Abstract
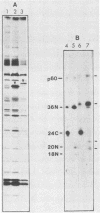
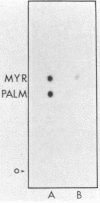
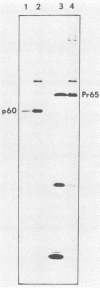
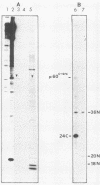
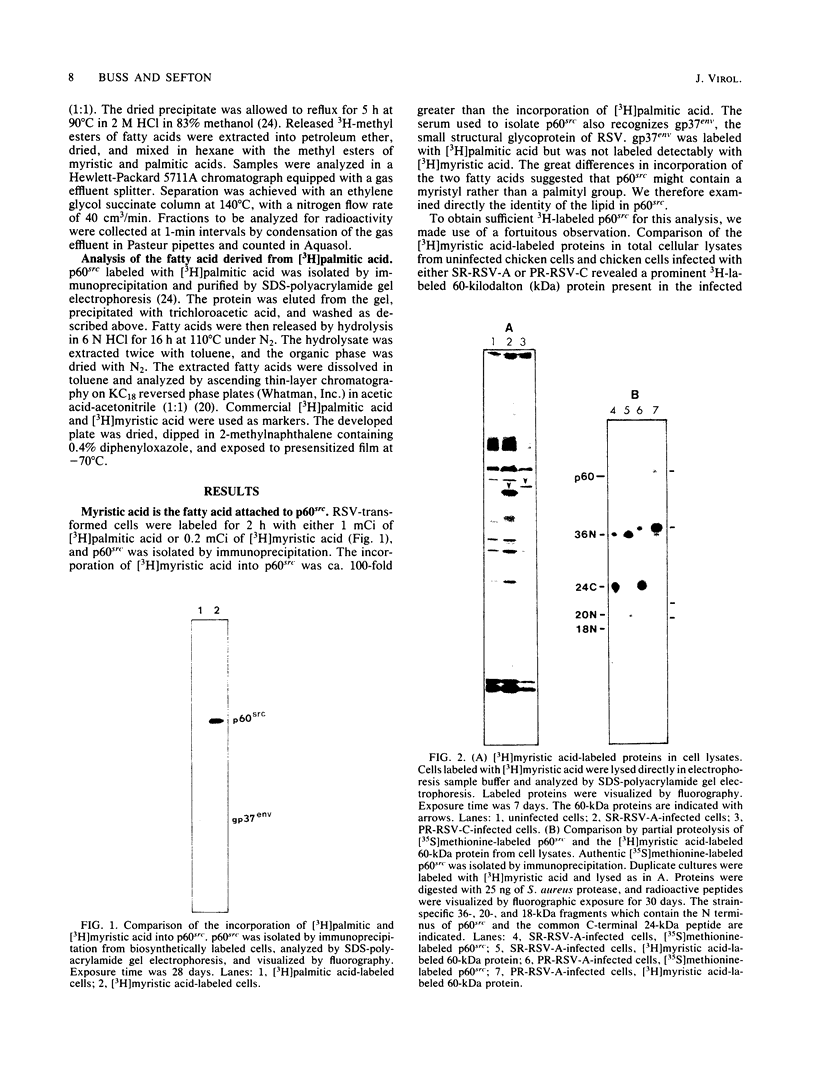
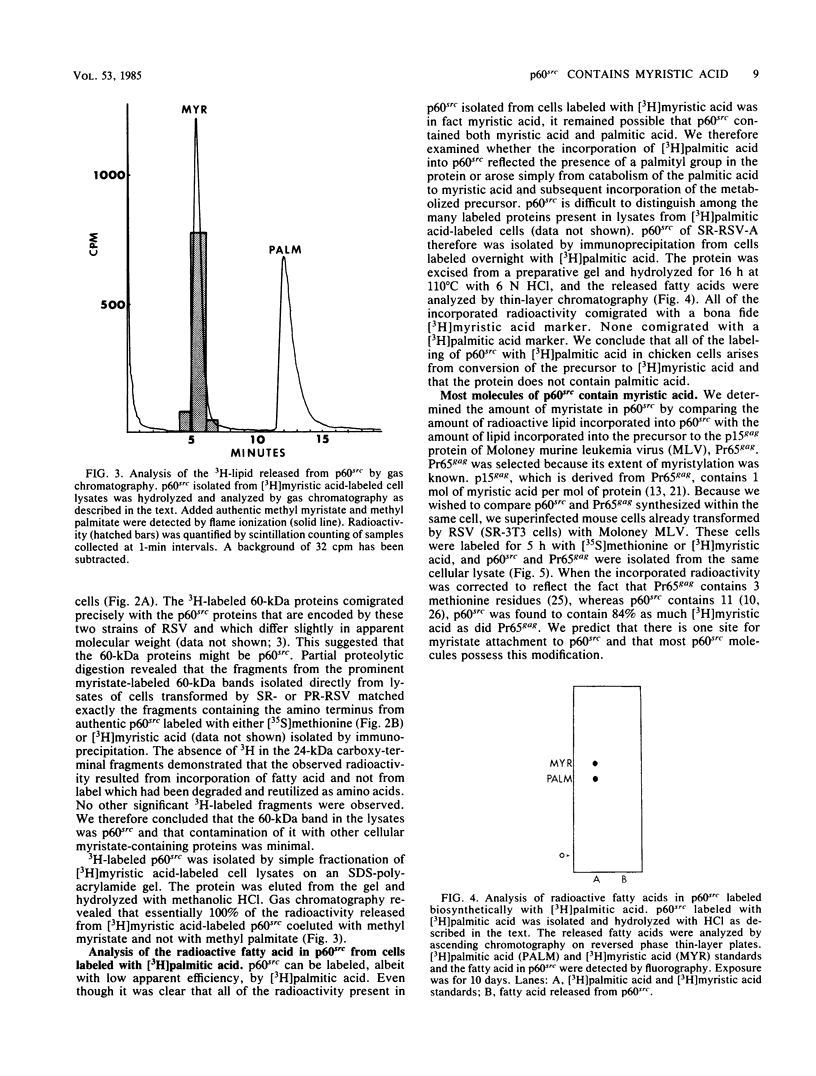
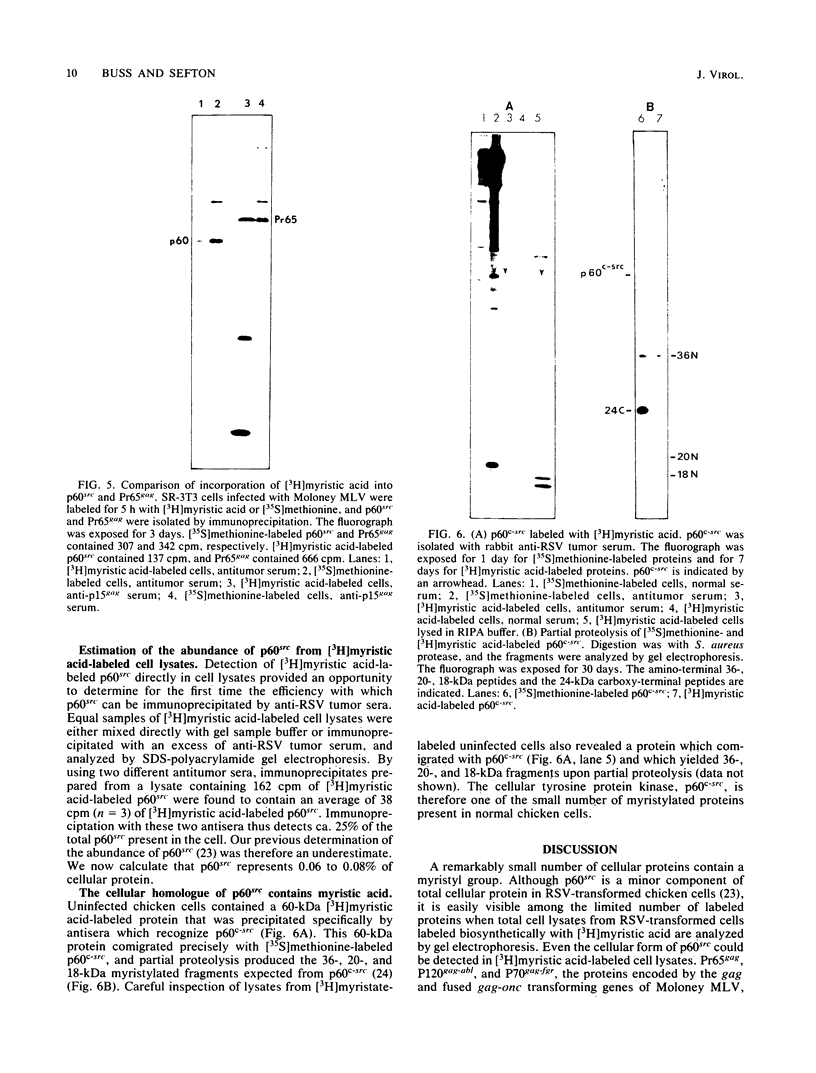
The lipid bound to p60src, the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus, has been identified by gas and thin-layer chromatography as the 14-carbon saturated fatty acid, myristic acid. The protein can be labeled biosynthetically with either [3H]myristic acid or [3H]palmitic acid. Incorporation of [3H]myristic acid was noticeably greater than incorporation of [3H]palmitic acid. All of the [3H]myristic acid-derived label in p60src was present as myristic acid. In contrast, none of the radioactivity derived from [3H]palmitic acid was recovered as palmitic acid. Instead, all 3H incorporated into p60src from [3H]palmitic acid arose by metabolism to myristic acid. The cellular tyrosine kinase, p60c-src also contains myristic acid. By comparison of the extent of myristylation of p60v-src with that of the Moloney murine leukemia virus structural protein precursor, Pr65gag, we estimate that greater than 80% of the molecules of p60v-src contain one molecule of this fatty acid. Myristylation is a rare form of protein modification. p60v-src contains 10 to 40% of the myristic acid bound to protein in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus