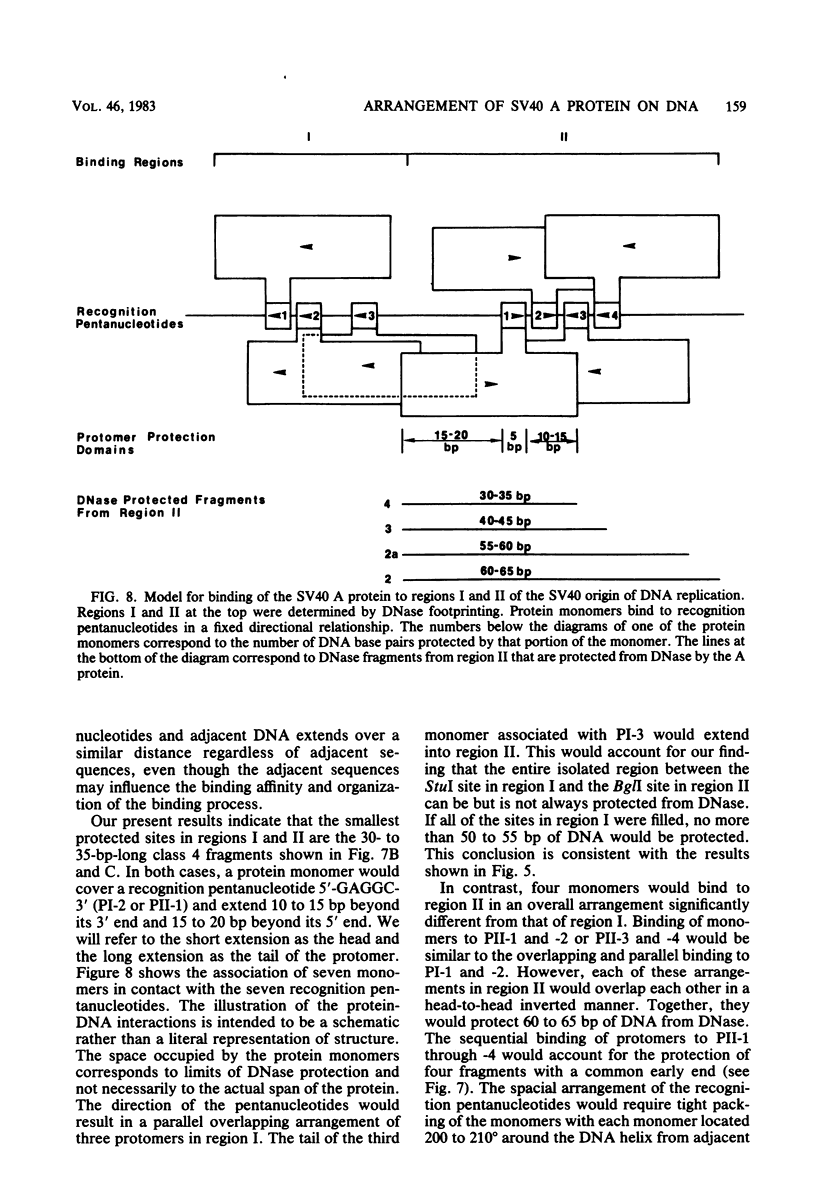
Abstract
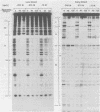
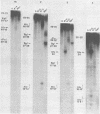
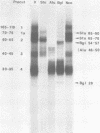
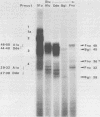
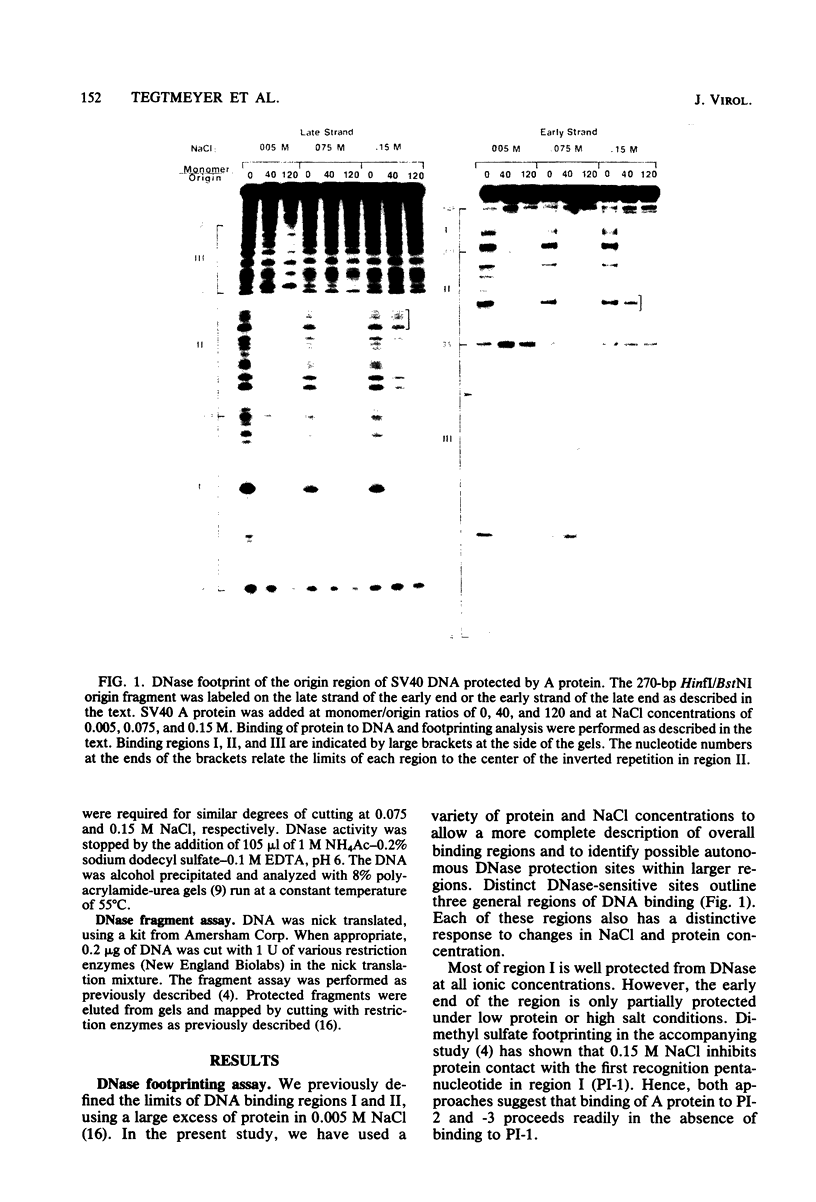
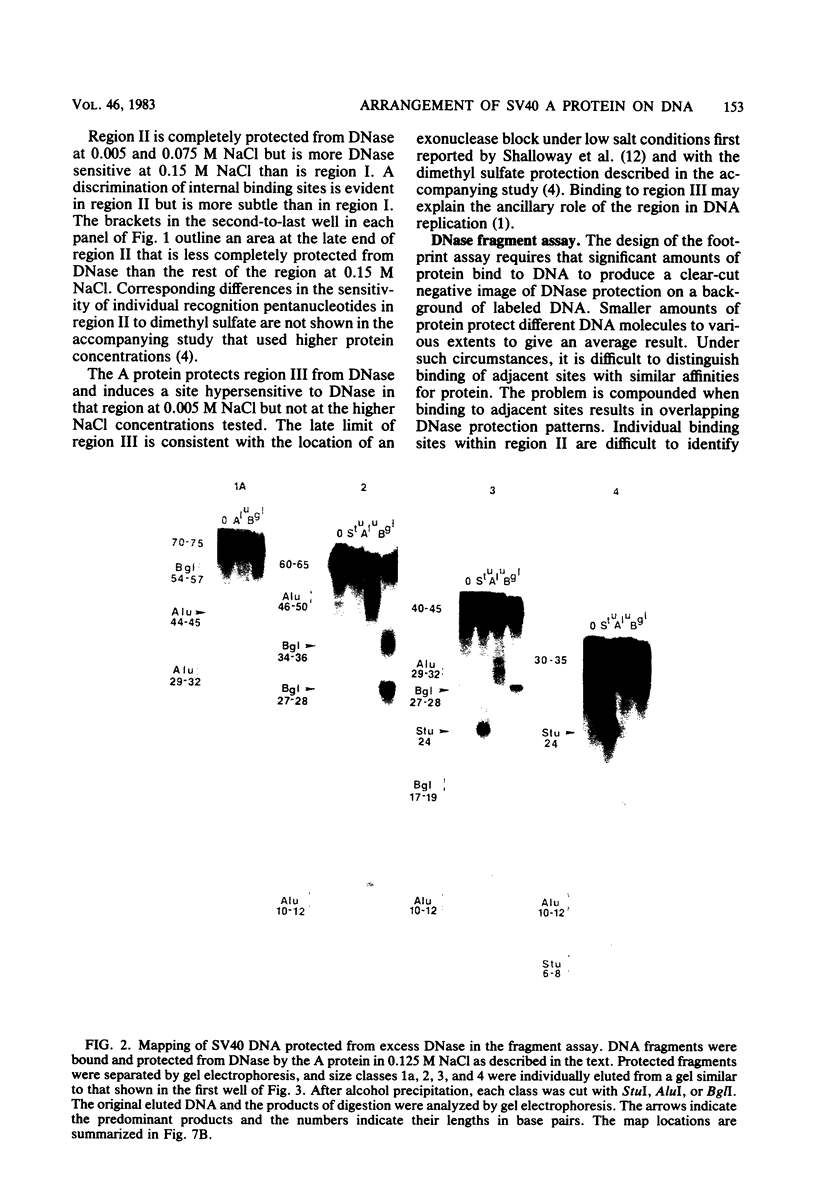
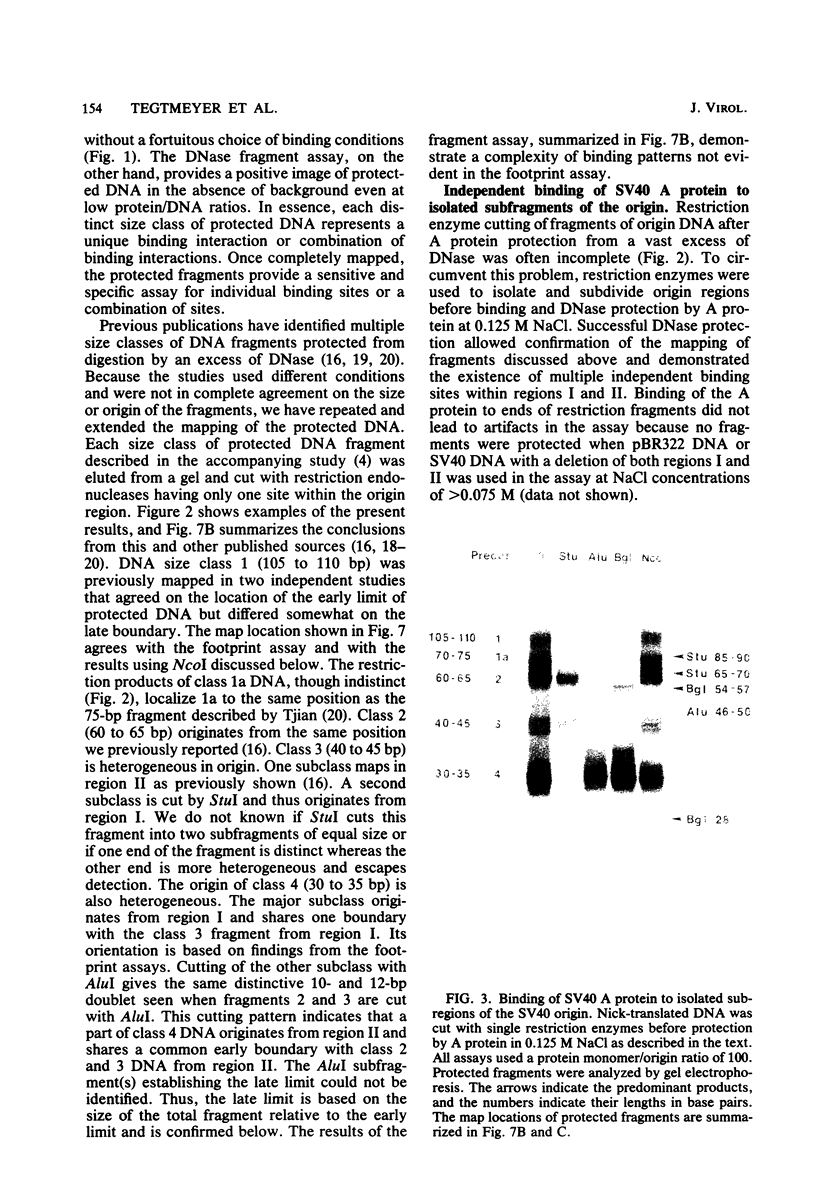
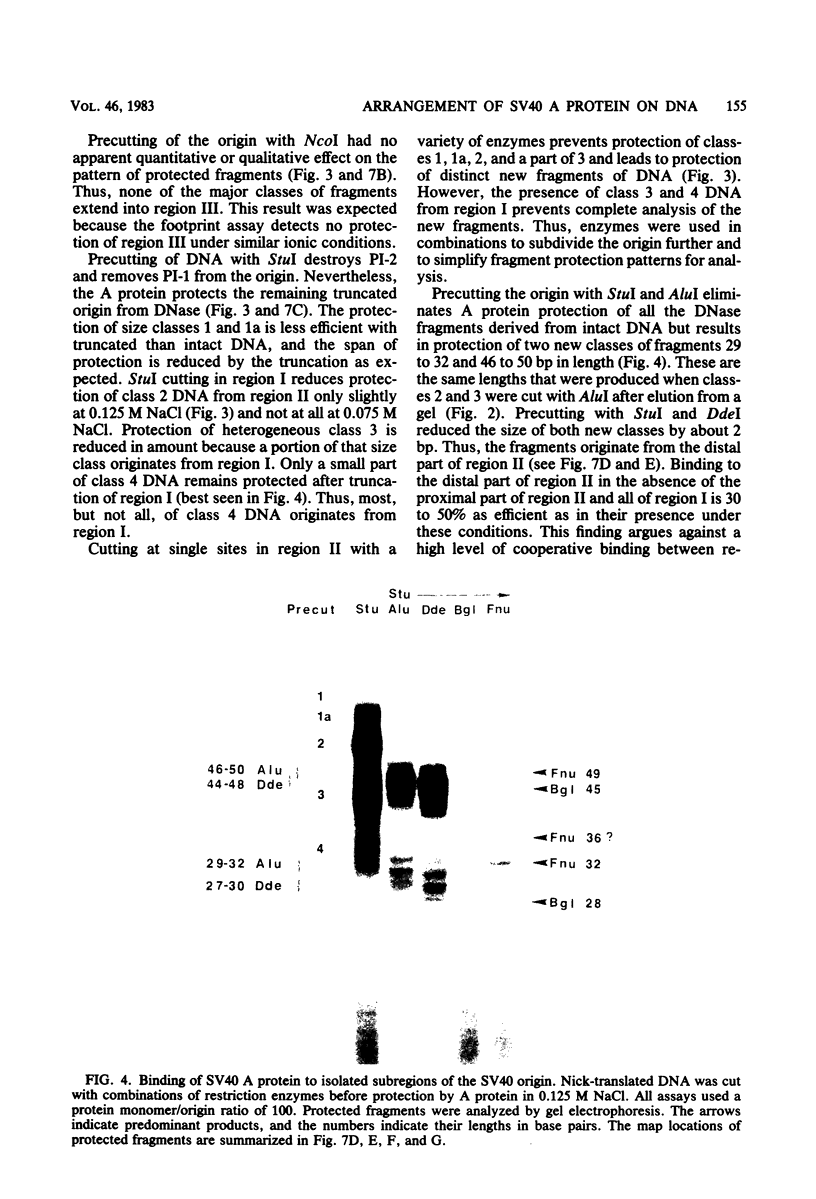
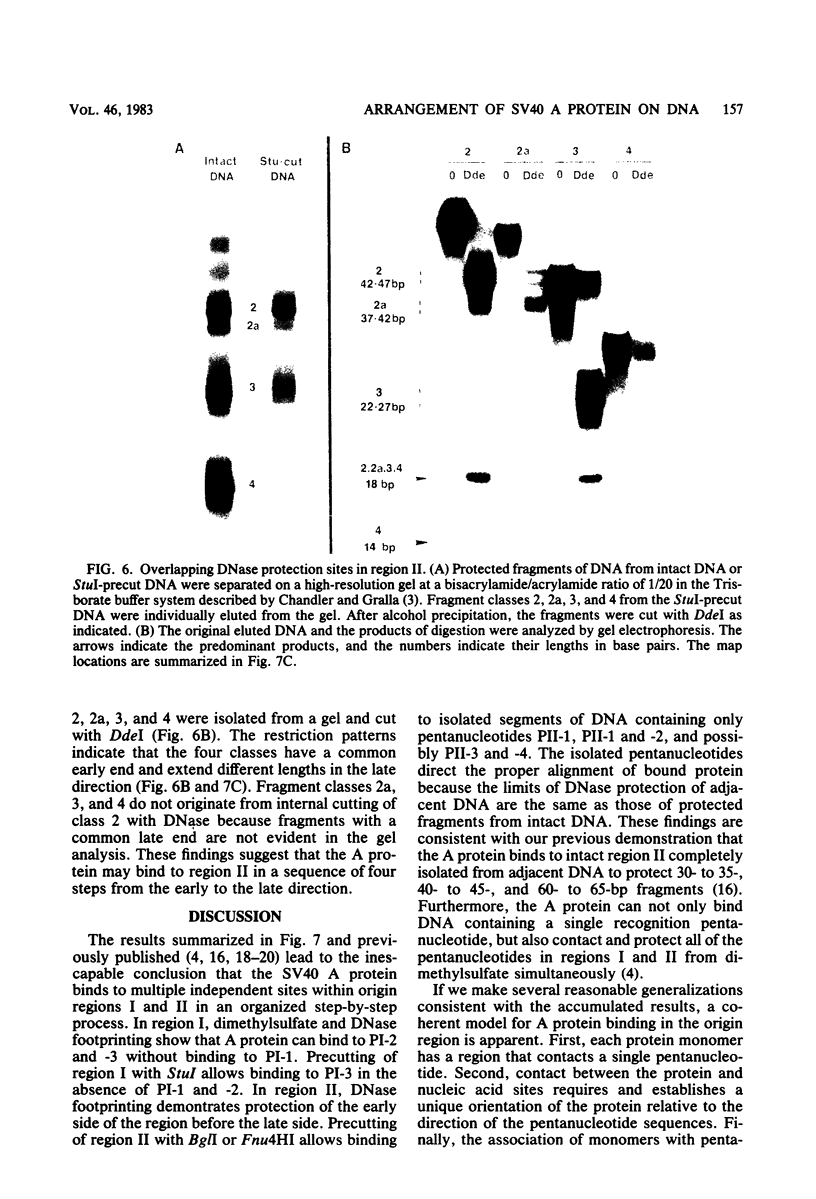
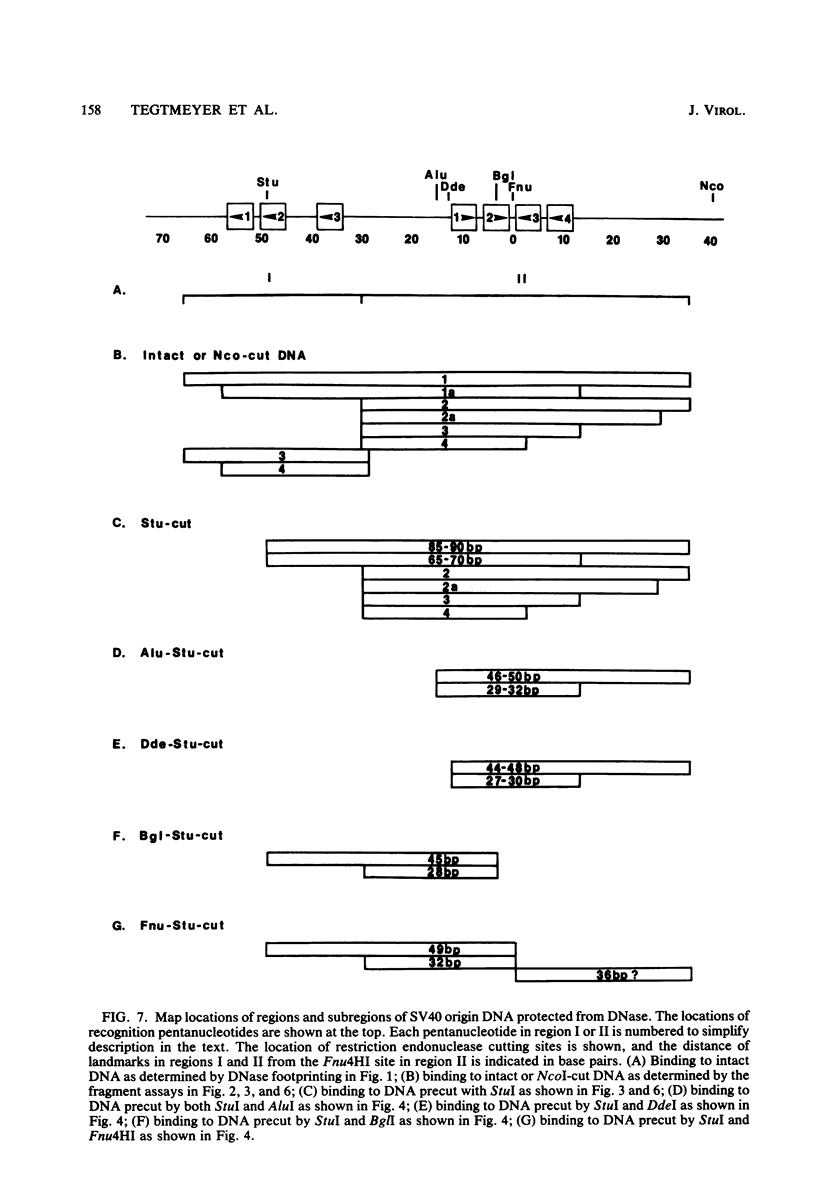
DNA binding regions I, II, and III at the origin of replication have different arrangements of A protein (T antigen) recognition pentanucleotides. The A protein also protects each region from DNase in distinctly different patterns. Footprint and fragment assays led to the