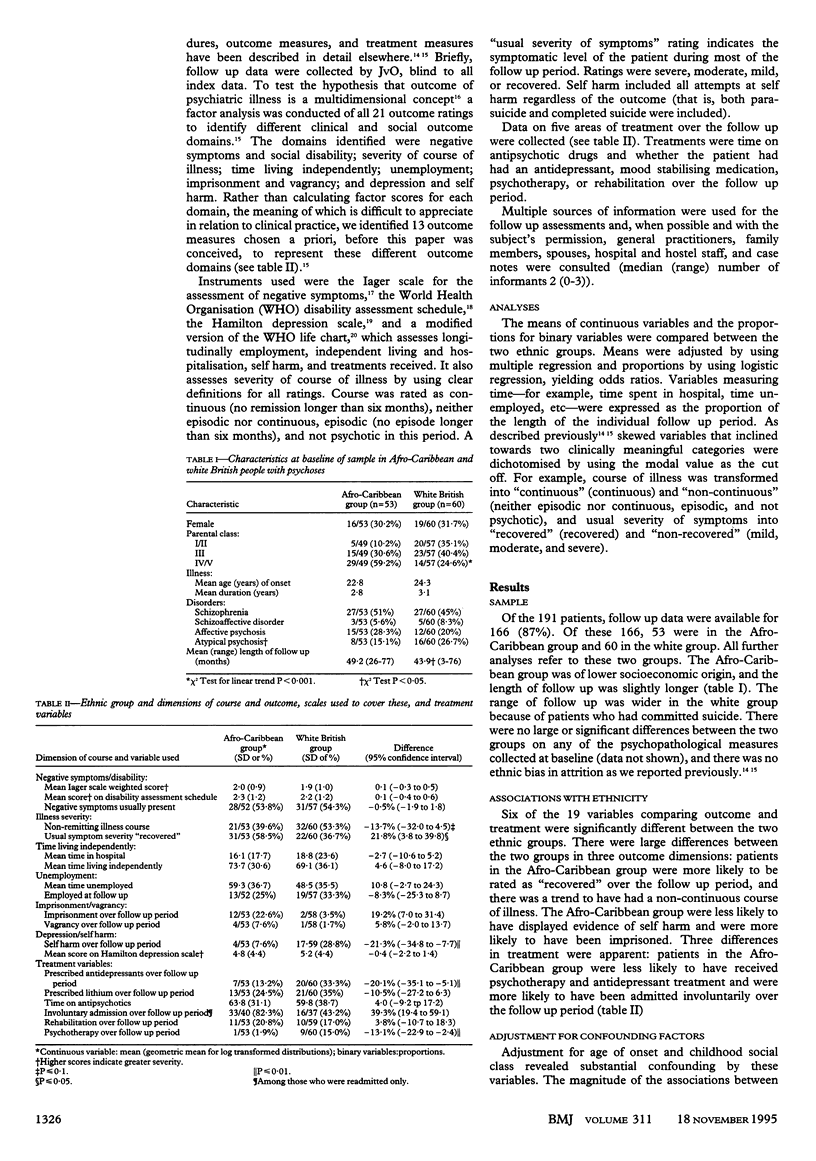
Abstract
OBJECTIVES--To compare the course and outcome of psychotic illness in a group of Afro-Caribbean patients resident in the United Kingdom and a group of white British patients. DESIGN--Cohort study of consecutive admissions followed up for four years. SUBJECTS--113 patients with psychotic illness of recent onset admitted to two south London hospitals. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Course of illness, history of self harm, social disability, treatment received, and hospital use adjusted for socioeconomic origin. RESULTS--The Afro-Caribbean group spent more time in a recovered state during the follow up period (adjusted odds ratio 5.0; 95% confidence interval 1.7 to 14.5), were less likely to have had a continuous illness (0.3; 0.1 to 0.8), were less at risk of self harm (0.2; 0.1 to 0.8), and were less likely to have been prescribed antidepressant treatment (0.3; 0.1 to 0.9). There were no differences in hospital use, but the Afro-Caribbean group had more involuntary admissions (8.9; 2.1 to 35.6) and more imprisonments over the follow up period (9.2; 1.6 to 52.3). CONCLUSIONS--Afro-Caribbean patients in the United Kingdom have a better outcome after psychiatric illness than do white people. The combination of high incidence and more benign course of illness of psychotic illness in this group may be due, at least in part, to a greater exposure to precipitants in the social environment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchwood M., Cochrane R., Macmillan F., Copestake S., Kucharska J., Carriss M. The influence of ethnicity and family structure on relapse in first-episode schizophrenia. A comparison of Asian, Afro-Caribbean, and white patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;161:783–790. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke A. W. Socio-cultural determinants of attempted suicide among West Indians in Birmingham: ethnic origin and immigrant status. Br J Psychiatry. 1976 Sep;129:261–266. doi: 10.1192/bjp.129.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1960 Feb;23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iager A. C., Kirch D. G., Wyatt R. J. A Negative Symptom Rating Scale. Psychiatry Res. 1985 Sep;16(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(85)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood R., Lipsedge M. Acute psychotic reactions in Caribbean-born patients. Psychol Med. 1981 May;11(2):303–318. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700052120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlashan T. H., Carpenter W. T., Jr, Bartko J. J. Issues of design and methodology in long-term followup studies. Schizophr Bull. 1988;14(4):569–574. doi: 10.1093/schbul/14.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern D., Hemmings P., Cope R., Lowerson A. Long-term follow-up of young Afro-Caribbean Britons and white Britons with a first admission diagnosis of schizophrenia. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1994 Feb;29(1):8–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00796443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin P., Farmer A., Harvey I. A polydiagnostic application of operational criteria in studies of psychotic illness. Development and reliability of the OPCRIT system. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Aug;48(8):764–770. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810320088015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. L., Endicott J., Robins E. Research diagnostic criteria: rationale and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Jun;35(6):773–782. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770300115013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman P. A. Outcome of schizophrenia in the Afro-Caribbean community. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1992 Mar;27(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00788513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAILLANT G. E. PROSPECTIVE PREDICTION OF SCHIZOPHRENIC REMISSION. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1964 Nov;11:509–518. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1964.01720290051007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J., Fahy T. A., Bebbington P., Jones P., Wilkins S., Sham P., Russell A., Gilvarry K., Lewis S., Toone B. The influence of life events on the subsequent course of psychotic illness. A prospective follow-up of the Camberwell Collaborative Psychosis Study. Psychol Med. 1994 May;24(2):503–513. doi: 10.1017/s003329170002746x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



