Abstract
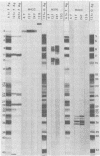
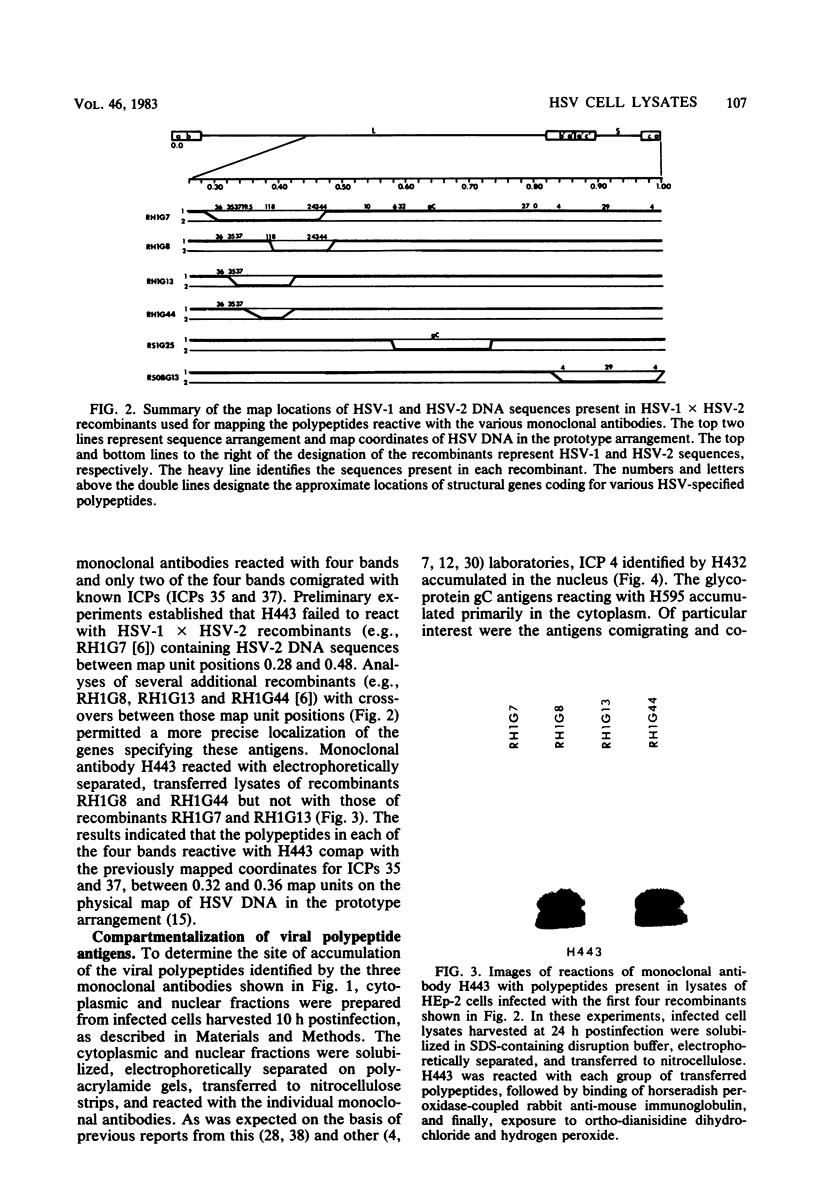
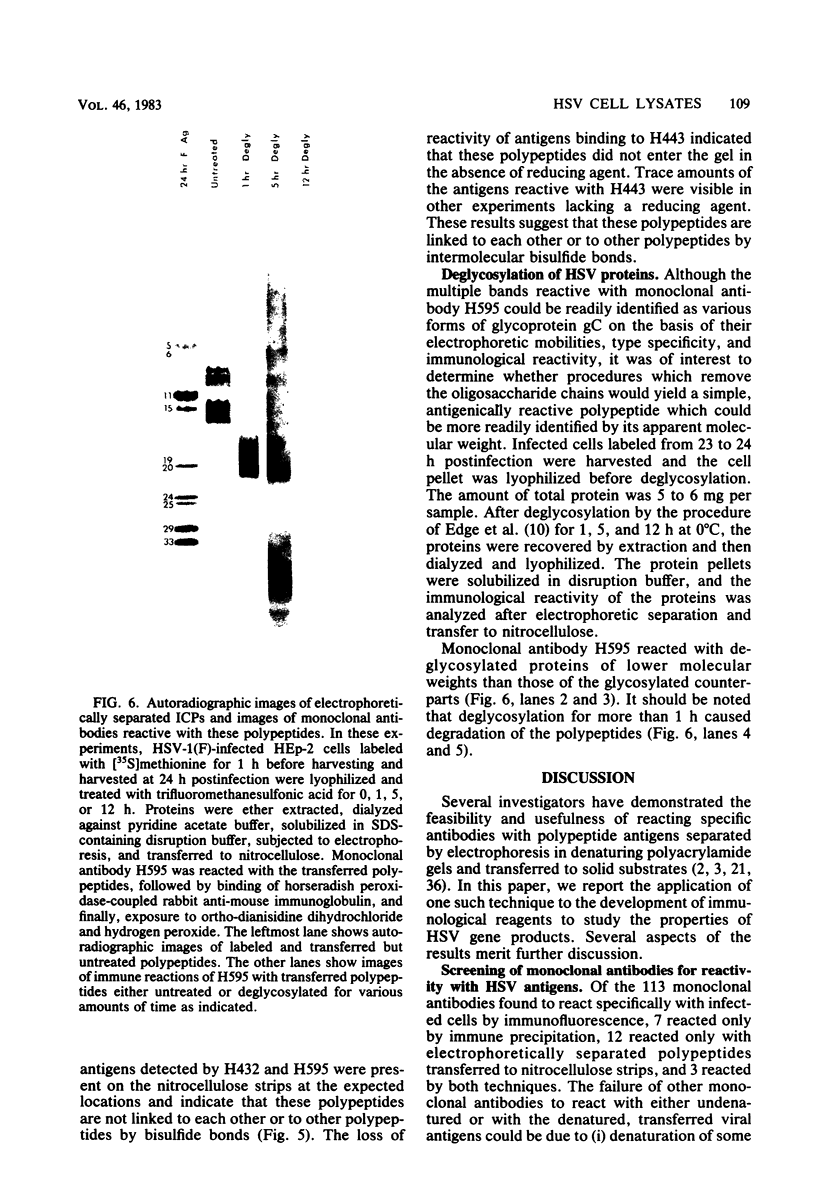
We report the use of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)- and HSV-2-infected cell polypeptides (ICPs) separated by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose to (i) detect monoclonal antibodies to viral polypeptides and to (ii) study the properties of the proteins with the monoclonal antibodies. Our results were as follows. (i) When the antigens were electrophoretically separated in denaturing gels and then immobilized on nitrocellulose strips, we detected a greater diversity of monoclonal antibodies to viral proteins than when we used the technique of immune precipitation of soluble, nondenatured viral antigens. The primary advantage of the technique is in the detection of nonprecipitating antibody and of antibody to poorly soluble antigens not available for reaction in preparations cleared by high-speed centrifugation before immune reaction. (ii) Studies of the viral polypeptides reactive with three monoclonal antibodies indicated that the technique can be used to investigate several properties of the antigens. Specifically, monoclonal antibody to ICP 4 confirmed the accumulation of viral protein in the nucleus and the mapping of the gene in the S component. The results showed, however, that HSV-1 and HSV-2 ICP 4 do have common antigenic determinants. The reaction of a nonprecipitating monoclonal antibody with electrophoretically separated, immobilized polypeptides contained in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, those chemically deglycosylated, or those specified by specific HSV-1 x HSV-2 intertypic recombinants identified the antigens reactive with the second monoclonal antibody as various forms of glycoprotein gC. Of particular interest was a set of four antigens, 39,000 to 46,500 in apparent molecular weight, reactive with each of several monoclonal antibodies. These studies showed that two polypeptides partition in the cytoplasm and two in the nucleus and that all comap with the previously mapped ICPs 35 and 37 in the region of the genome defined by the viral thymidine kinase gene on the left and the glycoprotein gA/B gene on the right. Unlike ICP 4 and gC, the four polypeptides are linked by intermolecular bisulfide bonds, inasmuch as the polypeptides were not at the expected locations upon denaturation and electrophoresis in the absence of reducing agents.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benecke B. J., Penman S. Large species differences in the pattern of snPI RNA which can distinguish ape from human. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):778–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral G. A., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A., Marciano-Cabral F. Ultrastructural characterization of an early, nonstructural polypeptide of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1192–1198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1192-1198.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J., Benyesh-Melnick M. Isolation and characterization of a large molecular-weight polypeptide of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):539–551. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A., Powell K. L. Synthesis of virus-specific polypaptides by temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):306–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge A. S., Faltynek C. R., Hof L., Reichert L. E., Jr, Weber P. Deglycosylation of glycoproteins by trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. S., Kaplan A. S. Synthesis of proteins in cells infected with herpesvirus. IX. Sulfated proteins. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):94–102. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J., Petkevich J. M. On the association of virus proteins with the nuclei of cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):519–529. