Noncovalent synthetic strategies, in contrast to most covalent strategies, allow for the spontaneous, selective formation of highly-stable and complex supramolecular structures with specific architectures and properties through the dynamic self-assembly of reversible yet strong linkages1. The majority of known supramolecular structures to date, however, have been prepared using a single recognition motif, with those examples that do utilize multiple binding algorithms being restricted to multistep processes2 or limited to functionalized polymers or crystal engineering3. Biological systems, by contrast, commonly exhibit multifunctionality wherein they possess many recognition motifs in their structure and function.4 Similar, purely synthetic multifunctional systems may also be designed by employing orthogonal, i.e. non-interacting and self-consistent, supramolecular recognition motifs in which a variety of noncovalent interactions allow for multiple complementary components to self-assemble into supramolecular species with complex functional architectures. Yet emulating nature’s use of multicomponent, orthogonal assembly poses considerable challenges.
Many nondirectional interactions – e.g. hydrogen-bonding, electrostatic forces, donor-acceptor, van der Waals forces, and other weak interactions – contribute to biological self-assembly. Synthetic chemists have also used such interactions in the construction of intricate supramolecular architectures such as rotaxanes and pseudorotaxanes5. Compared to these weak noncovalent interactions, metal coordination allows for the formation of stronger, directional metal–ligand dative bonds that play an essential role in the construction of polygons and polyhedra with well-defined shapes and considerable stability6. By utilizing the non-interfering orthogonal nature of these two types of interactions – weak and strong – novel supramolecular species have been obtained from specifically designed precursors via multiple noncovalent interactions in one simple step3. This important, multipronged method of construction has been little explored in the self-assembly of discrete nanoscopic supramolecular arrays, especially for those with predetermined shapes, geometries, and symmetries7.
We have demonstrated that planar hexagonal structures can be self-assembled by combining three 120° pyridyl donor building blocks and three 120° di-platinum acceptors6a Furthermore, the addition of functional groups at the vertex of individual building units, even with high generation dendrons, does not hinder their self-assembly8. Encouraged by the fact that macrocyclic polyethers are able to complex dialkylammonium ions (R2NH2+) to form rotaxanes and pseudorotaxanes9, which have been studied extensively, we envisioned that by attaching a dibenzo-24-crown-8 (DB24C8) macrocycle on the periphery of a 120° donor building block it will, when combined with a complementary 120° di-platinum acceptor, provide access to tris-DB24C8 derivatives. Such functionalized metallacyclic hexagons may then host dialkylammonium ions to provide, in a stepwise fashion, discrete supramolecular architectures employing multiple noncovalent interactions. This new type of cavity-cored tris[2]pseudorotaxane may also be readily generated in one concerted step simply by combining the donor, acceptor, and ammonium building blocks, thereby demonstrating the power of orthogonal self-assembly.
The 120° donor precursor 1, with both crown ether and pyridine binding sites, can be easily prepared via an etherification reaction of chloromethyl-DB24C8 and 3,5-bis-pyridin-4-ylethynl-phenol (Scheme S1). Stirring the mixture of 1 (3.08 mM) and 120° di-Pt(II) acceptor 2 or 3 in a 1:1 ratio in CD2C12 at 298 K for 30 minutes resulted in the formation of [3+3] hexagons with pendant DB24C8s at alternate vertexes (step I, Figure 1). Multinuclear NMR (1H and 31P) analysis of the reaction mixtures revealed the formation of discrete, highly symmetric species. The 31P {1H} NMR spectrum of hexagon 5, for example, displayed a sharp singlet (ca. 13.7 ppm) shifted upfield from the starting platinum acceptor 2 by approximately 3.6 ppm. Additionally, the protons of the pyridine rings exhibited downfield shifts (α-Hpy, 0.12 ppm; β-Hpy, 0.45 ppm) resulting from loss of electron density upon coordination of the pyridine-N atom with the Pt (II) metal center (Figure 2C).
Figure 1.
