Abstract
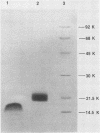
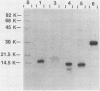
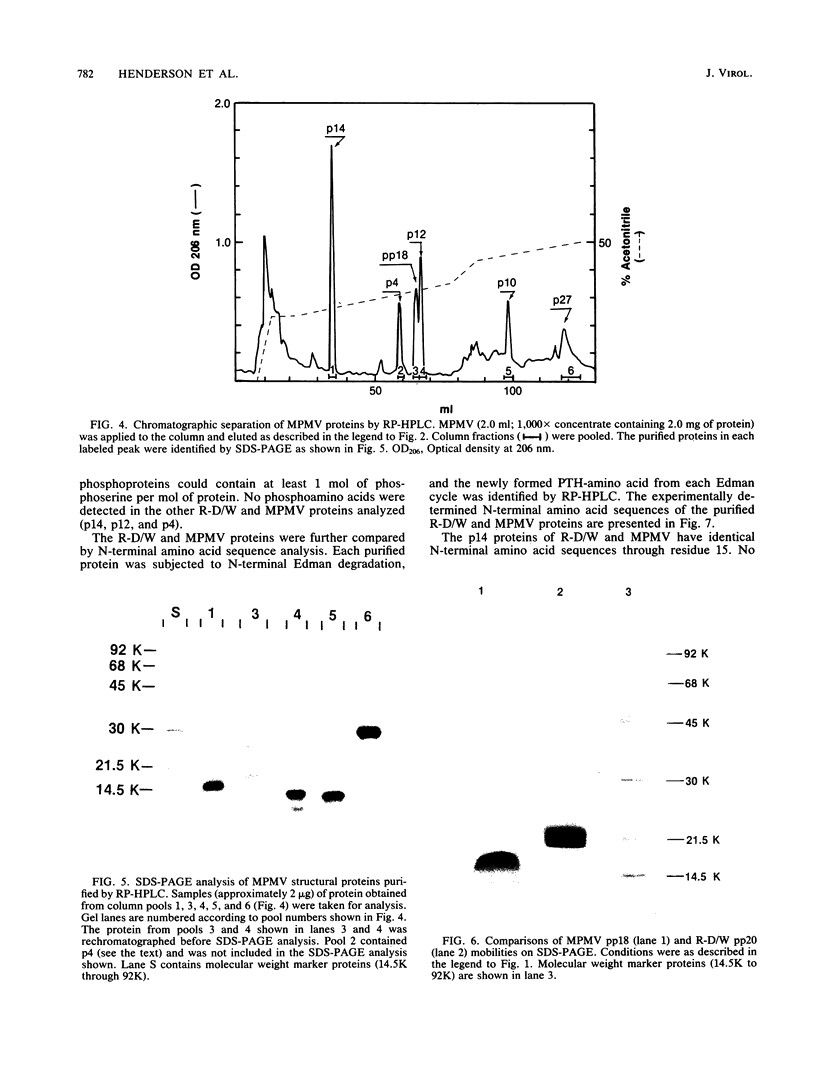
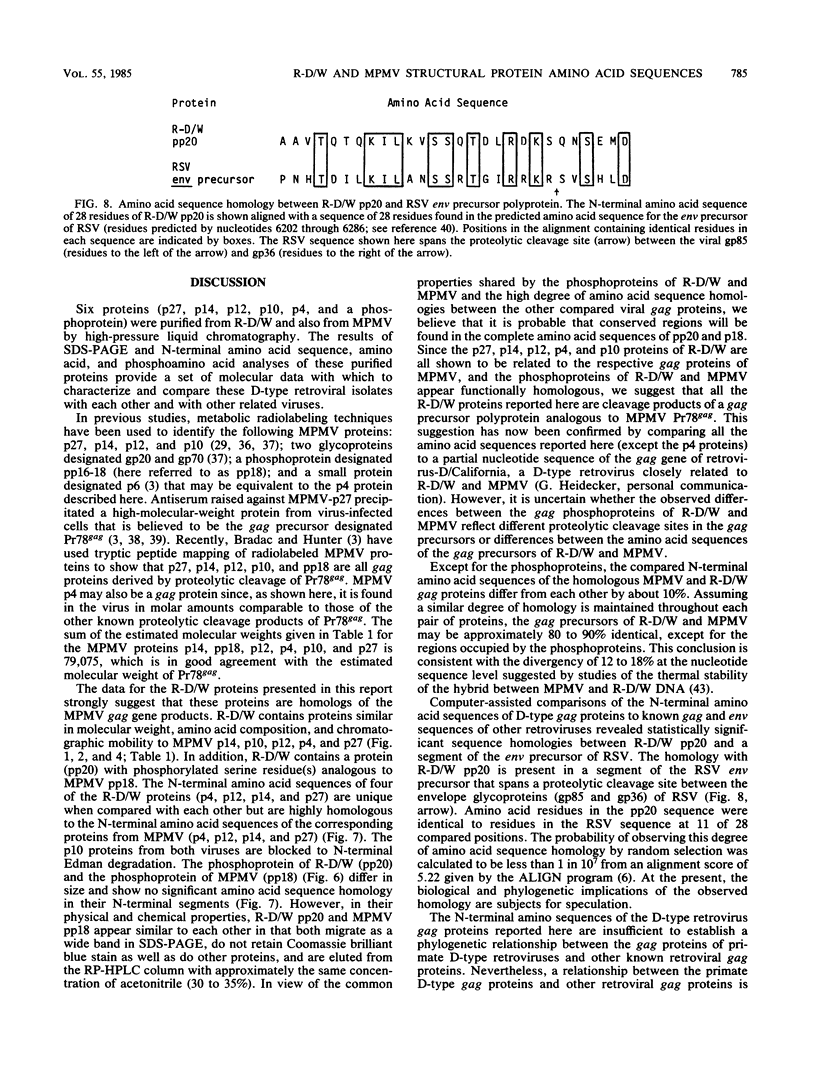
A new D-type retrovirus originally designated SAIDS-D/Washington and here referred to as retrovirus-D/Washington (R-D/W) was recently isolated at the University of Washington Primate Center, Seattle, Wash., from a rhesus monkey with an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and retroperitoneal fibromatosis. To better establish the relationship of this new D-type virus to the prototype D-type virus, Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (MPMV), we have purified and compared six structural proteins from each virus. The proteins purified from each D-type retrovirus include p4, p10, p12, p14, p27, and a phosphoprotein designated pp18 for MPMV and pp20 for R-D/W. Amino acid analysis and N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis show that the p4, p12, p14, and p27 proteins of R-D/W are distinct from the homologous proteins of MPMV but that these proteins from the two different viruses share a high degree of amino acid sequence homology. The p10 proteins from the two viruses have similar amino acid compositions, and both are blocked to N-terminal Edman degradation. The phosphoproteins from the two viruses each contain phosphoserine but are different from each other in amino acid composition, molecular weight, and N-terminal amino acid sequence. The data thus show that each of the R-D/W proteins examined is distinguishable from its MPMV homolog and that a major difference between these two D-type retroviruses is found in the viral phosphoproteins. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of D-type retroviral proteins were used to search for sequence homologies between D-type and other retroviral amino acid sequences. An unexpected amino acid sequence homology was found between R-D/W pp20 (a gag protein) and a 28-residue segment of the env precursor polyprotein of Rous sarcoma virus. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of the D-type major gag protein (p27) and the nucleic acid-binding protein (p14) show only limited amino acid sequence homology to functionally homologous proteins of C-type retroviruses.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Approaches to the isolation of RNA tumor viruses from primates. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5 Suppl):S2–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of primate oncornaviruses: An endogenous virus from langurs (Presbytis spp.) with related virogene sequences in other Old World monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4557–4561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradac J., Hunter E. Polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. I. Synthesis and processing of the gag-gene products. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):260–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra H. C., Mason M. M. A new virus in a spontaneous mammary tumor of a rhesus monkey. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2081–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., King N. W., Letvin N. L., Hunt R. D., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C. A new type D retrovirus isolated from macaques with an immunodeficiency syndrome. Science. 1984 Feb 10;223(4636):602–605. doi: 10.1126/science.6695172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar K. J., Moelling K. Biochemical properties of p15-associated protease in an avian RNA tumor virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):106–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.106-118.