following conclusions: (i) in some cases a single recognition pentanucleotide is sufficient to direct the binding and accurate alignment of A protein on DNA; (ii) the A protein binds within isolated region I or II in a sequential process leading to multiple overlapping areas of DNase protection within each region; and (iii) the 23-base pair span of recognition sequences in region II allows binding and protection of a longer length of DNA than the 23-base pair span in region I. We propose a model of protein binding that addresses the problem of variations in the arrangement of pentanucleotides in regions I and II and explains the observed DNase protection patterns. The central feature of the model requires each protomer of A protein to bind to a pentanucleotide in a unique direction. The resulting orientation of protein would protect more DNA at the 5' end of the 5'-GAGGC-3' recognition sequence than at the 3' end. The arrangement of multiple protomers at the origin of simian virus 40 replication is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. Relationship of oligomerization to enzymatic and DNA-binding properties of the SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. W., Gralla J. Specific binding and protection of form II SV40 deoxyribonucleic acid by ribonucleic acid polymerase II from wheat germ. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 15;19(8):1604–1612. doi: 10.1021/bi00549a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Cold-sensitive regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Scheller A., Barnet B., Hantzopoulos P., Oren M., Prives C. Different forms of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen varying in their affinities for DNA. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):456–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.456-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Williams R. C., Tjian R. Oligomeric structure of a simian virus 40 T antigen in free form and bound to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Specific interaction of the SV40 T antigen-cellular p53 protein complex with SV40 DNA. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90531-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Dhar R., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of a fragment of SV40 DNA that contains the origin of DNA replication and specifies the 5' ends of "early" and "late" viral RNA. III. Construction of the total sequence of EcoRII-G fragment of SV40 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):355–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B. Partial purification of SV40 A protein and a related cellular protein from permissive cells. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Andersen B., Shaw S. B., Wilson V. G. Alternative interactions of the SV40 A protein with DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Baygell P., Livingston D. M. Thermolabile T (tumor) antigen from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4351–4355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Haines L. L., Livingston D. M. Binding of an analog of the simian virus 40 T antigen to wild-type and mutant viral replication origins. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):473–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90472-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Tevethia M. J., Lewton B. A., Tegtmeyer P. DNA binding properties of simian virus 40 temperature-sensitive A proteins. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):458–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.458-466.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]