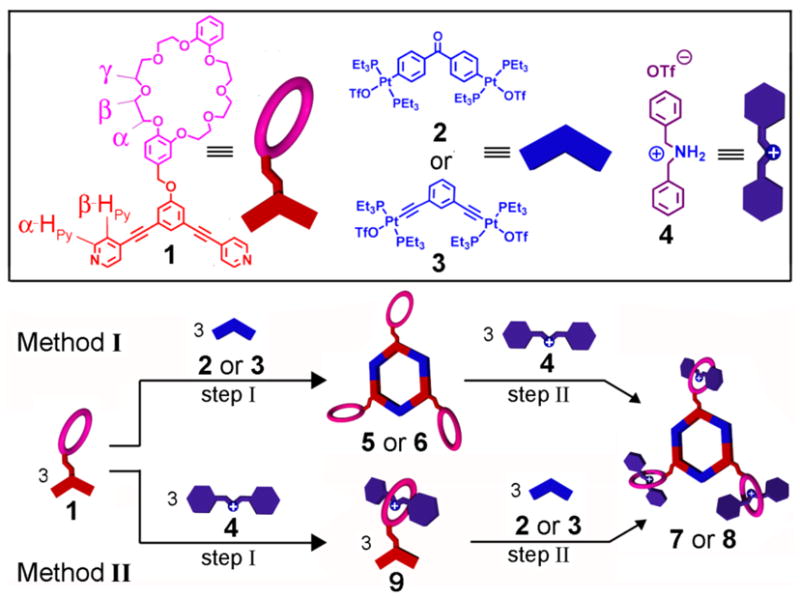
Molecular structures of 1 – 4, as well as a graphical representation of the self-assembly of hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivatives 5 and 6 (Method I, step I), pseudorotaxane 9 (Method II, step I), and tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8 (Methods I and II, step n).
Figure 2.
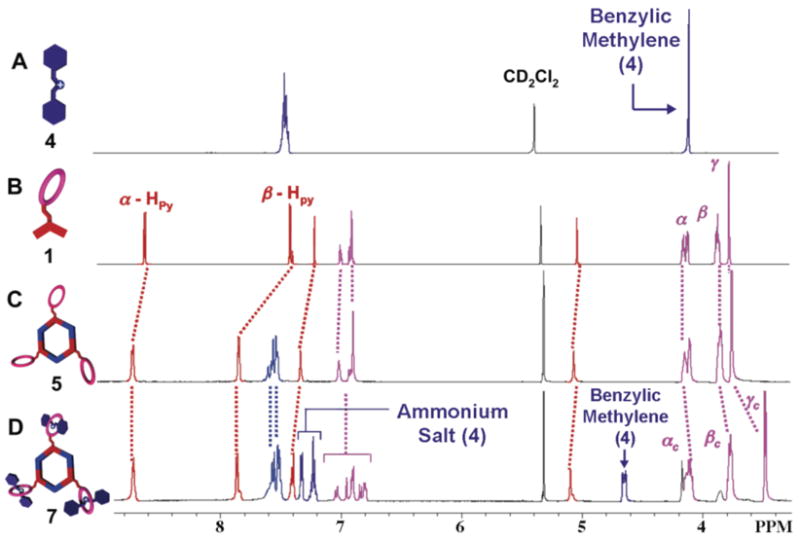
Partial 1HNMR spectra recorded at 500 MHz (CD2C12,298 K) of (A) dibenzylammonium 4, (B) precursor 1, (C) hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivative 5, and (D) tris[2]pseudorotaxane 7 (>95%), along with some signals for partially complexed, and uncomplexed species at equilibrium.
ESI-TOF mass spectrometry provides further evidence for the formation of new hexagonal assemblies. In the mass spectrum of 5, for example, peaks at m/z = 2995.89, m/z = 1423.47, and m/z = 1108.99, corresponding to [M – 2 OTf]2+, [M – 4 OTf]4+, and [M – 5 OXf]5+ respectively were observed and their isotopic resolutions are in excellent agreement with the theoretical distributions (Figure 3). The collective analytical results indicate that the tris-DB24C8 derivative can be easily prepared (>95% yields) through coordination-driven self-assembly, which avoids the time-consuming procedures and lower yields often encountered in covalent synthetic protocols.
Figure 3.