and is easily identified in total cell lysates when [3H]myristic acid-labeled proteins are separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Comparison of the amount of [3H]myristic acid-labeled p60src in total cell lysates and in immunoprecipitates suggests that immunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-Rous sarcoma virus tumor sera detects ca. 25% of the p60src present in cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Polymorphism of avian sarcoma virus src proteins. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):190–200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.190-200.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid is attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus during or immediately after synthesis and is present in both soluble and membrane-bound forms of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2697–2704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Structural analysis of the avian sarcoma virus transforming protein: sites of phosphorylation. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):770–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.770-781.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. Corrections to the nucleotide sequence of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):736–738. doi: 10.1038/301736b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Temperature-sensitive membrane association of pp60src in tsNY68-infected cells correlates with increased tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Koyama A. H., Malfer C., Wen D., Schlesinger M. J. Release of fatty acids from virus glycoproteins by hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 10;798(2):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Adams G. A., Gallione C. J. The presence of cysteine in the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is required for palmitate addition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for covalent attachment of fatty acids to Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1687–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Oroszlan S. Myristylation of gag-onc fusion proteins in mammalian transforming retroviruses. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Beemon K., Hunter T. Comparison of the expression of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):957–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.957-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Patschinsky T., Berdot C., Hunter T., Elliott T. Phosphorylation and metabolism of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.813-820.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. II. Comparison of the src genes of two strains of avian sarcoma virus and of the cellular homolog. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.12-18.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]