phage lambda DNA: terminase (ter) reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Waddell C. H., King J. Mechanism of head assembly and DNA encapsulation in Salmonella phage p22. I. Genes, proteins, structures and DNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):669–695. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Huang W. M. Initiation of sequential packaging of bacteriophage P22 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Botstein D. Genetics of bacteriophage P22. I. Isolation of prophage deletions which affect immunity to superinfection. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):257–267. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelala C. A., Margolin P. Effects of deletions on cotransduction linkage in Salmonella typhimurium: evidence that bacterial chromosome deletions affect the formation of transducing DNA fragments. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(2):97–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00266146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm R. L., Deans R. J., Jackson E. N., Jackson D. A., Rutila J. E. A physical gene map of the bacteriophage P22 late region: genetic analysis of cloned fragments of P22 DNA. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):172–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans R. J., Jackson E. N. Restriction endonuclease Hin dIII cleavage site map of bacteriophage P22. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):359–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deichelbohrer I., Messer W., Trautner T. A. Genome of Bacillus subtilis Bacteriophage SPP1: Structure and Nucleotide Sequence of pac, the Origin of DNA Packaging. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):83–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.83-90.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Casjens S. R. DNA packaging by the double-stranded DNA bacteriophages. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):319–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Bublitz A. Polarized packaging of bacteriophage lambda chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 5;94(4):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Fisher R. A., Siegele D. A., Nichols B. P., Donelson J. E. Packaging of the bacteriophage lambda chromosome: a role for base sequences outside cos. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):56–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Kobayashi I., Widner W. Separate sites for binding and nicking of bacteriophage lambda DNA by terminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):955–959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Siegele D. A. Packaging of the bacteriophage lambda chromosome: dependence of cos cleavage on chromosome length. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):190–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George M., Bukhari A. I. Heterogeneous host DNA attached to the left end of mature bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):175–176. doi: 10.1038/292175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M., Becker A. The bacteriophage lambda terminase. Partial purification and preliminary characterization of properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14619–14625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. DNA sequences necessary for packaging of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7456–7460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. N., Jackson D. A., Deans R. J. EcoRI analysis of bacteriophage P22 DNA packaging. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):365–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. N., Laski F., Andres C. Bacteriophage P22 mutants that alter the specificity of DNA packaging. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 5;154(4):551–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufer B., Backhaus H., Schmieger H. The packaging initiation site of phage P22. Analysis of packaging events by transduction. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):510–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00332636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwoh D. Y., Kemper J. Bacteriophage P22-mediated specialized transduction in Salmonella typhimurium: identification of different types of specialized transducing particles. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):535–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.535-550.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R., Messing J. Apple II software for M13 shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):39–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F., Jackson E. N. Maturation cleavage of bacteriophage P22 DNA in the absence of DNA packaging. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 5;154(4):565–579. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