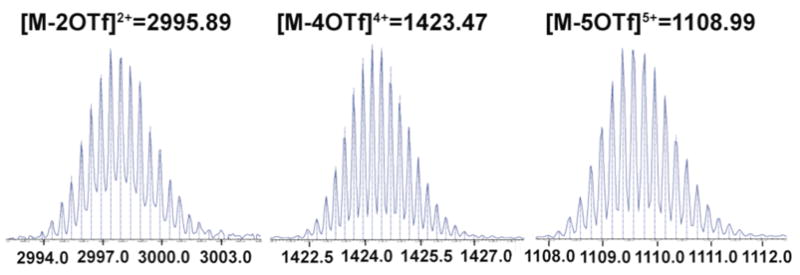
ESI-TOF-MS spectra of hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivative 5 (Vertical lines are the theoretical abundances).
Subsequent investigations into self-assembling hexagonal cavity-cored tris[2]pesudorotaxanes 7 and 8 were undertaken by adding three equiv of dibenzylammonium Inflate salt 4 to the CD2C12 solution of hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivatives 5 and 6 (1.44 mM for 5, 1.15 mM for 6), respectively (Method I, step II, Figure 1). Within ten minutes a pale yellow solution was obtained. Compared to the hexagonal assemblies 5 and 6, the 31P {1H} NMR spectra of new species 7 and 8 do not show any significant change, indicating that the incorporation of dibenzylammonium ions does not substantially change the chemical environment of the phosphorus atoms. The 1H NMR spectra of 7 and 8, however, exhibited characteristic shifts9 associated with the complexation of 4 by DB24C8. For example, in the 1H NMR spectrum of 7, a 0.45 ppm downfield shift of the signal for the benzylic methylene protons adjacent to the NH2+ center was observed. Moreover, the protons Hα, Hβ, and Hγ of DB24C8 exhibited upfield shifts of 0.03, 0.08, and 0.28 ppm, respectively (Figure 2D). In addition, the structures of hexagonal cavity-cored tris[2]pesudorotaxanes have also been confirmed by ESI mass spectrometry. In the ESI mass spectra of 7 and 8, peaks attributable to [M – 4 OTf]4+ for 7 (m/z =1684.6) and [M – 5 OTf]5+for 8 (m/z =1284.3),respectively, were found. These peaks were isotopically resolved and they agree very well with the theoretical distribution (Figure 4). Further characterization with two-dimensional spectroscopic techniques (1H-1H COSY and NOESY) are in agreement with the formation of the hexagonal cavity-cored tris[2]pseudorotaxane (See Supporting Information). It is important to note how 1H NMR spectroscopic results reveal the orthogonality of self-assembly in this stepwise approach to 7 and 8: only those signals associated with the pyridyl functionalities of 1 shift upon metal coordination while only those signals associated with DB24C8 shift upon complexation of 4.
Figure 4.
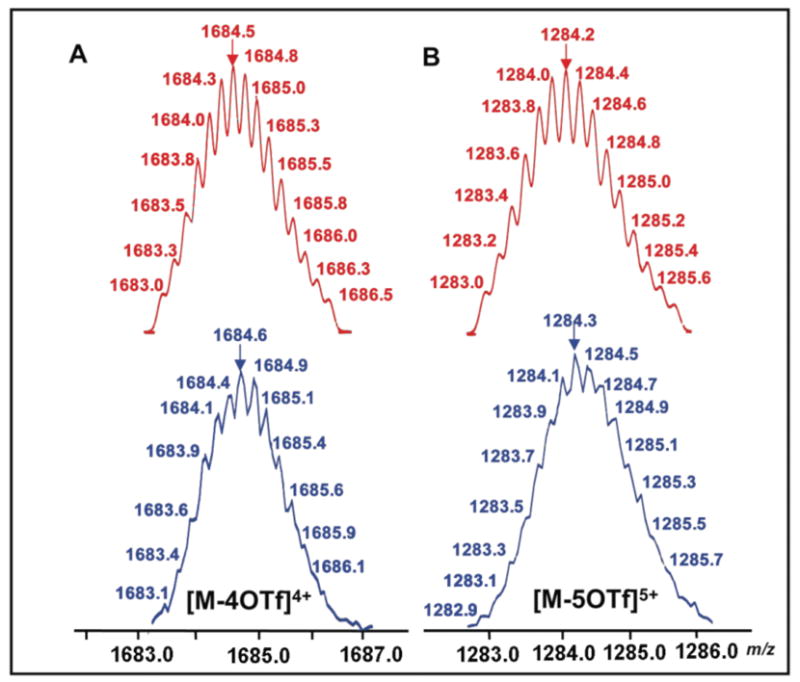
Calculated (top) and experimental (bottom) ESI-MS spectra of tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 (A) and 8 (B).
