Abstract
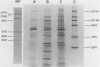
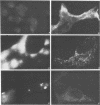
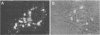
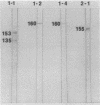
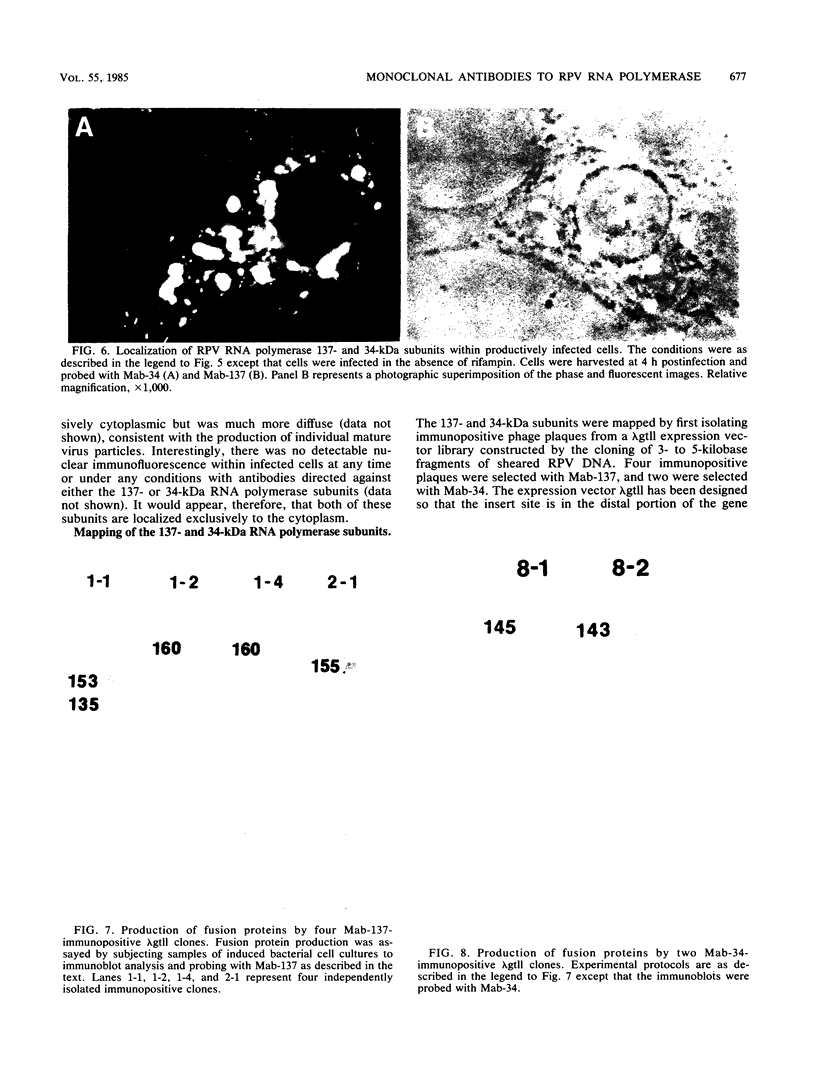
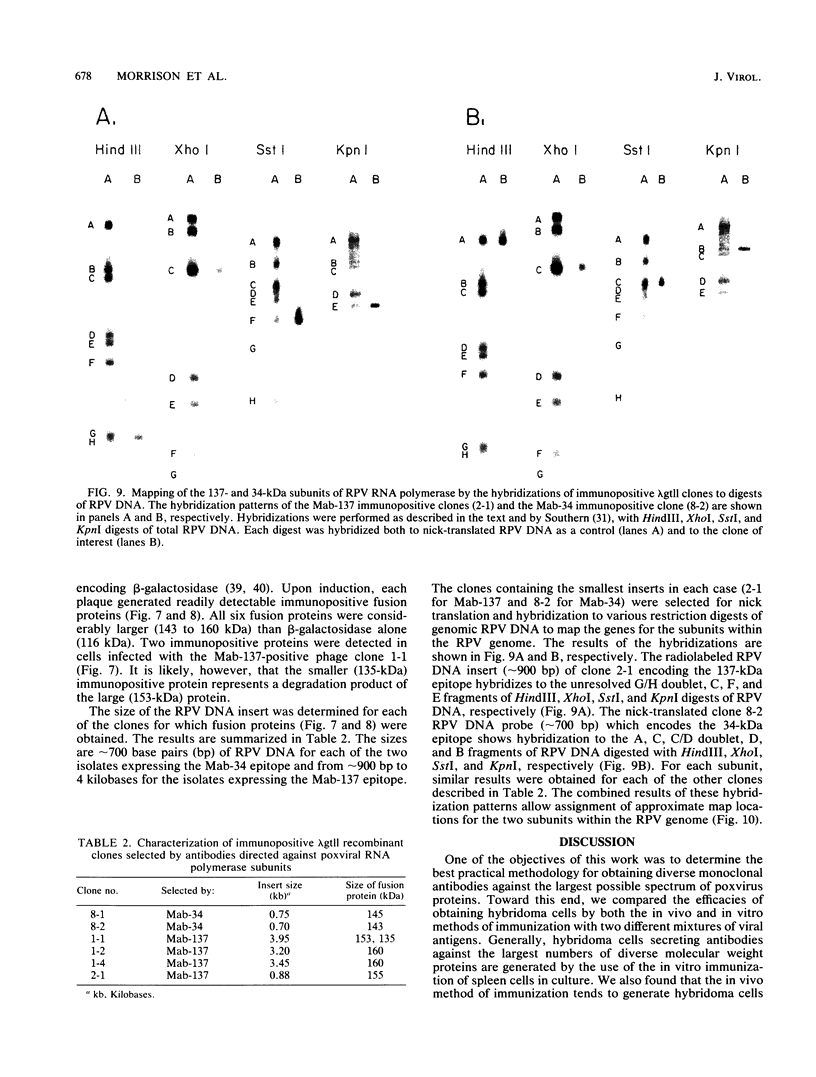
A library of monoclonal antibodies directed against individual proteins of the rabbit poxvirus (RPV) virion within a complex immunogenic mixture has been generated through the use of in vivo and in vitro immunization regimens. The relative efficacies of the two procedures were compared. Based on immunoblot analysis, the in vitro immunization regimen led both to a wider variety of monoclonal antibodies to different proteins and to a larger number of antibodies directed against proteins of higher molecular weights. Each method, however, has advantages, and the two procedures appear to be complementary. A simple method to recognize antibodies directed against the virion DNA-directed RNA polymerase was developed. Monoclonal antibodies directed against two subunits (137 and 34 kilodaltons [kDa]) of the RNA polymerase were identified and used to study the biogenesis of the enzyme and to map the two corresponding genes within the viral genome by using an RPV DNA library cloned into the lambda gtll expression vector. Both proteins are synthesized late in the infectious cycle and are restricted totally to the cytoplasm. Preliminary mapping data place the genes encoding the 137-kDa protein within the HindIII H fragment, whereas the gene for the 34-kDa protein is located within the left most region of the HindIII A fragment.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archard L. C. Synthesis of full-length, virus genomic DNA by nuclei of vaccinia-infected HeLa cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2561–2575. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4372–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Noy G. P., Weissbach A. Vaccinia virus infection of HeLa cells. II. Disparity between cytoplasmic and nuclear viral-specific RNA. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):138–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Pogo B. G. Biology of poxviruses. Virol Monogr. 1981;18:1–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blas A. L., Cherwinski H. M. Detection of antigens on nitrocellulose paper immunoblots with monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban M., Cabrera C. V., Holowczak J. A. Electron microscopic studies of transcriptional complexes released from vaccinia cores during RNA-synthesis in vitro: methods for fractionation of transcriptional complexes. J Virol Methods. 1983 Aug;7(2):73–92. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafford L. G., Randall C. C. Virus-specific RNA and DNA in nuclei of cells infected with fowlpox virus. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Rosenblum E. N., Mims S. J., Moss B. Interruption by Rifampin of an early stage in vaccinia virus morphogenesis: accumulation of membranes which are precursors of virus envelopes. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):519–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.519-533.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Lynn D. L., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication requires active participation of the host cell transcriptional apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1887–1890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Maki R. A., Miller D. B., Ball L. A. Fine structure analysis and nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3411–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaColla P., Weissbach A. Vaccinia virus infection of HeLa cells. I. Synthesis of vaccinia DNA in host cell nuclei. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):305–315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.305-315.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luben R. A., Mohler M. A. In vitro immunization as an adjunct to the production of hybridomas producing antibodies against the lymphokine osteoclast activating factor. Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N. Letter: Protein cleavage and poxvirus morphogenesis: tryptic peptide analysis of core precursors accumulated by blocking assembly with rifampicin. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L. The mechanism of cytoplasmic orthopoxvirus DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L. The white pock mutants of rabbit poxvirus. IV. The late white pock (mu) host range (hr) mutants of rabbit poxvirus are blocked in morphogenesis. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):332–346. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Rothe C. T. The white pock mutants of rabbit poxvirus. I. Spontaneous host range mutants contain deletions. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaya A., Pogo B. G., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: separation of early stages from maturation by means of rifampicin. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Joklik W. K. Isolation and properties of the vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6930–6938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H., Follett E. A. Inhibition of poxvirus maturation by rifamycin derivatives and related compounds. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):821–829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.821-829.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M., McFadden G., Wilton S., Dales S. Biogenesis of poxviruses: role for the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II of the host during expression of late functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4122–4125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Shuman S., Hurwitz J. Purification and properties of vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5388–5395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Gershowitz A., Moss B. Complete nucleotide sequences of two adjacent early vaccinia virus genes located within the inverted terminal repetition. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):637–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.637-646.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene and the nature of spontaneous frameshift mutations. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.530-537.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Regulation of expression and nucleotide sequence of a late vaccinia virus gene. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):662–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.662-669.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing D., Weissbach A. Vaccinia virus RNA polymerase associated with nuclei of infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):26–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.26-34.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]