Abstract
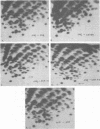
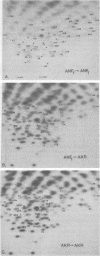
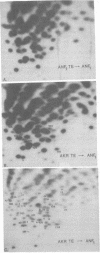
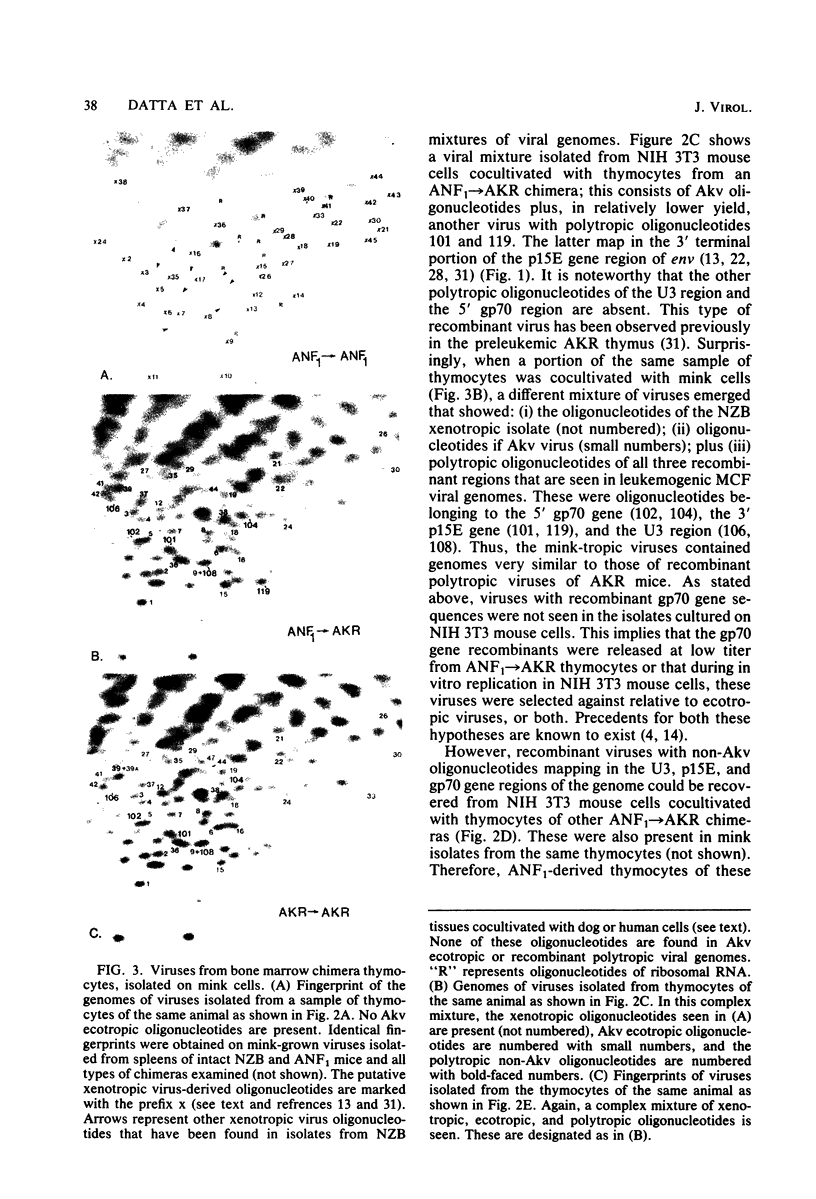
By using T1 oligonucleotide fingerprinting and mapping techniques, we analyzed the genomic structure of retroviruses produced by thymocytes and splenocytes of reciprocal bone marrow-and thymus-grafted chimeras. We found that the genetic factor(s) derived from NZB mice that suppresses the development of thymic leukemia in (AKR X NZB)F1 mice also prevents the formation of recombinant leukemogenic viruses and the expression of preleukemic changes in the (AKR X NZB)F1 thymocytes. The NZB mouse gene or genes appeared to exert this suppressive effect by acting on the thymic reticuloepithelial cells and not on the thymic lymphocytes of (AKR X NZB)F1 hybrids. Prospective studies with thymic epithelial grafts from young mice showed that the AKR thymic epithelium could mediate the formation and expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses and preleukemic changes in thymocytes that lead to the development of thymic leukemia, whereas the (AKR X NZB)F1 thymic epithelium was deficient in this regard. Our results also confirmed a previous observation that during in vivo generation of recombinant leukemogenic viruses, the acquisition of polytropic virus-related sequences in the 3' portion of the p15E gene and the U3 region and in the 5' part of the gp70 gene can occur independently.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Besmer P., Olshevsky U., Baltimore D., Dolberg D., Fan H. Virus-like 30S RNA in mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1168–1176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1168-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank K. J., Pincus T. Evidence that endogenous ecotropic virus is not expressed in AKR thymic lymphoid cells of chimeric hosts. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):458–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Owen F. L., Womack J. E., Riblet R. J. Analysis of recombinant inbred lines derived from "autoimmune" (NZB) and "high leukemia" (C58) strains: independent multigenic systems control B cell hyperactivity, retrovirus expression, and autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1539–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Schwartz R. S. Restricted expression of ecotropic virus by thymocytes of leukemia-resistant (AKR X NZB)F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):329–334. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Waksal S. D., Schwartz R. S. Phenotypic alteration in retroviral gene expression by leukemia-resistant thymocytes differentiating in leukemia-susceptible recipients. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Miller J. F., House W., Allman V. Regeneration of thymus grafts. I. Histological and cytological aspects. Transplantation. 1965 Sep;3(5):639–668. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196509000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., Koehne C. F., O'Donnell P. V. Leukemogenesis by Gross passage A murine leukemia virus: expression of viruses with recombinant env genes in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J. H-2 antigens of the thymus determine lymphocyte specificity. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):766–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Patch V. Genomic masking and rescue of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses: role of pseudotype virions in viral lymphomagenesis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.583-591.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I., Enjuanes L., Lee J. C., Ihle J. N. Resistance of cultures of normal T cells to infection with murine type C viruses. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):483–487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.483-487.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadish J. L., Basch R. S. Hematopoietic thymocyte precursors. I. Assay and kinetics of the appearance of progeny. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1082–1099. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima K., Ikeda H., Stockert E., Takahashi T., Old L. J. Age-related changes in cell surface antigens of preleukemic AKR thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):193–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Crowther R., Straceski A., Haseltine W. Nucleotide sequence of the Akv env gene. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):519–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.519-529.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hering C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Analysis of the genomes of mink cell focus-inducing murine type-C viruses: a progress report. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1269–1274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A., Duran-Reynals M. L., Lilly F. Fv-1 regulation of lymphoma development and of thymic ecotropic and xenotropic MuLV expression in mice of the AKR/J x RF/J cross. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., Old L. J. Leukemogenic properties of AKR dualtropic (MCF) viruses: amplification of murine leukemia virus-related antigens on thymocytes and acceleration of leukemia development in AKR mice. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):548–563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen F. S., Crowther R. L., Tenney D. Y., Reimold A. M., Haseltine W. A. Novel leukaemogenic retroviruses isolated from cell line derived from spontaneous AKR tumour. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):167–170. doi: 10.1038/292167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Quax W., van der Putten H., Berns A. Characterization of AKR murine leukemia virus sequences in AKR mouse substrains and structure of integrated recombinant genomes in tumor tissues. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of Akv-1 and Akv-2 type C viruses of AKR mice. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):690–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.690-694.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W. Status of the association of mink cell focus-forming viruses with leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1265–1268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeves R., Lilly F. Interactions between host and viral genomes in mouse leukemia. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:277–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksal S. D., Cohen I. R., Waksal H. W., Wekerle H., St Pierre R. L., Feldman M. Induction of T-cells differentiation in vitro by thymus epithelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:492–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara K., Hamada K., Seyama T., Imamura N., Yokoro K. In vitro studies of the mechanism of leukemogenesis. II. Characterization of endogenous murine leukemia viruses isolated from AKR thymic epithelial reticulum cell lines. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):360–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.360-366.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Breda M. Lack of AKR ecotropic provirus amplification in AKR leukemic thymuses. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.808-815.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski C. C., Datta S. K., Waksal S. D. Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(1-2):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00344310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski C. C., Waksal S. D., Datta S. K. Thymic epithelium is programmed to induce preleukemic changes in retrovirus expression and thymocyte differentiation in leukemia susceptible mice: studies on bone marrow and thymic chimeras. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):882–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski C. C., Waters D. L., Datta S. K., Waksal S. D. Analysis of intrathymic differentiation patterns during the course of AKR leukemogenesis. Cell Immunol. 1981 Apr;59(2):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]