The host:guest stoichiometry for supramolecular assemblies 7 and 8 was established by using the nonlinear leastsquares fit method10 based on the 1H NMR deration experiments (Figure 5, see also Supporting Information). Results for both hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivatives (5 and 6) indicate a 1:3 stoichiometry with relation to the dibenzylammonium guests, providing further support for the formation of tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8. Furthermore, thermodynamic binding constants were obtained through the titration experiments. Fitting the data to a 1:3 binding mode gave rise to the association constants: Ks.1 = (1.06 ± 0.15) × 104M−1, Ks.2 = (6.38 ± 0.10) × 103M−1, and Ks.3 = (4.16 ± 0.56) × 103M−1 for 7, and Ks.1 = (1.90 ± 0.28) × 104M−1, Ks.2 = (6.38 ± 0.34) × 103M−1, and Ks., = (1.76 ± 0.16) × 103M−1 for 8. These values suggest that both hexacationic tris-DB24C8 hosts (5 and 6) have a similar ability to bind dibenzylammonium guest(s) as does DB24C8 in non-polar solvent like dichloromethane.9a
Figure 5.
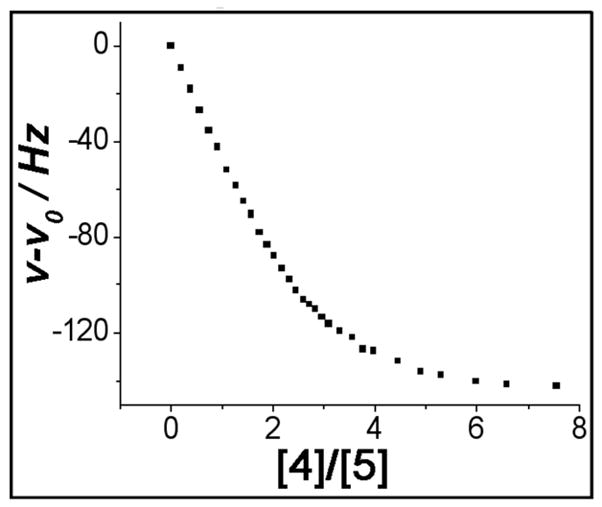
The 1H NMR titration isotherm of tris[2]pseudorotaxane 8 recorded at 500 MHz in CD2C12 at 298 K (▪ indicates the change in chemical shift of the proton signal corresponding to the γ-H of the crown ether).
Hexagonal cavity-cored tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8 can also be obtained via an alternative stepwise approach (Method II, Figure 1) wherein the order of orthogonal self-assembly steps is reversed. Stirring a 1:1 mixture of donor precursor 1 and ammonium salt 4 in CD2C12 afforded pseudorotaxane 9 (Method II, step 1). The addition of 1.0 equiv of 120° di-platinum acceptor 2 or 3 resulted (Method II, step 2) in the formation of tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8, respectively. Multinuclear NMR (1H and 31P) analysis of the reaction mixtures revealed the same characteristics as those observed in the spectra of 7 and 8 prepared stepwise by Method I, confirming the formation of the same species by this alternative stepwise procedure. The power of this orthogonal approach is perhaps best demonstrated by yet a third method of assembly. Simply mixing a 1:1:1 ratio of the three different components (Method III, Figure 6) also gives tris[2]pseudorotaxane 7 and 8, whose structures were confirmed by multinuclear NMR (1H and 31P) analysis11 In this process of construction, nine subunits are brought together to spontaneously form discrete, highly symmetric species as directed by multiple noncovalent interactions. These results demonstrate a number of ways that multiple complementary building blocks exhibiting a variety of orthogonal noncovalent molecular recognition motifs are able to self-assemble into discrete structures according to the specific information encoded within the individual components, a synthetic analogue to similar processes that have been investigated extensively in biological systems.4
Figure 6.
