Abstract
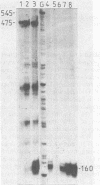
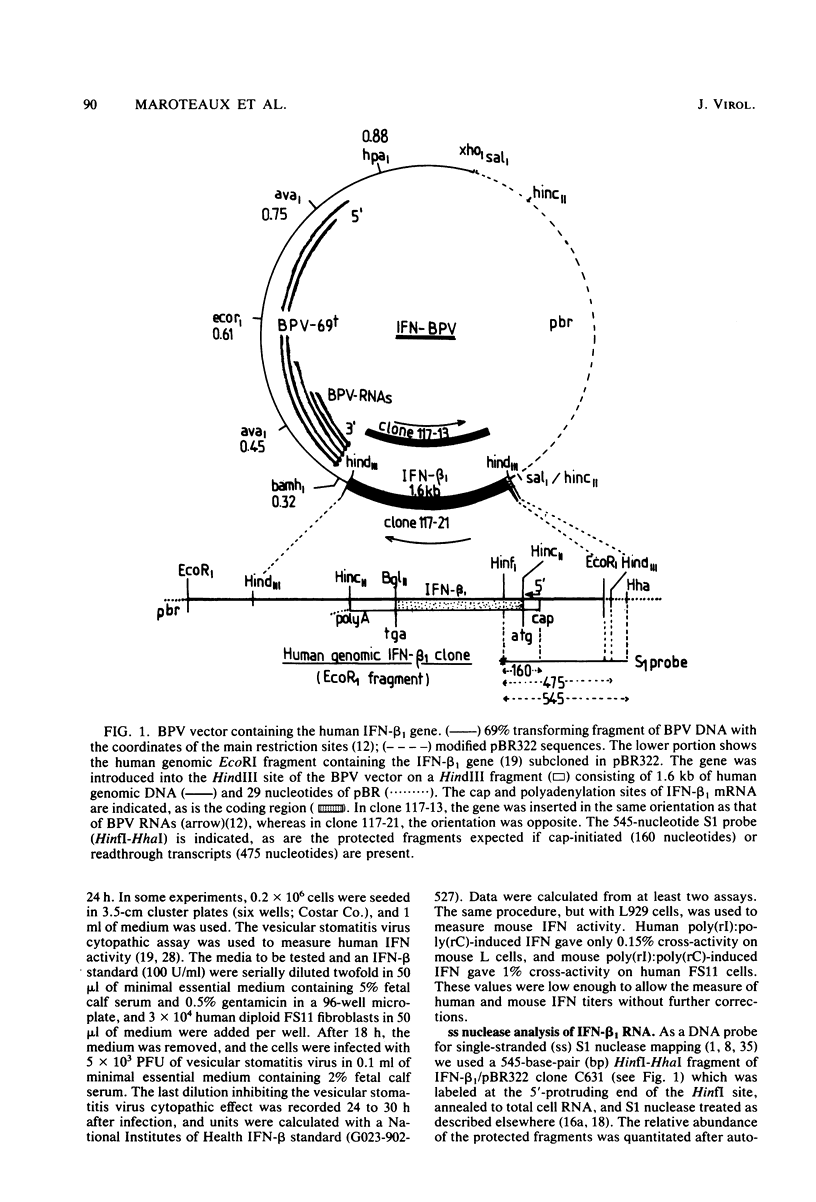
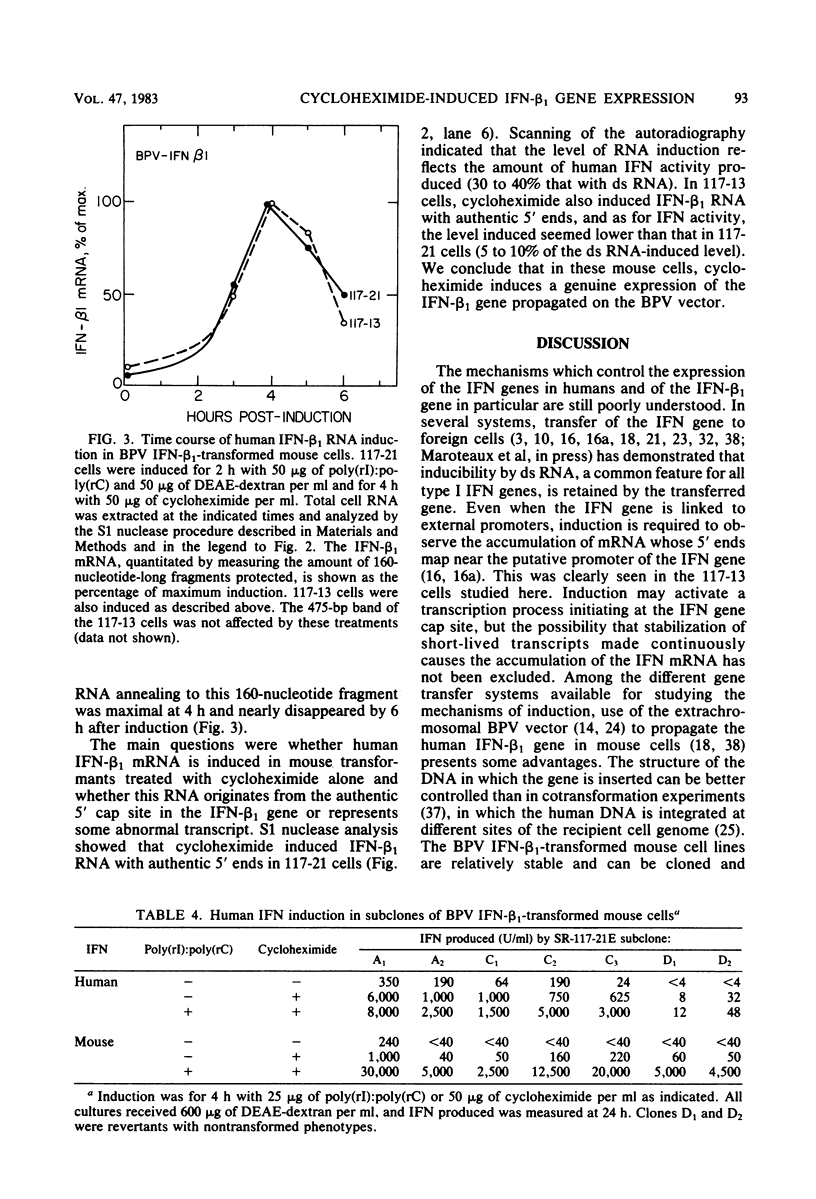
Mouse cells transformed by a bovine papillomavirus recombinant vector containing the human interferon (IFN) beta 1 (IFN-beta 1) gene could be induced to produce human as well as mouse IFNs. The optimal conditions for induction of human IFN and of its mRNA in these transformants resembled those needed for mouse IFN: high concentrations of DEAE-dextran and low concentrations of polyriboinosinic acid-polyribocytidylic acid. Superinduction by inhibitors of protein synthesis which strongly stimulate IFN-beta 1 induction in human cells had only a small effect on human IFN induction in bovine papillomavirus IFN-beta 1-transformed mouse cells. In contrast, cycloheximide without double-stranded RNA could induce significant levels of human IFN in the bovine papillomavirus IFN-beta 1 mouse transformants. After cycloheximide treatment, these cells contained IFN-beta 1 mRNA whose 5' ends originated in the authentic start site of the human IFN-beta 1 gene, as shown by S1 nuclease mapping. The transferred human gene, propagated extrachromosomally in the mouse cells, was, therefore, inducible under conditions different from those in human cells. The results also confirmed that the inhibitor of protein synthesis, cycloheximide, can induce expression of a human IFN gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Berg P. Regulated expression of human interferon beta 1 gene after transduction into cultured mouse and rabbit cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5166–5170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. L., Havell E. A., Vilcek J., Pestka S. Induction and decay of human fibroblast interferon mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4415–4419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Pierard D., Derynck R., De Clercq E., Fiers W. Secretory proteins induced in human fibroblasts under conditions used for the production of interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degrave W., Derynck R., Tavernier J., Haegeman G., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the chromosomal gene for human fibroblast (beta 1) interferon and of the flanking regions. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Cantagalli P., Gagnoni S., Rita G. Effect of DEAE-dextran on production of interferon induced by synthetic double-stranded RNA in L cell cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):708–710. