Abstract
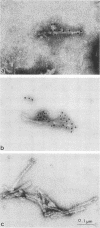
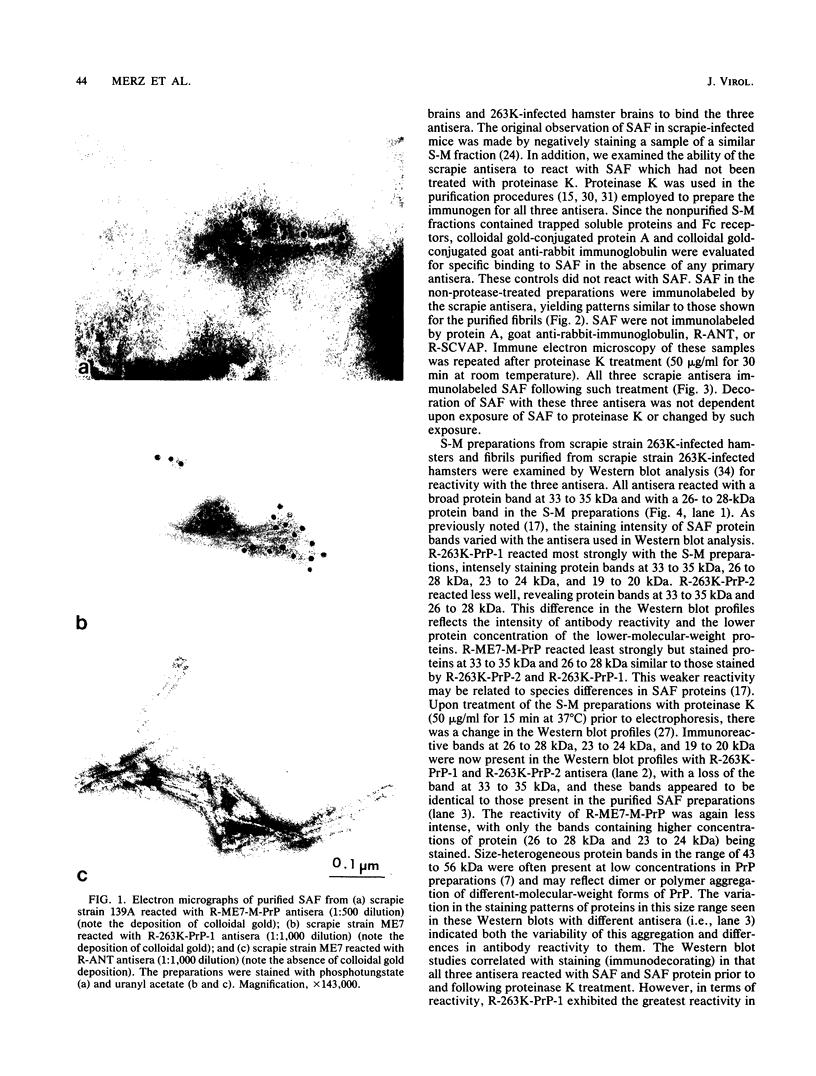
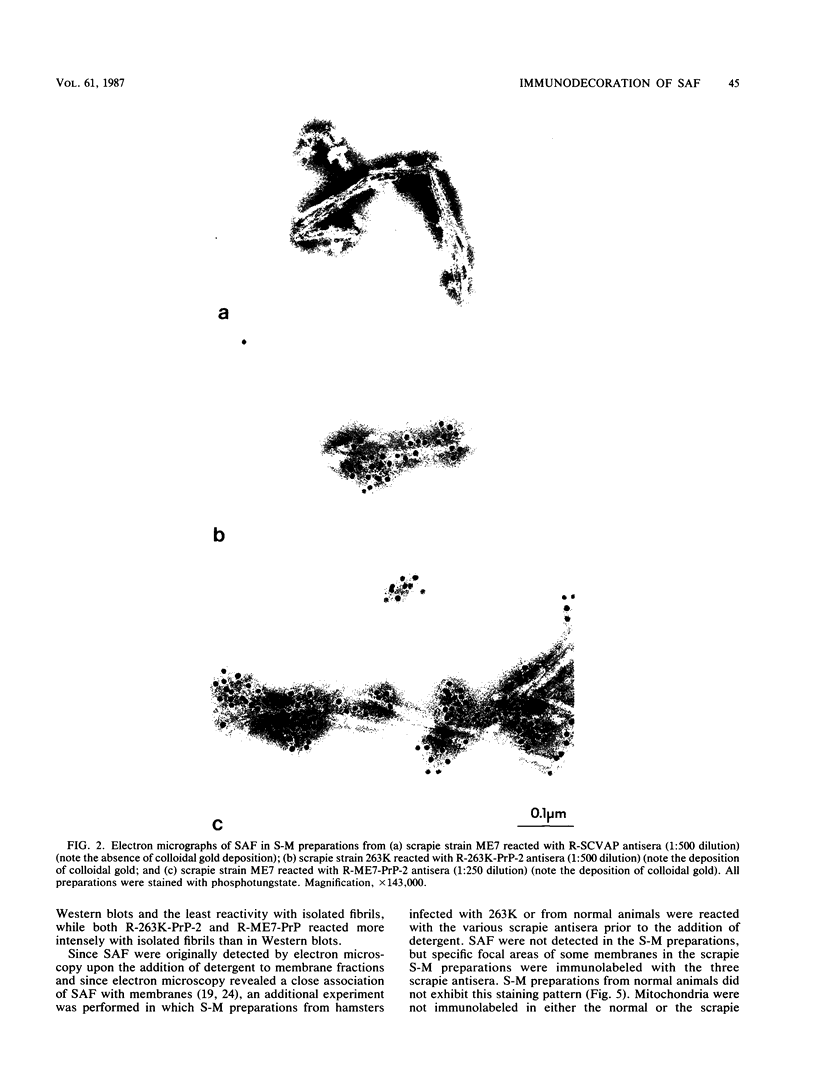
Scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) are an infection-specific structure observed in the unconventional-agent diseases. Polyclonal antisera raised to scrapie proteins were used to test the antigenic relationship between purified fibrils and SAF isolated from non-protease-treated synaptosomal-mitochondrial preparations. The experimental design utilized fibrils from scrapie strain 263K-infected hamsters, scrapie strain 139A-infected mice, and scrapie strain ME7-infected mice. Preparations were examined by negative-stain immune electron microscopy and Western blot analysis of the polypeptides. Fibrils and polypeptides from each preparation reacted with a rabbit antiserum raised to each of the following: hamster 263K prion protein (PrP 27-30), hamster 263K SAF protein, and mouse ME7 SAF protein. Immune electron microscopy and Western blot analysis revealed similar antigenic relationships among the three scrapie antisera. Thus, fibrils and polypeptides can be considered to be the same in each preparation. No reactivity of the fibrils was observed with antisera raised to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles or a synthetic peptide of cerebrovascular amyloid. Thus, the fibrils observed in purified preparations share structural and antigenic similarities plus biochemically related peptides with SAF present in non-protease-treated preparations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. A., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Lewis G. K., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to the scrapie protein decorate prion rods. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Bockman J. M., McKinley M. P., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins share physical properties and antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode L., Pocchiari M., Gelderblom H., Diringer H. Characterization of antisera against scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) from affected hamster and cross-reactivity with SAF from scrapie-affected mice and from patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2471–2478. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Meyer R. K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie PrP 27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):596–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.596-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Callahan S. M. In vitro interaction of scrapie agent and mouse peritoneal macrophages. Intervirology. 1981;16(1):8–13. doi: 10.1159/000149241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Rahn H. C., Bode L. Antibodies to protein of scrapie-associated fibrils. