Abstract
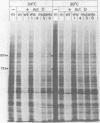
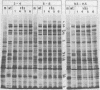
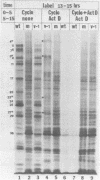
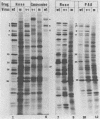
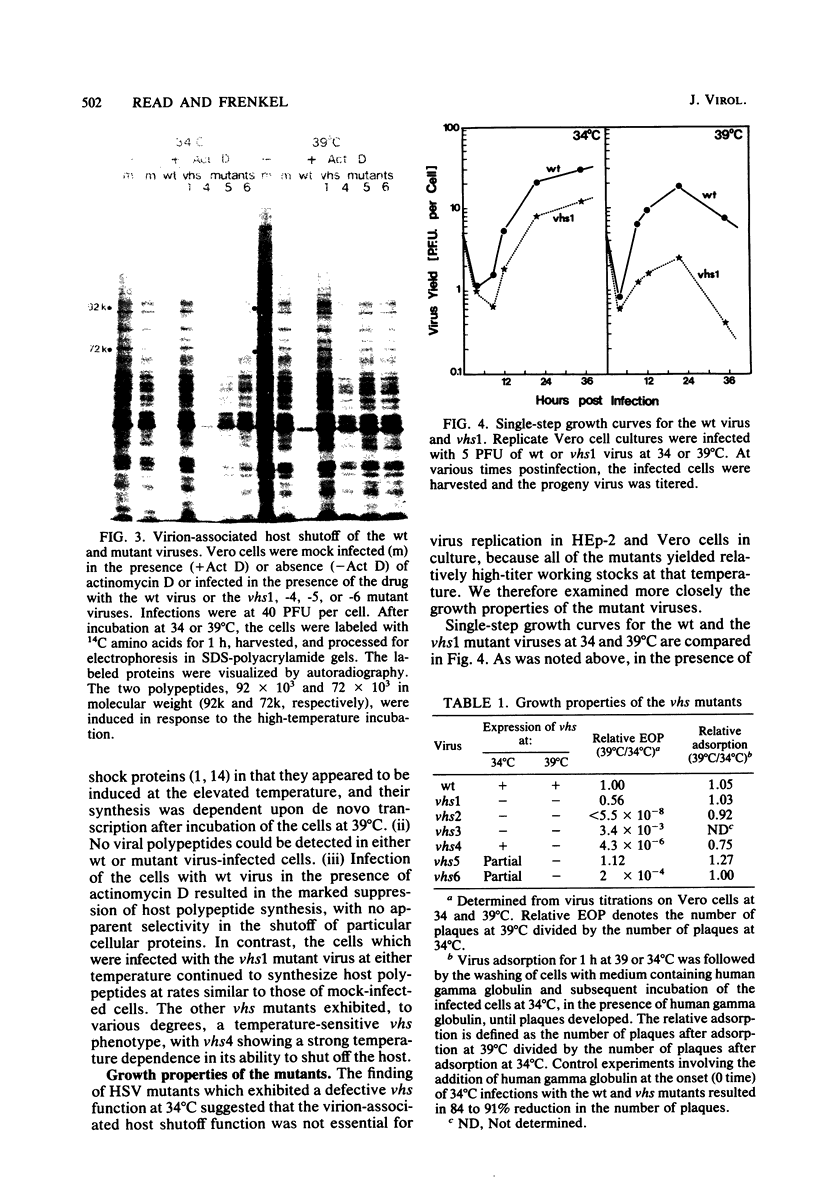
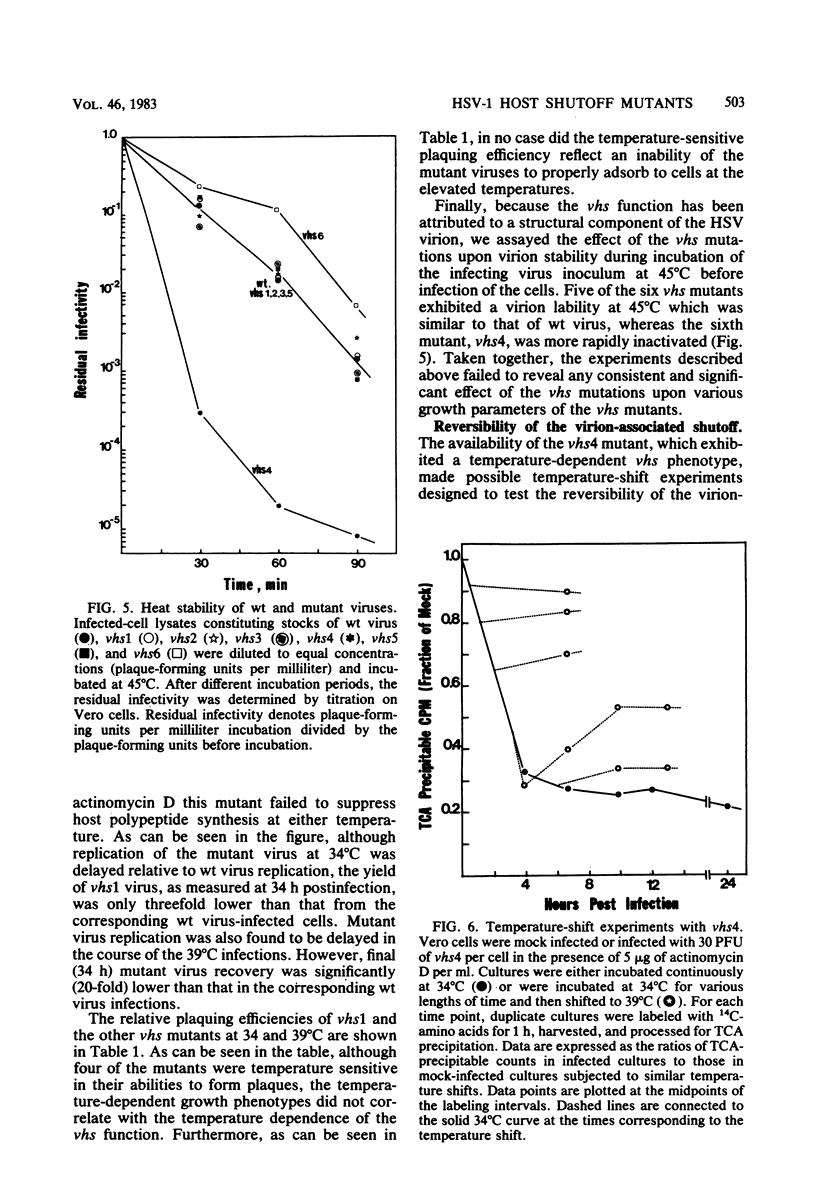
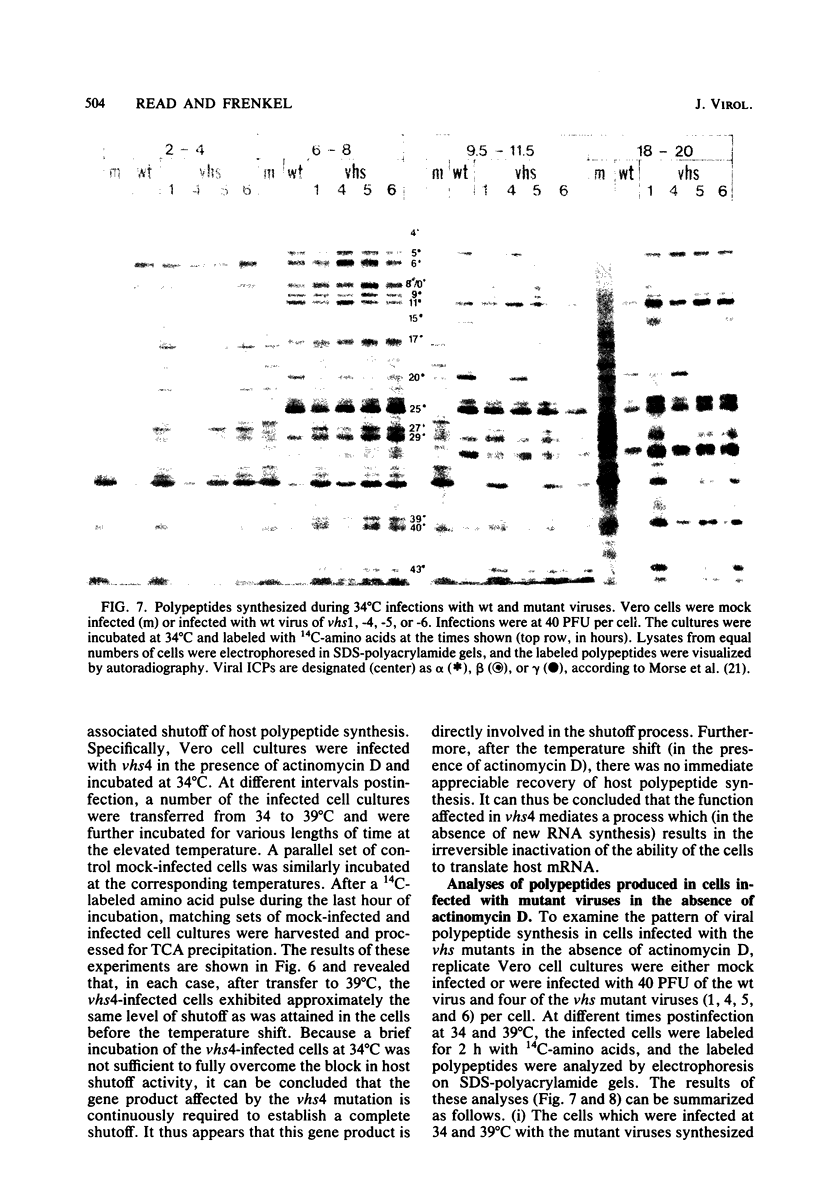
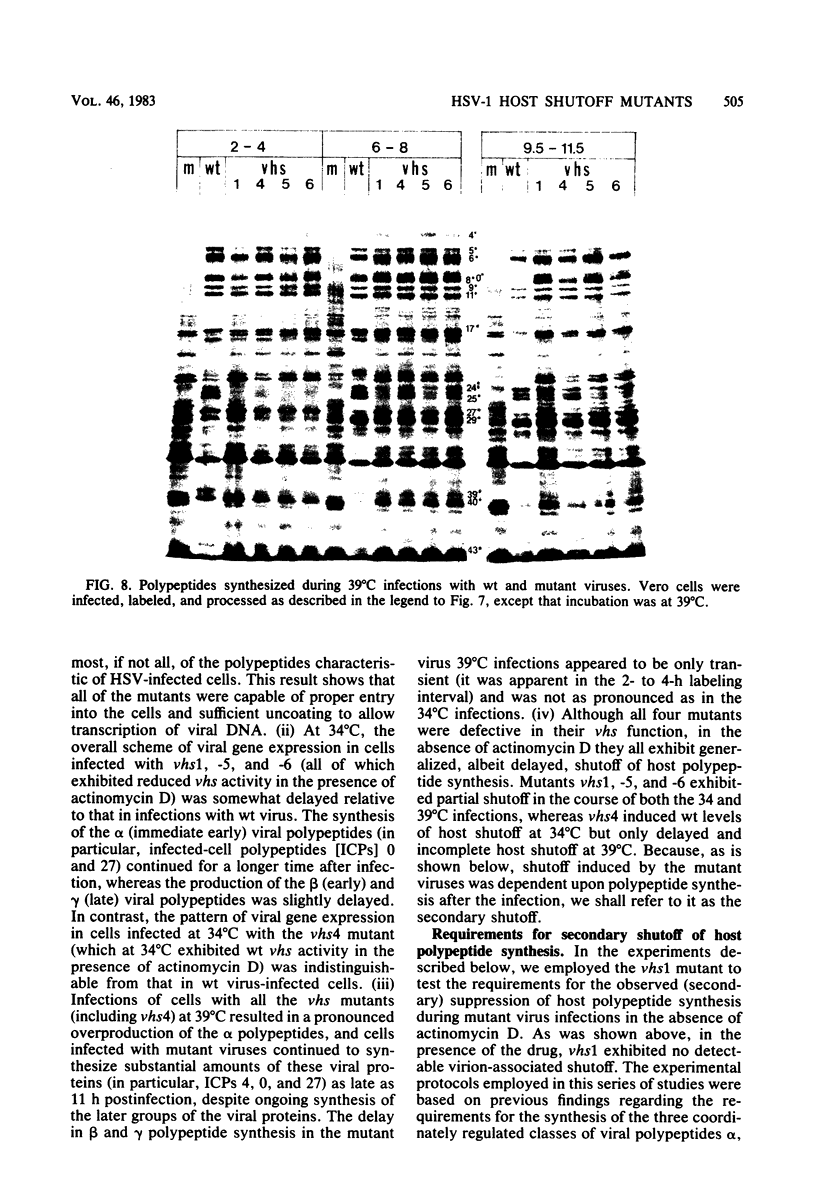
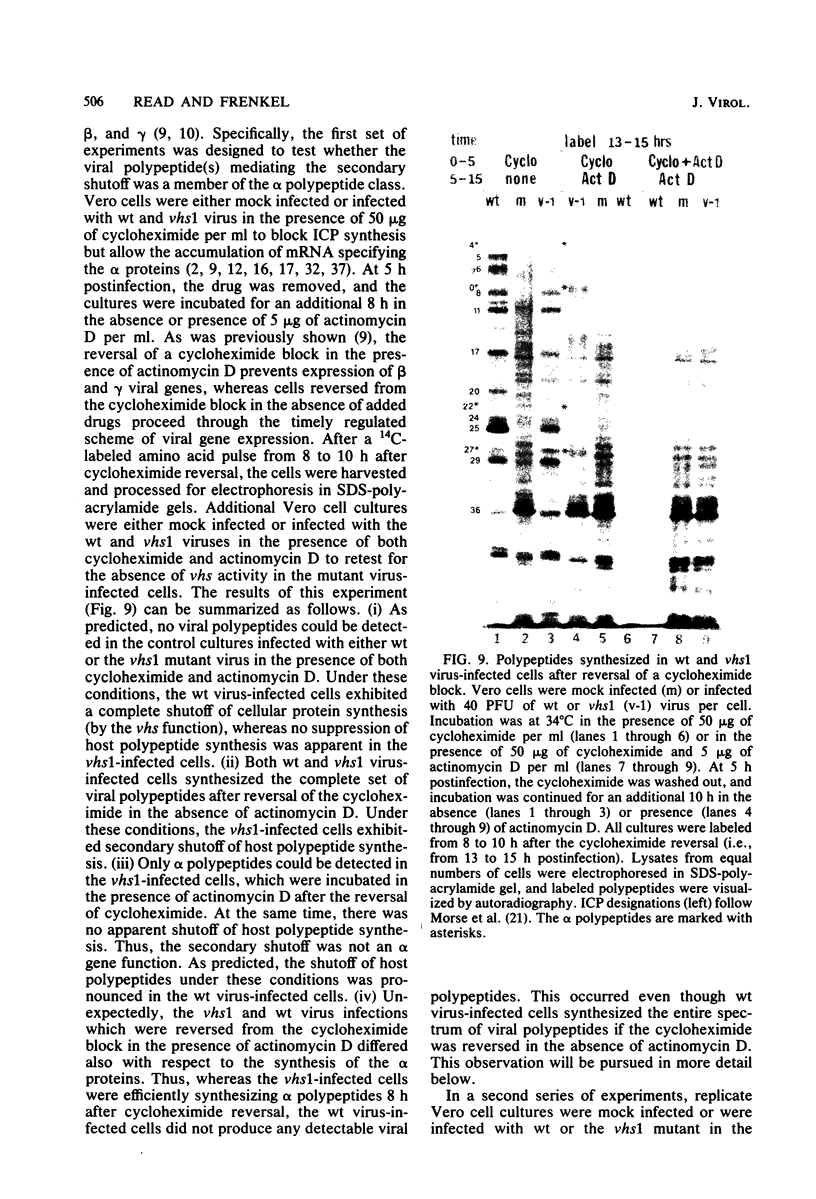
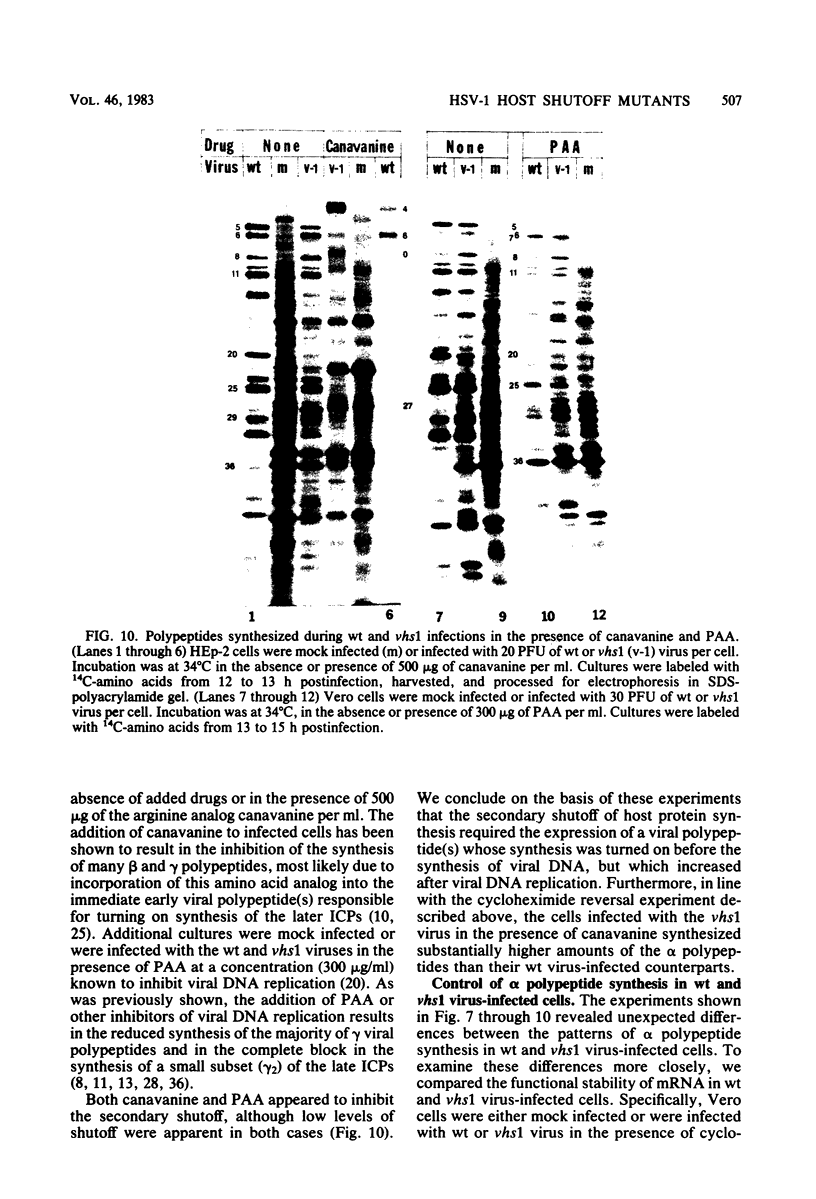
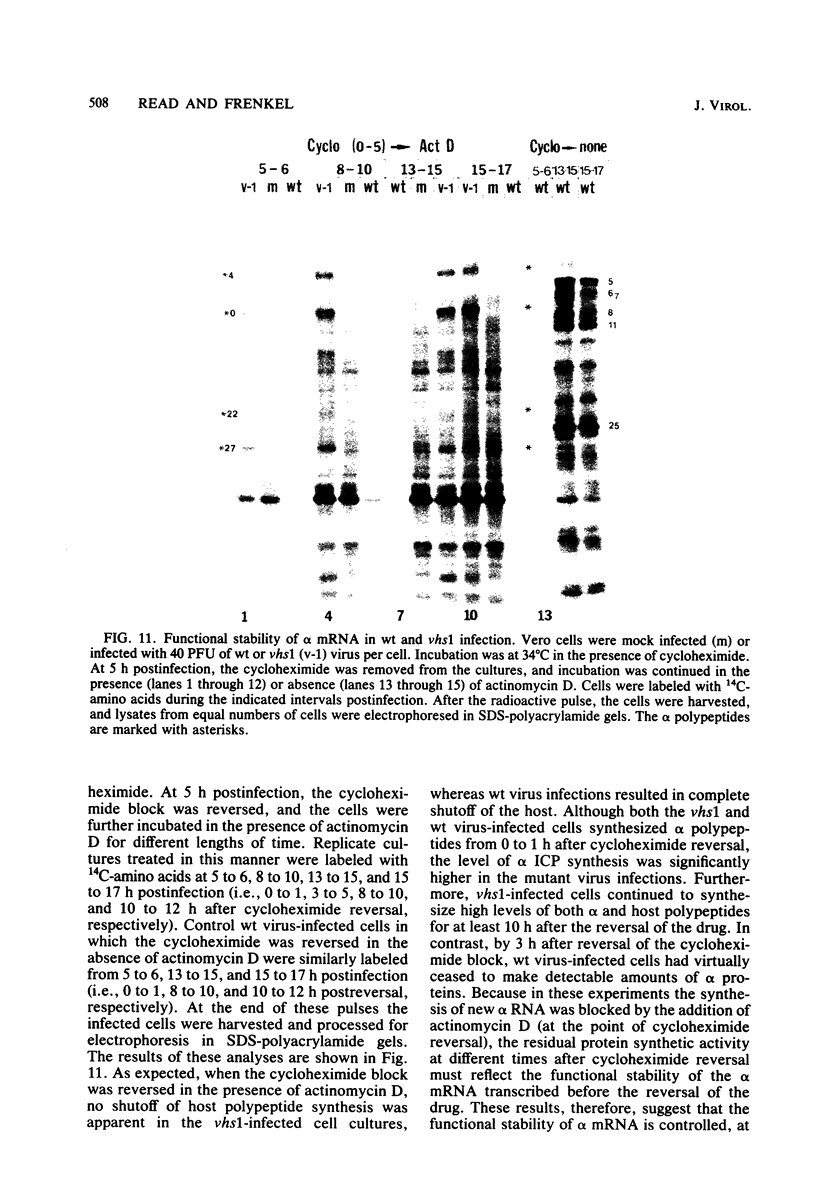
