Abstract
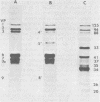
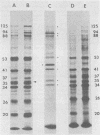
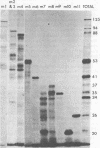
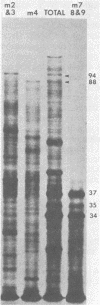
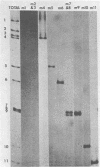
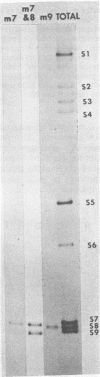
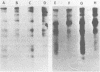
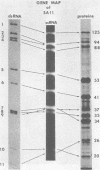
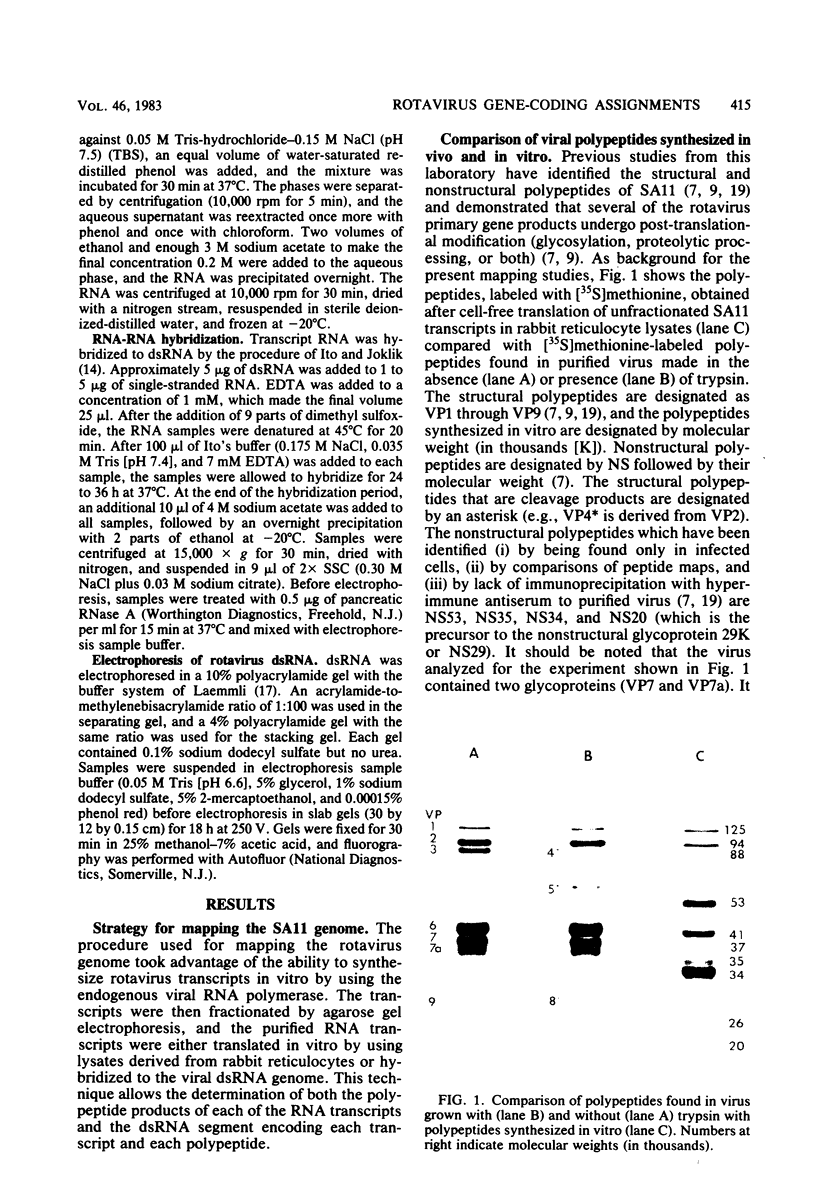
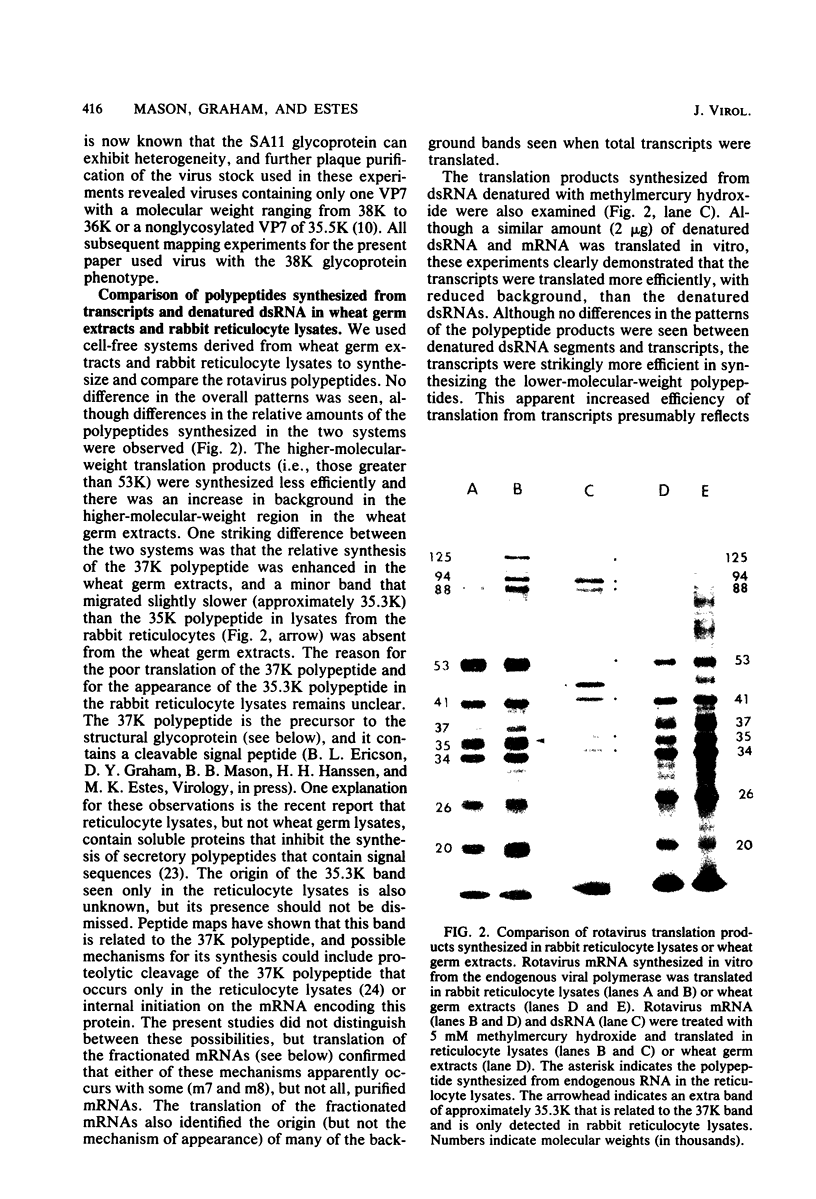
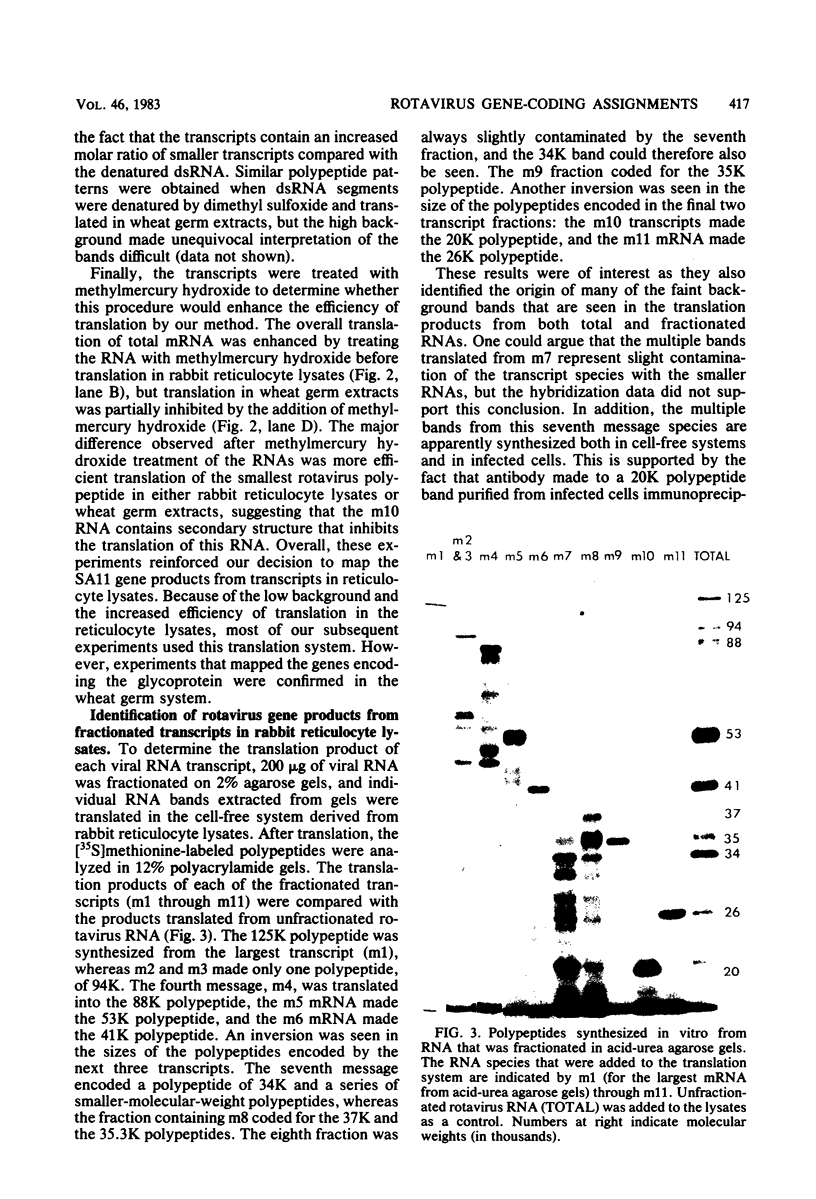
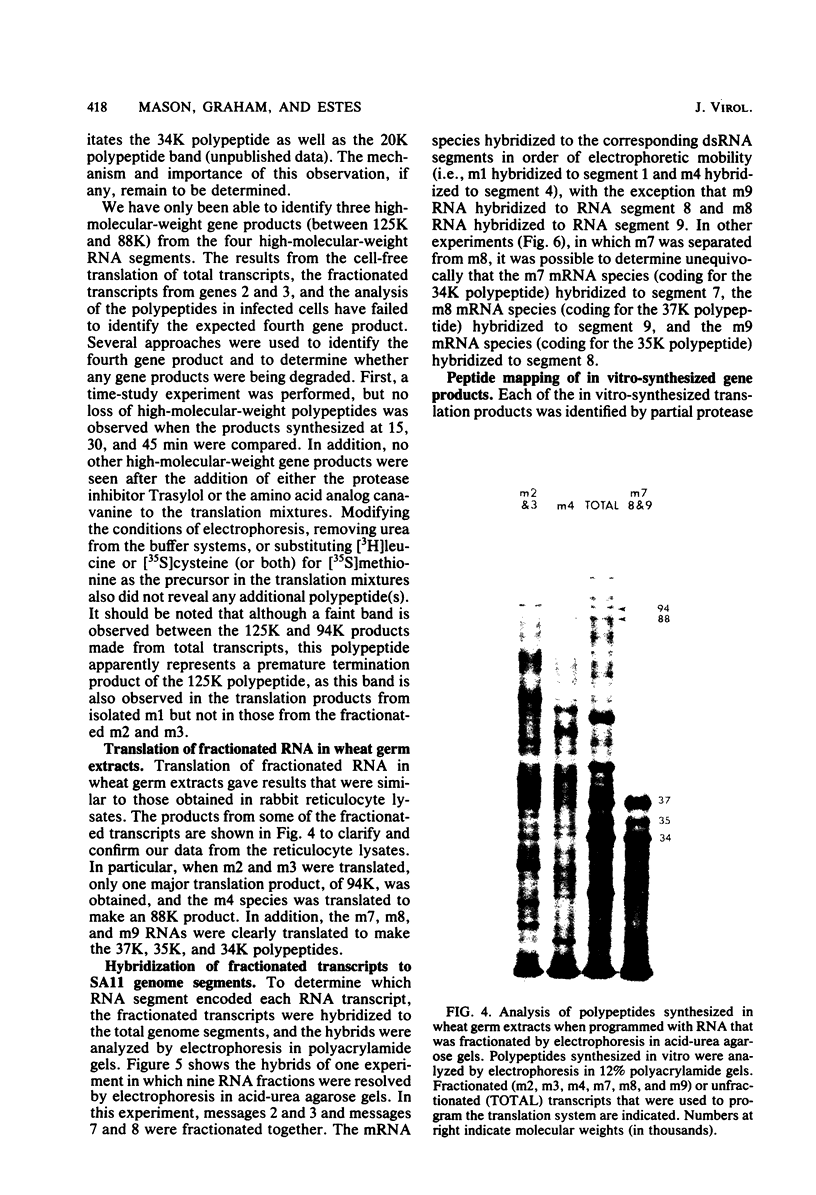
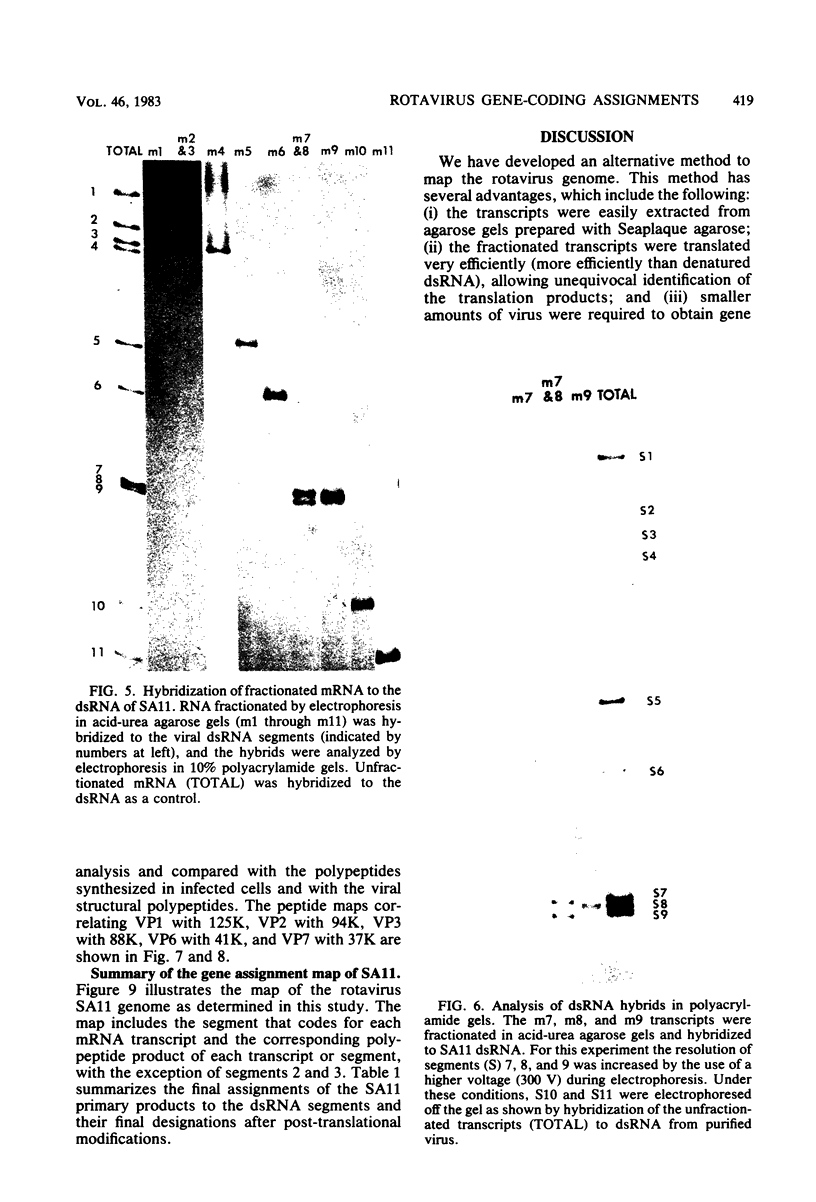
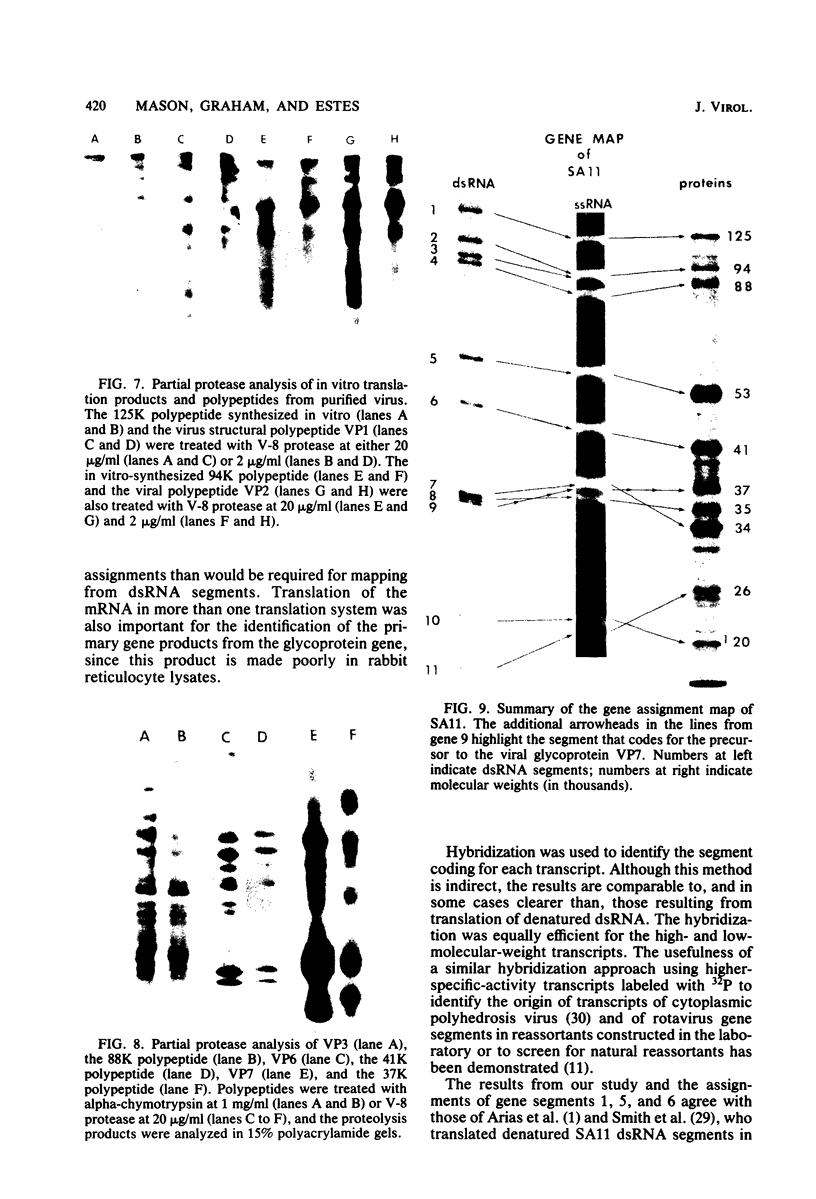
Biochemical mapping experiments of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome were performed to determine which double-stranded RNA segment coded for each of the viral polypeptides. Viral RNA transcripts were synthesized in vitro by using the endogenous viral RNA polymerase and fractionated by electrophoresis in acid-urea agarose gels. The fractionated transcripts were translated in two cell-free systems: micrococcal nuclease-treated reticulocyte lysates and wheat germ extracts. The polypeptide products were identified