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Anderson K. P., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 HindIII fragment L encodes spliced and complementary mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):559–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.559-572.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S. Two-dimensional gel analysis of HSV type 1-induced polypeptides and glycoprotein processing. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. J., Jr, Zweig M., Hampar B. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 intracellular p40: type-specific and cross-reactive antigenic determinants on peptides generated by partial proteolysis. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):508–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.508-515.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B., Halliburton I. W. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus: demonstration of regions of obligatory and nonobligatory identity within diploid regions of the genome by sequence replacement and insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Pogue-Geile K. L., Pereira L., Spear P. G. Expression of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein C from a DNA fragment inserted into the thymidine kinase gene of this virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6612–6616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Crombie I. K., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Control of protein synthesis in herpesvirus-infected cells: analysis of the polypeptides induced by wild type and sixteen temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV strain 17. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):347–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. IX. Apparent exclusion of some parental DNA arrangements in the generation of intertypic (HSV-1 X HSV-2) recombinants. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):231–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.231-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B., Roizman B. Immunological reactivity of herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 polypeptides electrophoretically separated and transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):660–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.660-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Norrild B., Roizman B. Differential immunologic reactivity and processing of glycoproteins gA and gB of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 made in Vero and HEp-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Abnormal properties of an immediate early polypeptide in cells infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):357–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.357-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Kellejmroian B. Proteins spcified by herpes simplex virus. II. Viral glycoprotins associated with cellular membranes. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.123-131.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Aurelian L. Proteins of herpesvirus type 2: I. Virion, nonvirion, and antigenic polypeptides in infected cells. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):438–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognon M., Furlong D., Conley A. J., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. V. Characterization of a mutant defective in ability to form plaques at low temperatures and in a viral fraction which prevents accumulation of coreless capsids at nuclear pores late in infection. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.870-880.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Rabin H., Hampar B. Shared antigenic determinants between two distinct classes of proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):644–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.644-652.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]