Abstract
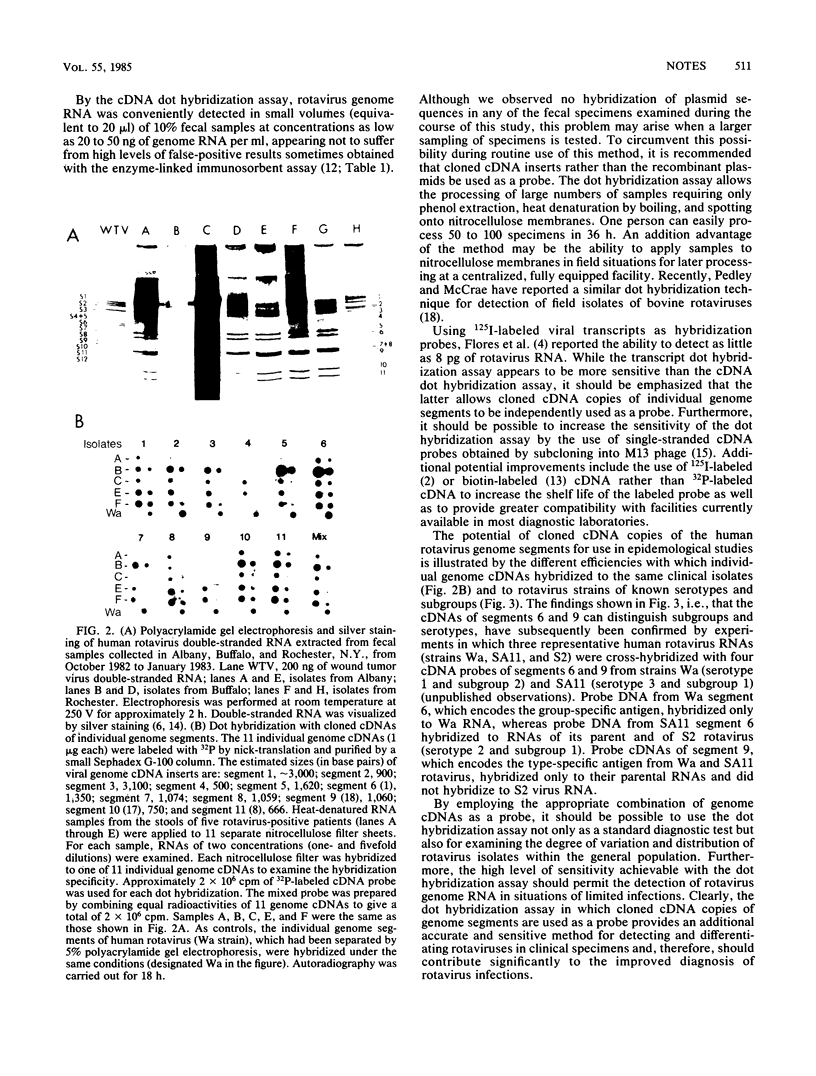
The diagnostic potential of cloned cDNA copies of human rotavirus (strain WA) genome segments for the detection of rotavirus in clinical specimens has been determined. A hybridization assay in which a mixture of 32P-labeled cDNAs representing the 11 rotavirus segments was used as a probe compared favorably with three frequently used diagnostic tests for rotavirus in terms of both specificity and sensitivity. Significantly, clinical isolates could be readily distinguished when cloned cDNA copies of individual genome segments were used independently as a probe. In assays in which genome RNA from rotaviruses of known subgroups and serotypes were tested, cloned probes that encode nonstructural viral proteins hybridized efficiently to genome RNAs of all strains, whereas cloned probes corresponding to genome segments 6 and 9 exhibited the potential for differentiating strains of different subgroups and serotypes. Cloned cDNA copies of rotavirus genome segments therefore offer considerable potential for improved general diagnosis of rotavirus in clinical specimens, as well as for epidemiological studies in which virus isolates can be distinguished on the basis of nucleotide sequence homology of individual genome segments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Both G. W., Siegman L. J., Bellamy A. R., Ikegami N., Shatkin A. J., Furuichi Y. Comparative sequence analysis of rotavirus genomic segment 6--the gene specifying viral subgroups 1 and 2. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.97-101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Boeggeman E., Purcell R. H., Sereno M., Perez I., White L., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A dot hybridisation assay for detection of rotavirus. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92811-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung J. C., Wicher K. Minimum number of bacteria needed for antigen detection by counterimmunoelectrophoresis: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):681–687. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.681-687.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Richardson M. A., Ikegami N., Shatkin A. J., Furuichi Y. Molecular cloning of double-stranded RNA virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Garon C. F., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., van Kirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Differentiation of human and calf reoviruslike agents associated with diarrhea using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of RNA. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Espejo R. T., Flores J., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Distinctive ribonucleic acid patterns of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):958–961. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.958-961.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause P. J., Hyams J. S., Middleton P. J., Herson V. C., Flores J. Unreliability of Rotazyme ELISA test in neonates. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):259–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Switzer R. C., Van Keuren M. L. Trace polypeptides in cellular extracts and human body fluids detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis and a highly sensitive silver stain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4335–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Richardson M. A., Ikegami N., Nomoto A., Furuichi Y. Nucleotide sequence of human rotavirus genome segment 10, an RNA encoding a glycosylated virus protein. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):856–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.856-859.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., McCrae M. A. A rapid screening assay for detecting individual RNA species in field isolates of rotaviruses. J Virol Methods. 1984 Oct;9(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. A., Iwamoto A., Ikegami N., Nomoto A., Furuichi Y. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the serotype-specific antigen of human (Wa) rotavirus: comparison with the homologous genes from simian SA11 and UK bovine rotaviruses. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):860–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.860-862.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Birch C., McLean B., Holmes I. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotaviruses in Melbourne, Australia, from 1973 to 1979, as determined by electrophoresis of genome ribonucleic acid. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):272–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.272-278.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Miller M. F. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay with electron microscopic procedures for detecting rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):938–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.938-944.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder B. A., Street J. E., Kalmakoff J., Bellamy A. R. Sequence relationships between the genome segments of human and animal rotavirus strains. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.379-385.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street J. E., Croxson M. C., Chadderton W. F., Bellamy A. R. Sequence diversity of human rotavirus strains investigated by northern blot hybridization analysis. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):369–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.369-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]