by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and partial peptide analysis and compared with polypeptides synthesized in infected cells or found in purified virus. The RNA segment that coded for each transcript was determined by hybridization of the fractionated transcripts to the double-stranded RNA genome and analysis of the hybrids by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels. Primary gene products were assigned for 10 of the rotavirus transcripts and 10 of the double-stranded RNA segments. The coding assignments are as follows: the inner-capsid polypeptides, VP1, VP2, and VP6, were assigned to segments 1, 2, and 6, respectively; the major outer-capsid polypeptides, VP3 and VP7, were assigned to segments 4 and 9, respectively; segments 5, 7, and 8 coded for nonstructural polypeptides with molecular weights of 53,000, 34,000, and 35,000, respectively; segment 10 coded for the 20,000-molecular-weight precursor to the 29,000-molecular-weight glycosylated nonstructural polypeptide; and segment 11 coded for a 26,000-molecular-weight polypeptide that may be the precursor to the minor outer-capsid polypeptide VP9. Several methods were used to determine the product of gene segment 3, and the problems associated with the identification of this gene product are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias C. F., López S., Espejo R. T. Gene protein products of SA11 simian rotavirus genome. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.42-50.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastardo J. W., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Sonza S., Mercer L. D., Holmes I. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to electrophoretically purified SA11 virus polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):641–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.641-647.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity associated with purified calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):395–402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. Comparisons of rotavirus polypeptides by limited proteolysis: close similarity of certain polypeptides of different strains. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):720–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.720-728.