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drohan W., Colcher D., Schochetman G., Schlom J. Distribution of Mason-Pfizer virus-specific sequences in the DNA of primates. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):36–43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.36-43.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasel N., Buetti E., Firzlaff J., Pearson K., Diggelmann H. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region and part of the gag gene of mouse mammary tumor virus; identification of the 5' splicing site for subgenomic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):6943–6955. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.6943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. L., Landon J. C., Pienta R. J., Kubicek M. T., Valerio M. G., Loeb W. F., Chopra H. C. Responses of infant rhesus monkeys to inoculation with Mason-Pfizer monkey virus materials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):651–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Laprevotte I., Galibert F., Fedele L. A., Sherr C. J. Nucleotide sequences of feline retroviral oncogenes (v-fes) provide evidence for a family of tyrosine-specific protein kinase genes. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberling R. L., Barker S. T., Kalter S. S., Smith G. C., Helmke R. J. Oncornavirus: isolation from a squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus) lung culture. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):289–292. doi: 10.1126/science.63993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography on phenylalkyl support. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Sowder R. C., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Primary structure of the low molecular weight nucleic acid-binding proteins of murine leukemia viruses. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8400–8406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Smythers G., Oroszlan S. Quantitative separation of murine leukemia virus proteins by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography reveals newly described gag and env cleavage products. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.492-500.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Sowder R., Smythers G., Oroszlan S. Terminal amino acid sequences and proteolytic cleavage sites of mouse mammary tumor virus env gene products. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.314-319.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrickson R. V., Maul D. H., Osborn K. G., Sever J. L., Madden D. L., Ellingsworth L. R., Anderson J. H., Lowenstine L. J., Gardner M. B. Epidemic of acquired immunodeficiency in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1983 Feb 19;1(8321):388–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91503-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., Eaton K. A., Aldrich W. R., Sehgal P. K., Blake B. J., Schlossman S. F., King N. W., Hunt R. D. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in a colony of macaque monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. W., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Isolation and characterization of low-molecular-weight DNA-binding proteins from retroviruses. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):491–496. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx P. A., Maul D. H., Osborn K. G., Lerche N. W., Moody P., Lowenstine L. J., Henrickson R. V., Arthur L. O., Gilden R. V., Gravell M. Simian AIDS: isolation of a type D retrovirus and transmission of the disease. Science. 1984 Mar 9;223(4640):1083–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.6695196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D., Sauer R., Allen D. W. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of two avian leukosis group specific antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Copeland T. D. Primary structure and processing of gag and env gene products of human T-cell leukemia viruses HTLV-ICR and HTLV-IATK. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;115:221–233. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70113-9_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Stephenson J. R., Copeland T. D., Long C. W., Ihle J. N., Gilden R. V. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences of proteins coded by gag gene of murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1404–1408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Sarngadharan M. G., Copeland T. D., Kalyanaraman V. S., Gilden R. V., Gallo R. C. Primary structure analysis of the major internal protein p24 of human type C T-cell leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1291–1294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perini F., Sadow J. B., Hixson C. V. Fluorometric analysis of polyamines, histamine, and 1-methylhistamine. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond S. M., Dickson C. Sequence and expression of the mouse mammary tumour virus env gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):125–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Stephens R. M., Burny A., Gilden R. V. The gag and pol genes of bovine leukemia virus: nucleotide sequence and analysis. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):357–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Stephens R. M., Couez D., Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A., Gilden R. V. The nucleotide sequence of the env gene and post-env region of bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Boehm-Truitt M., Schlom J. Antigenic analysis of the major structural protein of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):168–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Kortright K., Schlom J. Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: analysis and localization of virion proteins and glycoproteins. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1208–1219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1208-1219.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg K., Benveniste R. E., Arthur L. O., Rabin H., Giddens W. E., Jr, Ochs H. D., Morton W. R., Tsai C. C. Characterization of exogenous type D retrovirus from a fibroma of a macaque with simian AIDS and fibromatosis. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):289–282. doi: 10.1126/science.6200929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T. A. Provirus of M7 baboon endogenous virus: nucleotide sequence of the gag-pol region. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):137–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.137-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J., Schlom J., Schidlovsky G., Stephenson J. R. Isolation and characterization of a new type D retrovirus from the asian primate, Presbytis obscurus (spectacled langur). Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Immunological properties of two polypeptides of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.125-132.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. C., Fujitaki J. M., Smith R. A. Separation of phosphohydroxyamino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 15;122(2):360–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90295-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus protease is encoded by the gag-pol gene and is synthesized through suppression of an amber termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1618–1622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]