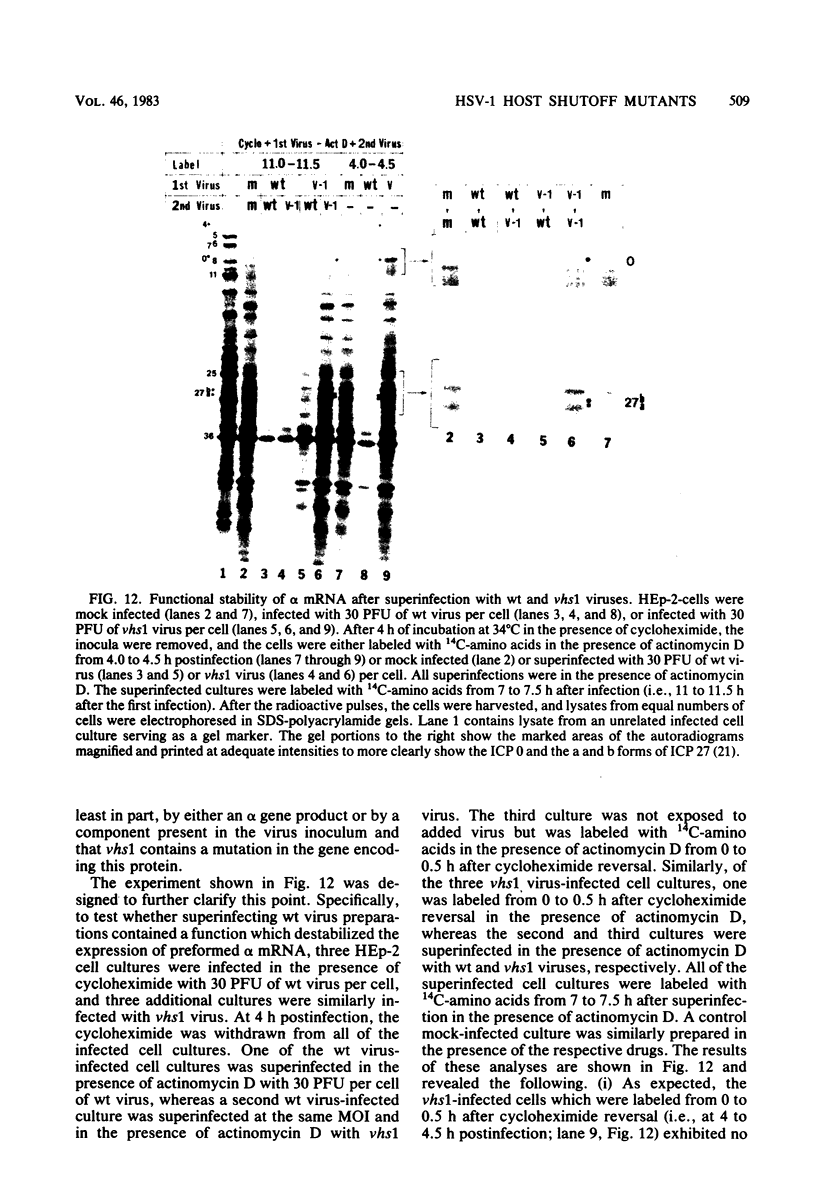
Six mutants isolated from herpes simplex virus type 1 were judged to be defective with respect to the virion-associated function acting to rapidly shut off host polypeptide synthesis in herpes simplex virus-infected cells. The mutants were capable of proper entry into the cells, but, unlike the parent wild-type virus, they failed to shut off host polypeptide syntehsis in the presence