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyall-Smith M. L., Holmes I. H. Gene-coding assignments of rotavirus double-stranded RNA segments 10 and 11. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.1099-1103.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson B. L., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B., Estes M. K. Identification, synthesis, and modifications of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):825–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.825-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., López S., Arias C. Structural polypeptides of simian rotavirus SA11 and the effect of trypsin. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.156-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Ramig R. F., Ericson B. L. Heterogeneity in the structural glycoprotein (VP7) of simian rotavirus SA11. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Greenberg H. B., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Use of transcription probes for genotyping rotavirus reassortants. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):288–295. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul S. K., Simpson T. F., Woode G. N., Fulton R. W. Antigenic relationships among some animal rotaviruses: virus neutralization in vitro and cross-protection in piglets. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.495-503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin K. H., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. purification and characterization of the small-sized class mRNAs of reovirus type 3: coding assignments and translational efficiencies. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90216-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Faulkner-Valle G. P. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. I. Characterization of basic growth parameters and pattern of macromolecular synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., McCorquodale J. G. The molecular biology of rotaviruses. II. Identification of the protein-coding assignments of calf rotavirus genome RNA species. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Pickett C. B., Zimmerman M., Strauss A. W. Protease activities present in wheat germ and rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M. Isolation and characterization of purified rat casein messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5263–5271. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Miura Y., Tokuhisa S., Matumoto M. Antigenic relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by neutralization and immunofluorescence. Arch Virol. 1982;73(1):45–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01341726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Holmes I. H. Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA 11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):976–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.976-982.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., James W. D., Pittman A. L., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Definition of human rotavirus serotypes by plaque reduction assay. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):110–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.110-115.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]