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Mayr U., Bruns W., Grosveld F., Dahl H. M., Collins J. The structure of a thirty-six kilobase region of the human chromosome including the fibroblast interferon gene IFN-beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2495–2507. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Gross G., Bruns W., Hochkeppel H. K., Mayr U., Collins J. Inducibility of human beta-interferon gene in mouse L-cell clones. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):650–654. doi: 10.1038/297650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. A., Engel L., Lowy D. R., Howley P. M. Virus-specific transcription in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):22–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Jackson I. J., Porter A. G., Doel S. M., Catlin G. H., Barber C., Carey N. H. The absence of introns within a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):247–266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Adelman J., Franke A. E., Houck C. M., Gross M., Najarian R., Goeddel D. V. Human fibroblast interferon gene lacks introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantei N., Weissmann C. Controlled transcription of a human alpha-interferon gene introduced into mouse L cells. Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):128–132. doi: 10.1038/297128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L., Kahana C., Mory Y., Groner Y., Revel M. Sequences involved in the regulated expression of the human interferon-beta1 gene in recombinant SV40 DNA vectors replicating in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):325–332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrani-Rosenbaum S., Maroteaux L., Mory Y., Revel M., Howley P. M. Inducible expression of the human interferon beta 1 gene linked to a bovine papilloma virus DNA vector and maintained extrachromosomally in mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):233–240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory Y., Chernajovsky Y., Feinstein S. I., Chen L., Nir U., Weissenbach J., Malpiece Y., Tiollais P., Marks D., Ladner M. Synthesis of human interferon beta 1 in Escherichia coli infected by a lambda phage recombinant containing a human genomic fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Inducer-responsive expression of the cloned human interferon beta 1 gene introduced into cultured mouse cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):967–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Taniguchi T. Structure of a chromosomal gene for human interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Gavis E. R., Buchan A., Raj