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):345–345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92708-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. J., Jr, Joy A., Heffner R., Franko M., Miyazaki M., Asher D. M., Parisi J. E., Brown P. W., Gajdusek D. C. Clinical and pathological features and laboratory confirmation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a recipient of pituitary-derived human growth hormone. N Engl J Med. 1985 Sep 19;313(12):734–738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198509193131207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer paired helical filaments: immunochemical identification of polypeptides. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;62(4):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00687607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilmert H., Diringer H. A rapid and efficient method to enrich SAF-protein from scrapie brains of hamsters. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Carp R. I., Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Immunological comparison of scrapie-associated fibrils isolated from animals infected with four different scrapie strains. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.676-683.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Biochemical differences among scrapie-associated fibrils support the biological diversity of scrapie agents. J Gen Virol. 1985 Aug;66(Pt 8):1715–1722. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-8-1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P., Hooks J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Altered plasma membranes in experimental scrapie. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;19(2):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00688486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Valley S., Manuelidis E. E. Specific proteins associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie share antigenic and carbohydrate determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4263–4267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Some speculations about prions, amyloid, and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):661–663. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein R., Kascsak R. J., Merz P. A., Papini M. C., Carp R. I., Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M. Detection of scrapie-associated fibril (SAF) proteins using anti-SAF antibody in non-purified tissue preparations. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):671–681. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siakotos A. N., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Traub R. D., Bucana C. Partial purification of the scrapie agent from mouse brain by pressure disruption and zonal centrifugation in sucrose-sodium chloride gradients. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville R. A., Merz P. A., Carp R. I. Partial copurification of scrapie-associated fibrils and scrapie infectivity. Intervirology. 1986;25(1):48–55. doi: 10.1159/000149654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Kozlowski P. B. Evidence for blood-brain barrier changes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;396:119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb26848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]