Abstract
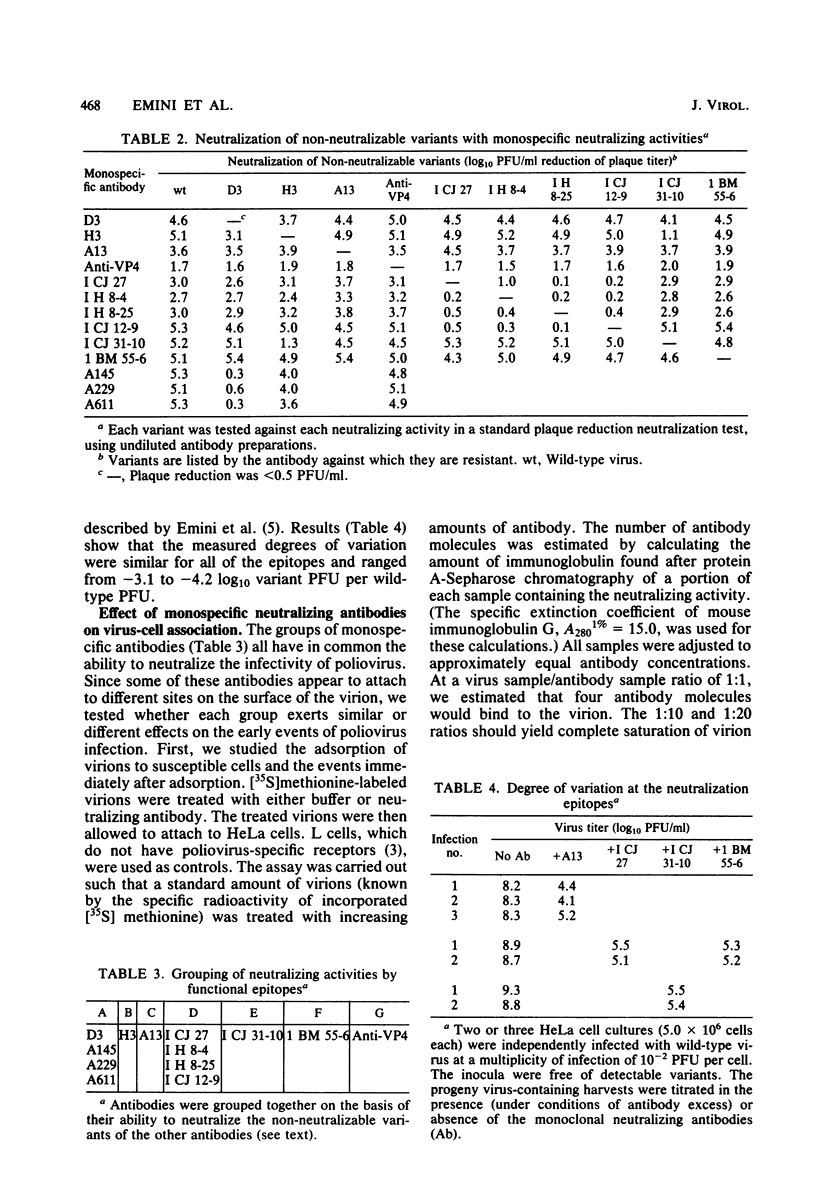
Antibody-mediated poliovirus neutralization was studied by using a series of 13 monospecific neutralizing antibodies. These antibodies were found to recognize seven individual viral epitopes, several of which functionally overlap one another. Each epitope was capable of undergoing variation so that the variant virus was no longer capable of being neutralized by antibody directed against that epitope. The measured degree of variation for each site varied from -3.1 to -4.2 log10 variant PFU per wild-type PFU. Under nonsaturating but neutralizing conditions, the antibodies, with the exception of those directed to one specific epitope, failed to completely inhibit the virion's binding to the cell. Similarly, none of the neutralizing antibodies completely inhibited viral penetration, but all prevented virus-specific transcription. A strong correlation was established between the binding of each of the neutralizing antibodies, with one exception, to the virion and a significant shift in the virion's pI from 7.0 to ca. 4.0.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F. Le polypeptide structural VP1 du poliovirus type 1 induit des anticorps neutralisants. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Jan 11;294(2):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crainic R., Couillin P., Cabau N., Boue A., Horodniceanu F. Determination of type 1 poliovirus subtype classes with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Dev Biol Stand. 1981;50:229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E., Anderson C. W. Identification of the initiation site of poliovirus polyprotein synthesis. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1017-1028.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Dorner A. J., Dorner L. F., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Identification of a poliovirus neutralization epitope through use of neutralizing antiserum raised against a purified viral structural protein. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Lewis A. J., Larsen G. R., Wimmer E. Poliovirus neutralization epitopes: analysis and localization with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):997–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.997-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Schild G. C., Minor P. D., Yates P. J., Spitz M. A hybridoma cell line secreting antibody to poliovirus type 3 D-antigen: detection in virus harvest of two D-antigen populations. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):437–442. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Yi-hua Q., Minor P. D., Magrath D. I., Spitz M., Schild G. C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the Sabin vaccine strain of poliovirus 3. Lancet. 1982 Jul 17;2(8290):122–124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. D., Kew O. M., Feorino P. M. Monoclonal antibodies of four different specificities for neutralization of type 1 polioviruses. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):841–843. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.841-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Gilbert S. F., Grieves J., Anderegg J., Rueckert R. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody against poliovirus and its reaction with related antigens. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):211–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Nottay B. K., Hatch M. H., Nakano J. H., Obijeski J. F. Multiple genetic changes can occur in the oral poliovaccines upon replication in humans. J Gen Virol. 1981 Oct;56(Pt 2):337–347. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-2-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Anderson C. W., Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Cleavage sites within the poliovirus capsid protein precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):340–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.340-344.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Gosser L. B., Kauer J. C. Early alteration of poliovirus in infected cells and its specific inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):329–342. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. Studies on the interactions of poliomyelitis virus, antibody, and host cells in tissue culture system. Virology. 1958 Oct;6(2):424–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Characterization of type 1 poliovirus by electrophoretic analysis. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):554–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Neutralization of poliovirus: a hypothesis to explain the mechanism and the one-hit character of the neutralization reaction. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The interaction of neutralized poliovirus with HeLa cells. I. Adsorption. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medrano L., Green H. Picornavirus receptors and picornavirus multiplication in human-mouse hybrid cell lines. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterhaus A. D., van Wezel A. L., van Steenis G., Hazendonk A. G., Drost G. Production and potential use of monoclonal antibodies against polio viruses. Dev Biol Stand. 1981;50:221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALK J. E. Principles of immunization as applied to poliomyelitis and influenza. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Nov;43(11):1384–1398. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.11.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama T., Hagiwara A., Hara M., Shimojo H. Alteration in oligonucleotide fingerprint patterns of the viral genome in poliovirus type 2 isolated from paralytic patients. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):46–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.46-53.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



