Abstract
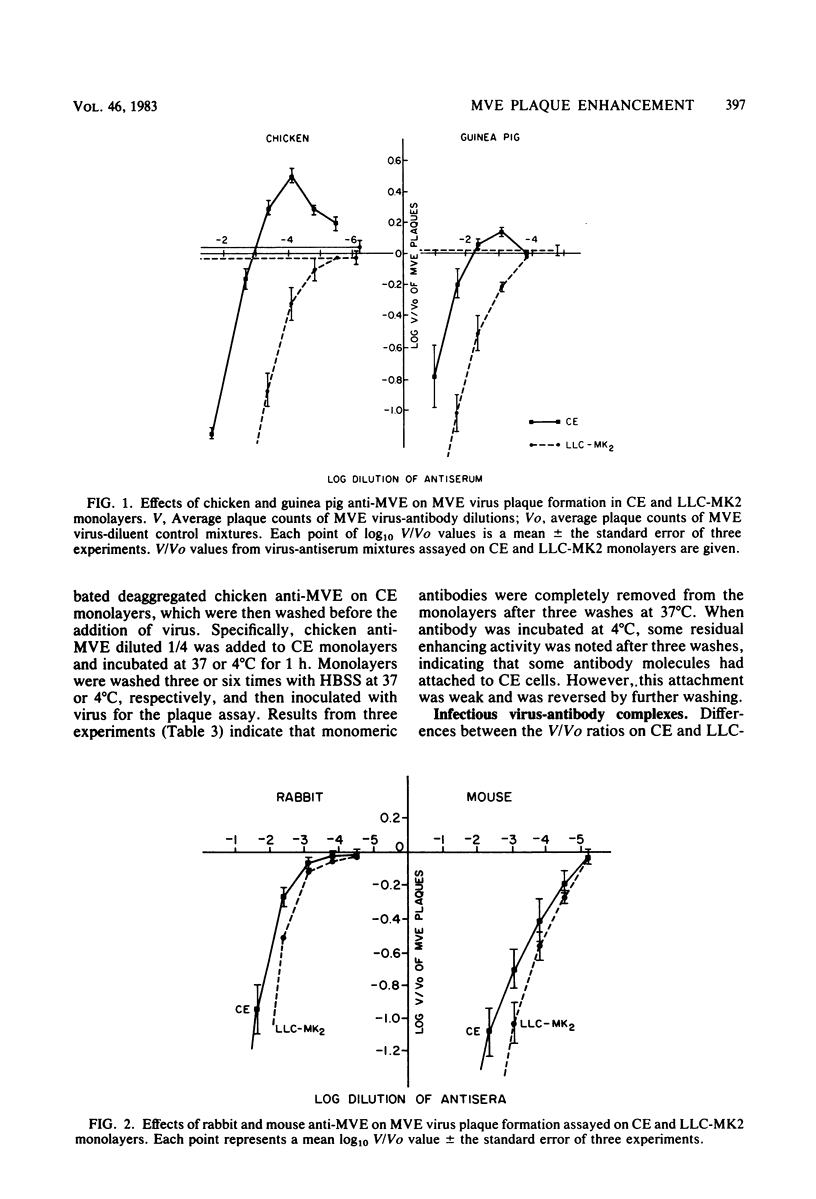
Chicken antisera to Murray Valley encephalitis (MVE) virus, when incubated with virus and assayed for plaques on chicken embryo (CE) monolayers, neutralized MVE virus at high concentrations of antibody, but caused increases in plaque counts at low concentrations of antibody. Plaque enhancement did not occur when the same virus-antibody mixtures were assayed on a continuous line of rhesus monkey kidney cells (LLC-MK2), nor when the anti-MVE antibody was of mammalian origin and the assay system was CE monolayers. Correspondingly, chicken anti-MVE did not enhance the plaque formation of MVE virus in a stable line of mouse macrophages, P-388D1, whereas rabbit and mouse anti-MVE did enhance plaque formation. This enhancing activity was associated with noncytophilic immunoglobulin G (IgG). The Fc terminus of the IgG molecule was required, as no plaque enhancement occurred with chicken anti-MVE Fab. These data indicate that there is a requirement for taxonomic complementarity between Fc termini and Fc receptors in the above systems. CE cell monolayers were found to contain approximately 2% of Fc receptor-bearing cells among the fibroblast-like cells. Fc receptor-bearing cells in CE monolayers were isolated and found to be of the mononuclear phagocytic lineage. These mononuclear phagocytes, which originate in lymphoid tissues and blood associated with CE tissue fragments, are integrated into primary CE monolayers and form infectious centers in the presence of virus and low dilutions of antibody.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., ABBOT A., ANDERSON S. G., COLLINS F. D. Particle counts and some chemical properties of Murray Valley encephalitis virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Sep;29:165–170. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. E., Buescher E. L., Hetrick F. M. Production and characterization of arbovirus antibody in mouse ascitic fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1967 May;16(3):339–347. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1967.16.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Madrid A. T., Porterfield J. S. A simple micro-culture method for the study of group B arboviruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(1):113–121. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della-Porta A. J., Westaway E. G. A multi-hit model for the neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):1–19. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Studies of the human lymphocyte receptor for heat-aggregated or antigen-complexed immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R. Production of Plaques in Monolayer Tissue Cultures by Single Particles of an Animal Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Aug;38(8):747–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.8.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald S., Freedman L., Sanders B. G. EA rosette forming lymphoid cells: distribution as to cell types and organs from chickens of different developmental stages. Cell Immunol. 1976 Apr;23(1):158–170. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewald S., Freedman L., Sanders B. G. EA rosette-forming lymphoid cells in chickens: specificity of the Fc receptor and its relationship to other surface antigens. Immunology. 1976 Dec;31(6):847–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKES R. A. ENHANCEMENT OF THE INFECTIVITY OF ARBOVIRUSES BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA PRODUCED IN DOMESTIC FOWLS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Aug;42:465–482. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL R. N., CHERRY W. R., TRITCH O. J. Growth characteristics of monkey kidney cell strains LLC-MK1, LLC-MK2, and LLC-MK2(NCTC-3196) and their utility in virus research. J Exp Med. 1962 May 1;115:903–918. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.5.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. In vivo enhancement of dengue virus infection in rhesus monkeys by passively transferred antibody. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):527–533. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., O'Rourke E. J., Allison A. C. Dengue viruses and mononuclear phagocytes. II. Identity of blood and tissue leukocytes supporting in vitro infection. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):218–229. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., O'Rourke E. J. Dengue viruses and mononuclear phagocytes. I. Infection enhancement by non-neutralizing antibody. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):201–217. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., Simasthien P. Observations related to the pathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever. II. Antigenic and biologic properties of dengue viruses and their association with disease response in the host. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Apr;42(5):276–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B., Udomsakdi S., Simasthien P., Singharaj P., Sukhavachana P., Nisalak A. Observations related to pathogenesis of dengue hemorrhagic fever. I. Experience with classification of dengue viruses. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Apr;42(5):261–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R. A., Lafferty K. J. The enchancement of virus infectivity by antibody. Virology. 1967 Oct;33(2):250–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A., Allison A. C., Ward P., Kight N. Identification of human mononuclear leucocyte populations by esterase staining. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):289–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJELLEN L. E., SCHLESINGER R. W. Influence of host cell on residual infectivity of neutralized vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1959 Feb;7(2):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Ueba N., Minekawa Y. Studies on the mechanism of antibody-mediated enhancement of Getah virus infectivity. Biken J. 1981 Jun;24(1-2):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliks S. C., Halstead S. B. An explanation for enhanced virus plaque formation in chick embryo cells. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):504–505. doi: 10.1038/285504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Hoffman T., Ferrarini M., Kunkel H. G. The demonstration of acid alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase activity in human lymphocytes: usefulness as a T-cell marker. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jan;35(1):112–123. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAFFERTY K. J. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN VIRUS AND ANTIBODY. I. KINETIC STUDIES. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:61–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F. In vitro assay of mitogen stimulation of avian peripheral lymphocytes. Avian Dis. 1974 Oct-Dec;18(4):602–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majer M., Link F. Studies on the non-neutralizable fraction of vaccinia virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Aug;7(2):283–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya O., Ichikawa Y. Ontogeny of spontaneous antigen-binding cells in developing chick embryos. Immunology. 1979 Aug;37(4):857–861. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke E. J., Halstead S. B., Allison A. C., Platts-Mills T. A. Specific lethality of silica for human peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes, in vitro. J Immunol Methods. 1978;19(2-3):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiris J. S., Porterfield J. S. Antibody-mediated enhancement of Flavivirus replication in macrophage-like cell lines. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):509–511. doi: 10.1038/282509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porterfield J. S. Antibody-mediated enhancement of rabies virus. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):542–542. doi: 10.1038/290542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Nathanson N. Acute rabies death mediated by antibody. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):590–591. doi: 10.1038/290590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reade P. C. The development of bactericidal activity in rat peritoneal macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Apr;46(2):231–247. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. Macrophage heterogeneity in receptor activity: the activation of macrophage Fc receptor function in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):976–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. K., Nisalak A., Sukhavachana P., Vivona S. A plaque reduction test for dengue virus neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli A. C., Fischer D. S., Downs W. G. Use of sarcoma 180/TG to prepare hyperimmune ascitic fluid in the mouse. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):676–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger J. J., Brandriss M. W. Growth of 17D yellow fever virus in a macrophage-like cell line, U937: role of Fc and viral receptors in antibody-mediated infection. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):659–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardley R. C., Lawman M. J., Hamilton F. The establishment of continuous macrophage cell lines from peripheal blood monocytes. Immunology. 1980 Jan;39(1):67–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. C., Scott F. W. Pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis: nature and development of viremia. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Mar;42(3):382–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



