Abstract
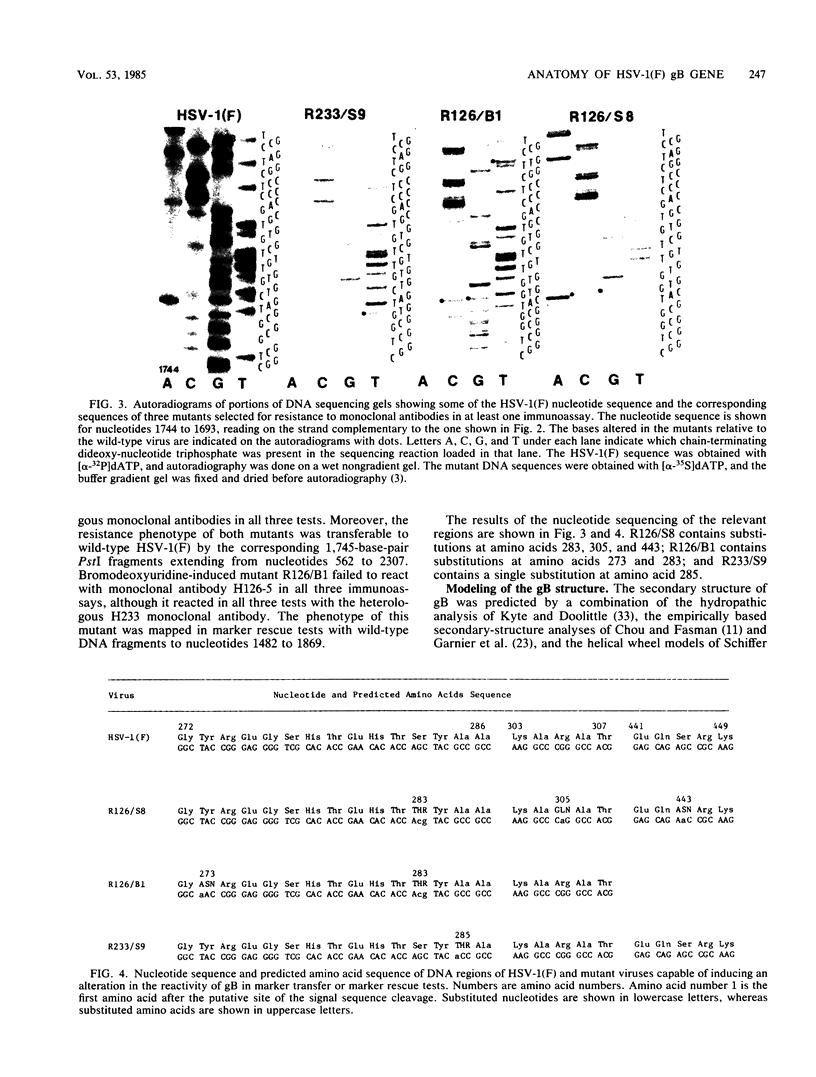
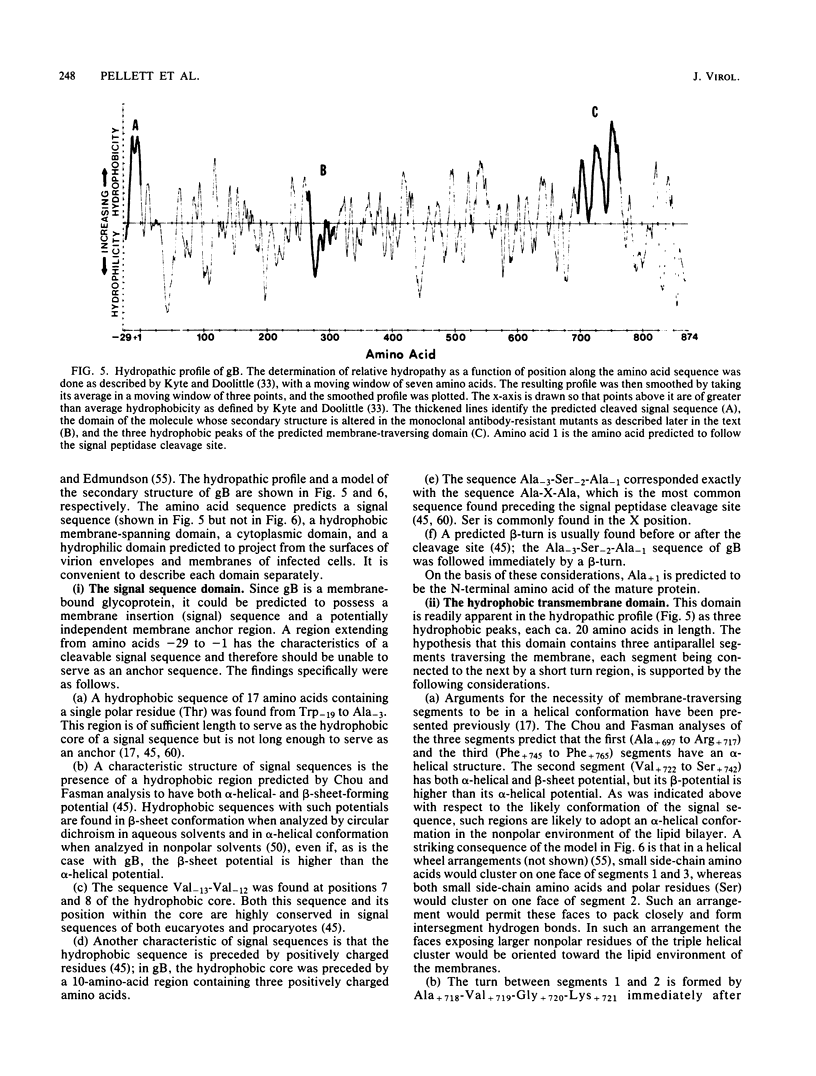
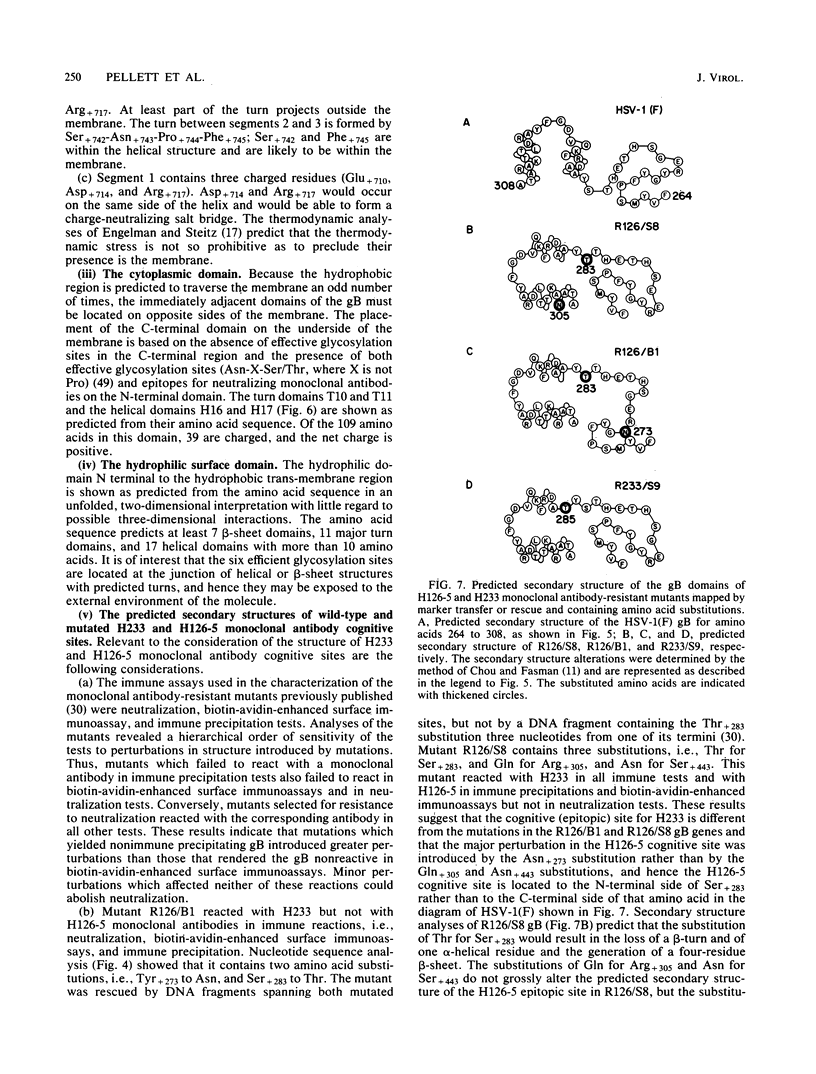
In this paper we report the nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus 1 strain F and the amino acid substitutions in the domains of the glycoprotein B gene of three mutants selected for resistance to monoclonal antibody H126-5 or H233 but not to both. Analyses of the amino acid sequence with respect to hydropathicity and secondary structure yielded a two-dimensional model of the protein. The model predicts an N-terminal, 29-amino-acid cleavable signal sequence, a 696-amino-acid hydrophilic surface domain containing six potential sites for N-linked glycosylation, a 69-amino-acid hydrophobic domain containing three segments traversing the membrane, and a charged 109-amino-acid domain projecting into the cytoplasm and previously shown to marker rescue glycoprotein B syn mutations. The nucleotide sequence of the mutant glycoprotein B DNA fragments previously shown to marker transfer or rescue the mutations revealed that the amino acid substitutions cluster in the hydrophilic surface domain between amino acids 273 and 305. Analyses of the secondary structure of these regions, coupled with the experimentally derived observation that the H126-5- and H233-antibody cognitive sites do not overlap, indicate the approximate locations of the epitopes of these neutralizing, surface-reacting, and immune-precipitating monoclonal antibodies. The predicted perturbations in the secondary structure introduced by the amino acid substitutions correlate with the extent of loss of reactivity with monoclonal antibodies in various immunoassays.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J., Niemann H., Smeekens S., Rottier P., Warren G. Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):751–752. doi: 10.1038/308751a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond V. C., Person S. Fine structure physical map locations of alterations that affect cell fusion in herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):368–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond V. C., Person S., Warner S. C. The isolation and characterization of mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 that induce cell fusion. J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):245–254. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braell W. A., Lodish H. F. The erythrocyte anion transport protein is contranslationally inserted into microsomes. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock C. J., Tanner M. J., Kempf C. The human erythrocyte anion-transport protein. Partial amino acid sequence, conformation and a possible molecular mechanism for anion exchange. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):577–586. doi: 10.1042/bj2130577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence specifying the glycoprotein gene, gB, of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Bzik D. J., Bond V. C., Person S., Snipes W. Nucleotide sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) affecting virus entry, cell fusion, and production of glycoprotein gb (VP7). Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):411–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the genes for the major herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA-binding protein and a new late function. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):343–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.343-353.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz M. E., Nahmias A. J. Reversed polarity in transmembrane potentials of cells infected with herpesviruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Apr;139(4):1159–1161. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffey M. L., Spear P. G. Alterations in glycoprotein gB specified by mutants and their partial revertants in herpes simplex virus type 1 and relationship to other mutant phenotypes. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):114–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.114-128.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional and genetic analyses of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome: coordinates 0.29 to 0.45. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):947–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.947-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Reithmeier R. A., MacLennan D. H. Alignment of the major tryptic fragments of the adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6562–6568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousoulas K. G., Pellett P. E., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mutations affecting conformation or sequence of neutralizing epitopes identified by reactivity of viable plaques segregate from syn and ts domains of HSV-1(F) gB gene. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):379–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Schaffer P. A. Expression of the syncytial (syn) phenotype in HSV-1, strain KOS: genetic and phenotypic studies of mutants in two syn loci. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):686–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and their expression on the cell surface. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.395-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancake B. A., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of herpes simplex virus type 1 mutants conditionally resistant to immune cytolysis. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):568–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.568-585.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake M. L., Nystrom P., Pizer L. I. Herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis and insertion into plasma membranes. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):678–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.678-690.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Lee G. T., Shapira S. K., Spear P. G. Fine mapping of mutations in the fusion-inducing MP strain of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafield L. F., Knipe D. M. Characterization of the major mRNAs transcribed from the genes for glycoprotein B and DNA-binding protein ICP8 of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):960–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.960-969.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Person S., Keller P. M. Genetic studies of cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.105-113.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doolittle R. F., Anilionis A., Curtis P. J., Wunner W. H. Homology between the glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):361–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.361-364.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt M., Beaudette N. V., Fasman G. D. Conformational studies of the synthetic precursor-specific region of preproparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3983–3987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Identical 3'-terminal octanucleotide sequence in 18S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from different eukaryotes. A proposed role for this sequence in the recognition of terminator codons. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):609–615. doi: 10.1042/bj1410609a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Suggs S. V., Miyoshi K., Bhatt R., Itakura K. A set of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide primers for DNA sequencing in the plasmid vector pBR322. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



