Abstract
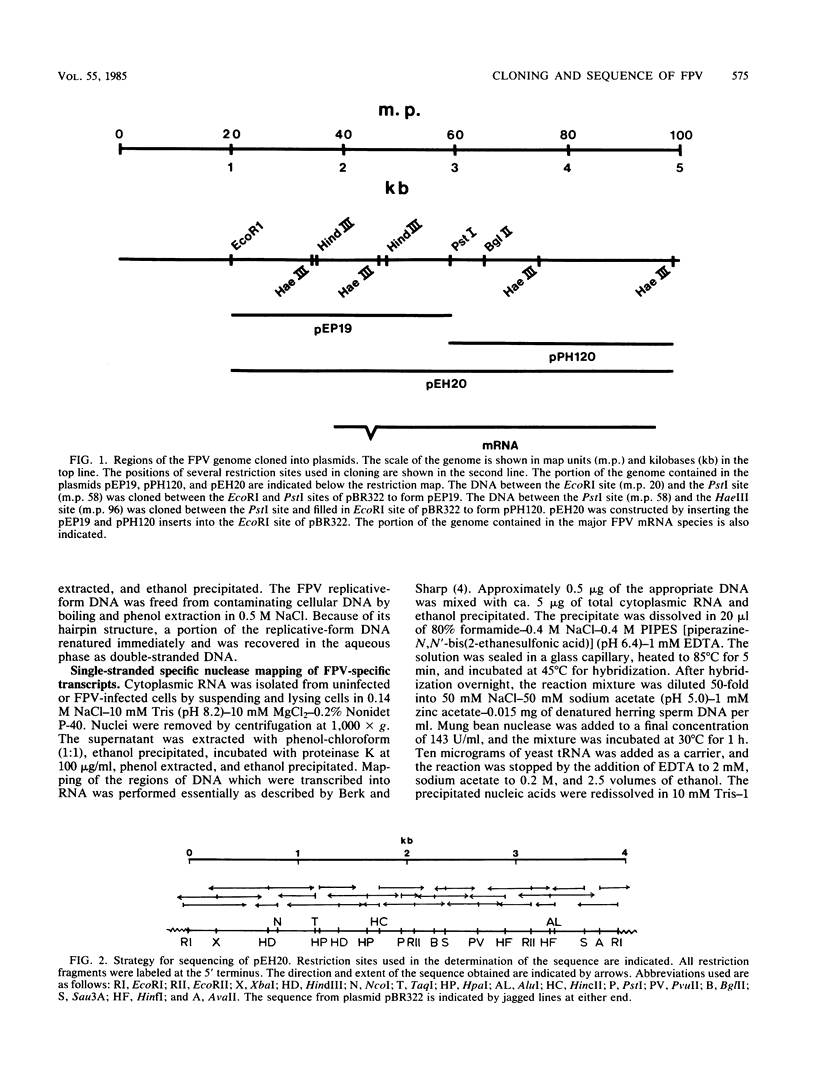
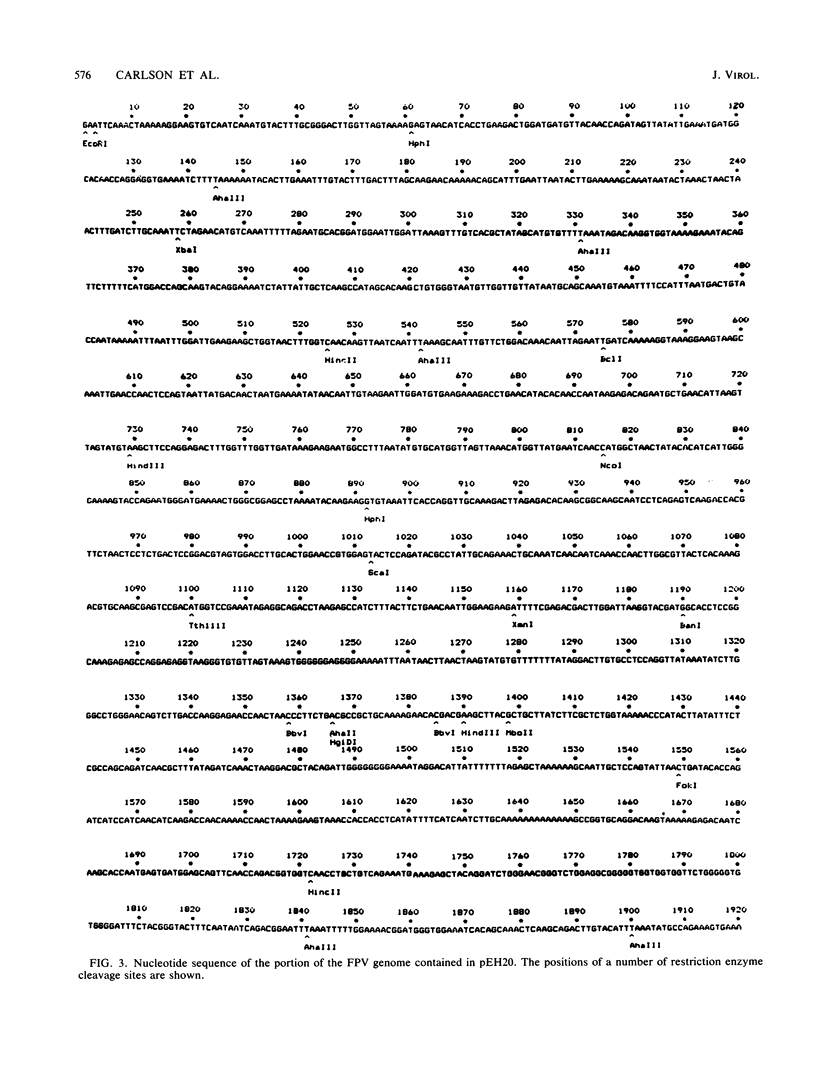
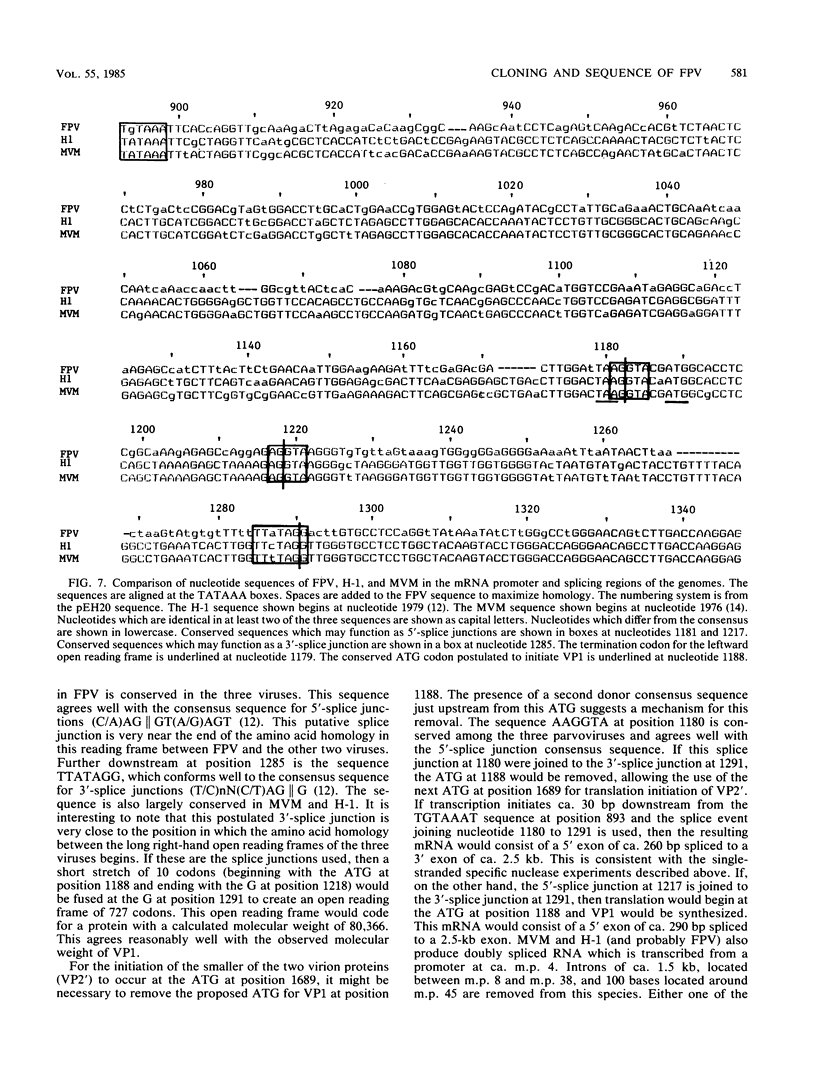
Approximately 80% of the genome of feline panleukopenia virus was cloned into pBR322. This DNA included the transcription unit for the major viral mRNA species. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned portion of the genome was determined. Comparison of the feline panleukopenia virus sequence with the sequences of the parvoviruses minute virus of mice and H-1 revealed considerable homology between the three viruses on both the nucleic acid and protein levels. Based on this homology, a model for the generation of the two size classes of viral structural proteins (VP1 and VP2') is proposed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Smith M., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Structure of the 3' hairpin termini of four rodent parvovirus genomes: nucleotide sequence homology at origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):691–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Merchlinsky M., Ward D. C. The complete DNA sequence of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):999–1018. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P. T., Olson W. H., Allison D. P., Bates R. C., Snyder C. E., Mitra S. Electron microscopic comparison of the sequences of single-stranded genomes of mammalian parvoviruses by heteroduplex mapping. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):257–272. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Tattersall P. J., Ward D. C. DNA of minute virus of mice: self-priming, nonpermuted, single-stranded genome with a 5'-terminal hairpin duplex. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):290–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.290-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael L. E., Binn L. N. New enteric viruses in the dog. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1981;25:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Expression of the autonomous parvovirus H1 genome: evidence for a single transcriptional unit and multiple spliced polyadenylated transcripts. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):967–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCumber M., Ornstein R. L. Molecular model for messenger RNA splicing. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):402–405. doi: 10.1126/science.6200933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Tratschin J. D., Siegl G. Comparison of canine parvovirus with mink enteritis virus by restriction site mapping. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):368–371. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.368-371.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R., Williams K. R., Costantino R. L. Mapping of the amino terminus of the H-1 parvovirus major capsid protein. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.77-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Carmichael L. E. Antigenic structure and variation of canine parvovirus type-2, feline panleukopenia virus, and mink enteritis virus. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Dadachanji D., Astell C. R., Ward D. C. The genome of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, encodes two overlapping transcription units. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1019–1038. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Klaassen B. DNA sequence of the 5' terminus containing the replication origin of parvovirus replicative form DNA. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):990–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.990-999.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Paradiso P. R. Parvovirus genome: nucleotide sequence of H-1 and mapping of its genes by hybrid-arrested translation. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.173-184.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Sequence homology between the structural polypeptides of minute virus of mice. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., McMaster G. K., Kronauer G., Siegl G. Canine parvovirus: relationship to wild-type and vaccine strains of feline panleukopenia virus and mink enteritis virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):33–41. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]