of actinomycin D. They were consequently designated as virion-associated host shutoff (vhs) mutants. In the presence of actinomycin D, three of the mutants, vhs1, -2, and -3, failed to shut off the host at both 34 and 39 degrees C, whereas vhs4, -5, and -6 exhibited a temperature-dependent vhs phenotype. Since the mutants were capable of growth at 34 degrees C, it appeared that the vhs function was not essential for virus replication in cultured cells. Temperature-shift experiments performed with the vhs4 mutant showed that an active vhs function was required throughout the shutoff process and that, once established, the translational shutoff could not be reversed. In the absence of actinomycin D, the mutants induced a generalized, secondary shutoff of host translation, which required the synthesis of beta (early) or gamma (late) viral polypeptide(s). The vhs mutants appeared to be defective also with respect to post-transcriptional shutoff of alpha (immediate early) viral gene expression, since (i) cells infected with mutant viruses overproduced alpha viral polypeptides, (ii) there was an increased functional stability of alpha mRNA in the vhs1 mutant virus-infected cells, and (iii) superinfection of vhs1-infected cells with wild-type virus, in the presence of actinomycin D, resulted in a more pronounced shutoff of alpha polypeptide synthesis from preformed alpha mRNA than equivalent superinfection with vhs1 virus. The data suggest that the synthesis of alpha polypeptides in wild-type virus infections is subject to a negative post-transcriptional control involving viral gene product(s) present in infected cell lysates constituting virus stocks. The vhs1 mutant and possibly other vhs mutants contain a mutation in the gene encoding this function.