N. B., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Expression of human beta-interferon cDNA under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter from herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):598–601. doi: 10.1038/297598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Gruss P., Law M. F., Khoury G., Howley P. M. Bovine papilloma virus deoxyribonucleic acid: a novel eucaryotic cloning vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;1(6):486–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scangos G., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms and applications of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells - a review. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Lyles D. S., Tamm I. Superinduction of human fibroblast interferon production: further evidence for increased stability of interferon mRNA. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):186–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D. Heterogeneity of poly(I) x poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon mRNA species. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):95–97. doi: 10.1038/288095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Armstrong J. A., Ke Y. H., Ho M. Regulation of cellular interferon production: enhancement by antimetabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):464–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Berthold W. A mechanism for the induction and regulation of human fibroblastoid interferon genetic expression. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):401–411. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Tan C., Berthold W. Genetic control of the interferon system. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Gheysen D., Duerinck F., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W. Deletion mapping of the inducible promoter of human IFN-beta gene. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):634–636. doi: 10.1038/301634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapman J. A systematic study of interferon production by mouse L-929 cells induced with poly(I).poly(C) and DEAE-dextran. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Ng M. H. Post-transcriptional control of interferon synthesis. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):588–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.588-594.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Mellon P., Ptashne M., Maniatis T. Regulated expression of an extrachromosomal human beta-interferon gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]