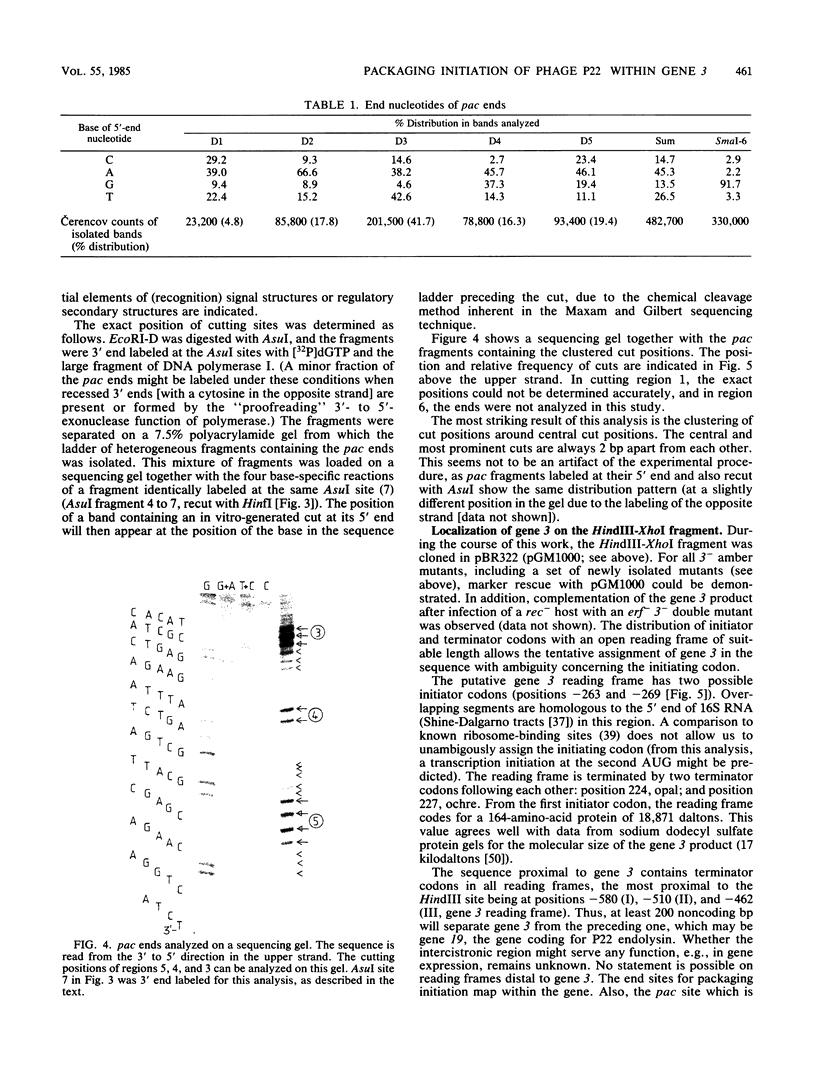
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Matsubara K. Identification of sequences necessary for packaging DNA into lambda phage heads. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Matsubara K. Lambda phage DNA sequences affecting the packaging process. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Thomas R. Ter, a function which generates the ends of the mature lambda chromosome. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):242–244. doi: 10.1038/221242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteete A. R., Botstein D. Purification and properties of proteins essential to DNA encapsulation by phage P22. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteete A. R., Jarvik V., Botstein D. Encapsulation of phage P22 DNA in vitro. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):550–564. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj A. S., Raj A. Y., Schmieger H. Phage genes involved in the formation generalized transducing particles in Salmonella--Phage P22. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(2):175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00264784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades M., MacHattie L. A., Thomas C. A., Jr The P22 bacteriophage DNA molecule. I. The mature form. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieger H., Backhaus H. Altered cotransduction frequencies exhibited by HT-mutants of Salmonella-phage P22. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Feb 2;143(3):307–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00269408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Defective phage formation by lysogens of integration deficient phage P22 mutants. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):203–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Emrich J., Stahl M. M. Chromosome structure in phage t4, iii. Terminal redundancy and length determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):292–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel E., Behnisch W., Schmieger H. In vitro packaging of mature phage DNA by Salmonella phage P22. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner-Smith M., Becker A., Gold M. DNA packaging in the lambdoid phages: the role of lambda genes Nu1 and A. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):642–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susskind M. M., Botstein D. Molecular genetics of bacteriophage P22. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):385–413. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.385-413.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K. A mutant of phage P22 with randomly permuted DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):421–426. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Chan R. K., Botstein D. Packaging of an oversize transducing genome by Salmonella phage P22. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):485–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Huberman J. A., Botstein D. Non-random circular permutation of phage P22 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):501–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S., Levine M. Replication in situ and DNA encapsulation following induction of an excision-defective lysogen of Salmonella bacteriophage P22. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):389–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Taylor E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. II. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Susskind M. M. Identification of the products of bacteriophage P22 genes, including a new late gene. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):258–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan R. Structure and mechanism of multifunctional restriction endonucleases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:285–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]