Full text
PDF

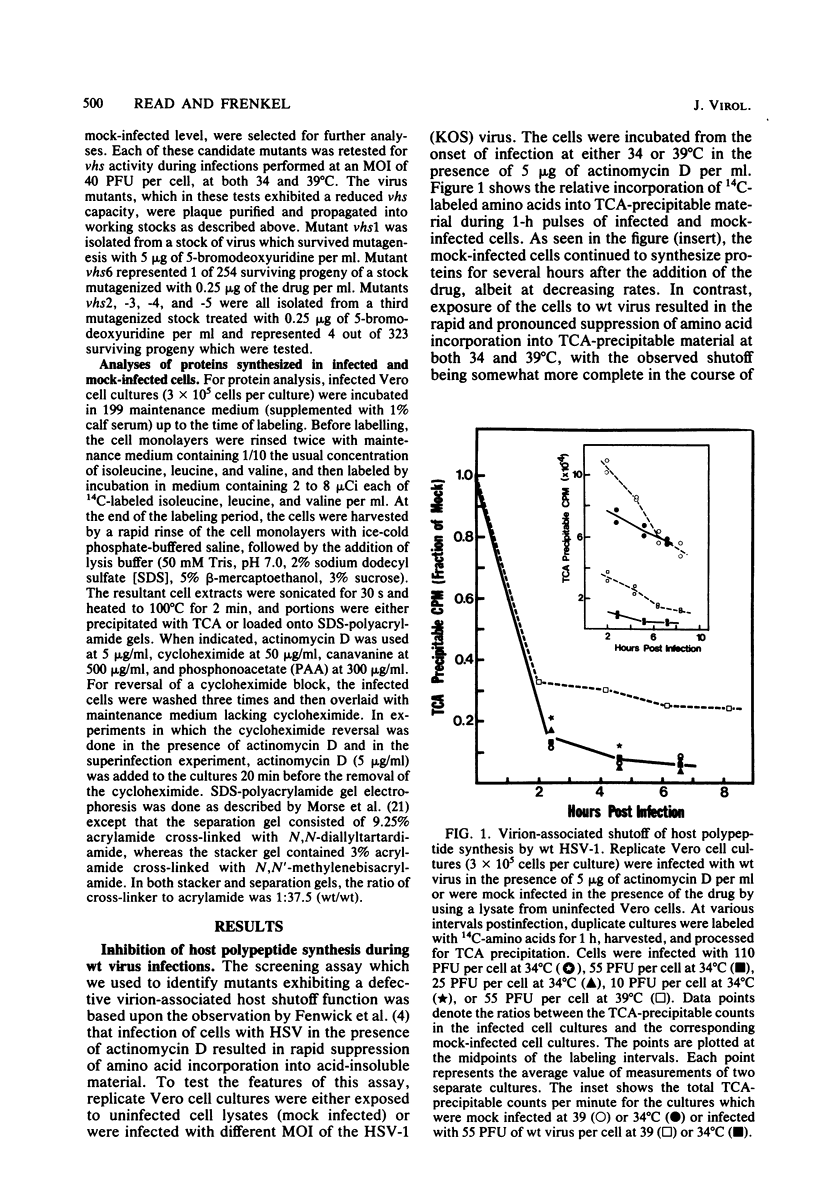
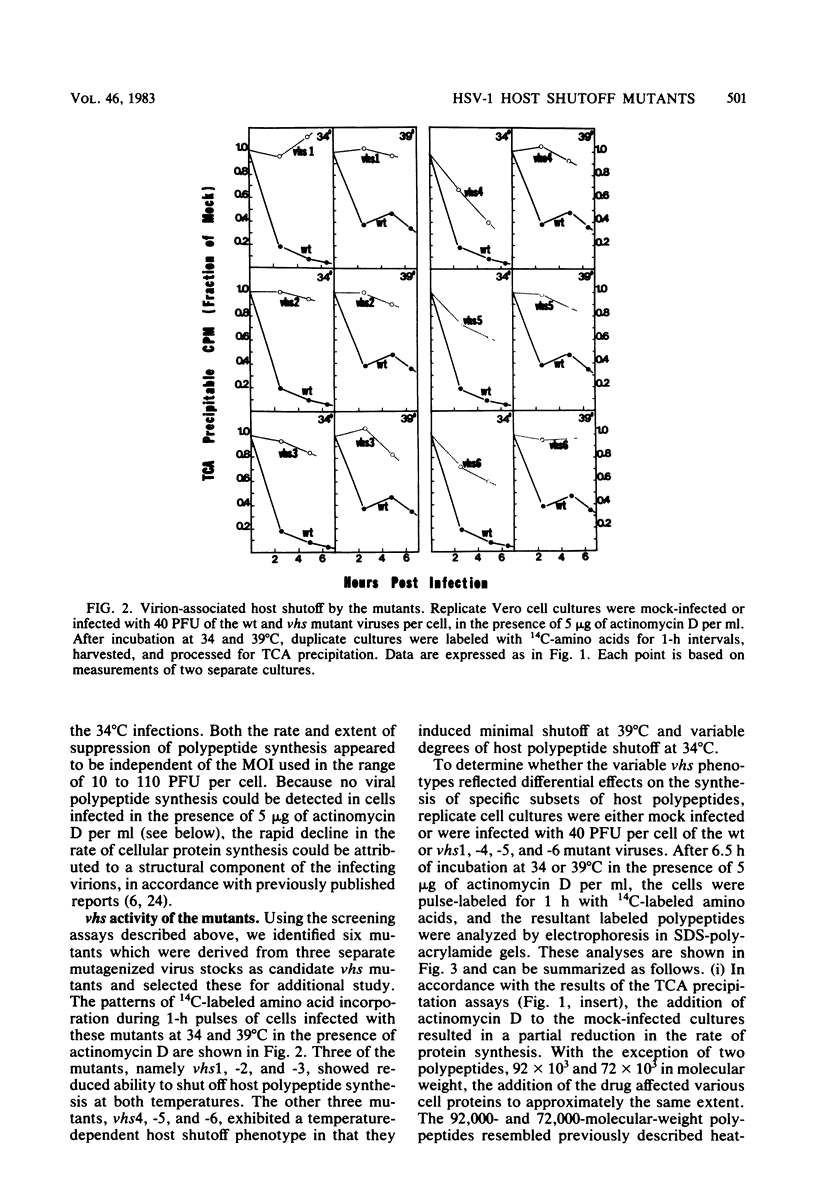



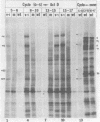
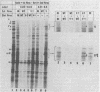
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Phosphorylation of a ribosomal protein and of virus-specific proteins in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):397–405. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Walker M. J. Suppression of the synthesis of cellular macromolecules by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):37–51. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VI. Synthesis and modification of viral polypeptides in enucleated cells. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):720–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.720-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Shipman C., Jr, Wagner E. K. Viral DNA synthesis is required for the efficient expression of specific herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA species. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):10–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA VII. alpha-RNA is homologous to noncontiguous sites in both the L and S components of viral DNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.268-276.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. M., Stevely W. S., Leader D. P. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins in hamster fibroblasts infected with pseudorabies virus or herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.359-366.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: nuclear retention of nontranslated viral RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: transcription-initiation sites and domains of alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7122–7126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E. Mode of inhibition of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase by phosphonoacetate. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5475–5479. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Alterations in the protein synthetic apparatus of Friend erythroleukemia cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus or herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.422-426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Requirement of protein synthesis for the degradation of host mRNA in Friend erythroleukemia cells infected wtih herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):619–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.619-627.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J., Courtney R. J. The synthesis of herpes simplex virus proteins in the absence of virus DNA synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):262–271. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Borman G. S., Rousta M. K. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1374–1375. doi: 10.1038/2061374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S., Engelhardt D. L. Alterations in the protein synthetic apparatus of cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R., Holland L. E., Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Quantitation of herpes simplex virus type 1 RNA in infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):889–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.889-901.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Restricted transcription of the herpes simplex virus genome occurring early after infection and in the presence of metabolic inhibitors. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. Polysomes and protein synthesis in cells infected with a DNA virus. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. The sedimentation profiles of cytoplasmic polyribosomes in mammalian cells productively and abortively infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1968 Mar;34(3):562–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Stevens J. G. Effect of cytosine arabinoside on viral-specific protein synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.71-80.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]