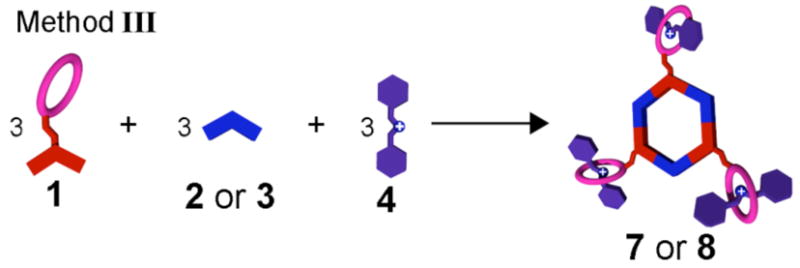
Schematic representation of the one-pot self-assembly of tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8 by using Method III.
Molecular force-field simulations were used to gain further insight into the structural characteristics of hexagonal hosts 5 and 6 and cavity-cored tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8.12 A 1.0 ns molecular dynamics simulation (MMFF force field) was used to equilibrate supramolecules 5–8, followed by energy minimization of the resulting structures to full convergence. The modeled structure of tris[2]pseudorotaxane 8, for example, is shown in Figure 7 (for compounds 5–7 see Supporting Information). Simulations revealed very similar planar hexagonal structures for each supramolecule. The addition of dibenzylammonium to tris-DB24C8 hosts 5 and 6 does not disrupt the underlying hexagonal scaffolds as ammonium salts are complexed by their pendant DB24C8 macrocycles, further illustrating the orthogonality of the interactions involved during self-assembly. Simulations reveal internal diameters of 3.2 and 2.9 nm for 7 and 8, respectively (See Supporting Information).
Figure 7.
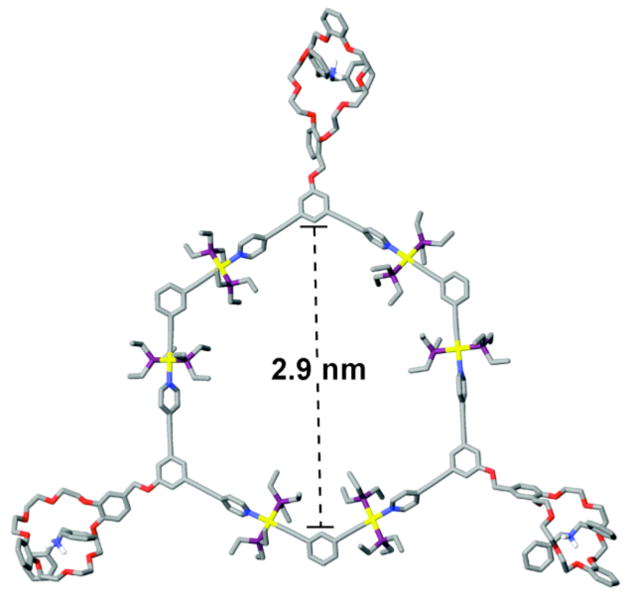
Simulated molecular model of tris[2]pseudorotaxane 8 optimized with the MMFF force-field. Color scheme: C = gray, O = red, N = blue, P = purple, Pt = yellow, and R2NH2+ hydrogen atoms = white, all other hydrogen atoms have been removed for clarity.
Herein, we have combined coordination-driven self-assembly with the crown ether-dialkylammonium binding motif to generate novel tris[2]pseudorotaxanes in which the molecular structures incorporate a discrete hexagonal cavity as their main scaffold and pendant pseudorotaxanes at alternate vertexes. During self-assembly, both hydrogen bonding and metal coordination simultaneously play essential roles. This methodology demonstrates that novel artificial supramolecular architectures can be synthesized from several different components via multiple, orthogonal noncovalent interactions in one simple self-assembly step. We are currently extending this strategy to combine coordination-driven self-assembly with other noncovalent assembly methodologies to further explore its application to the construction of multifunctional supramolecular architectures.
Supplementary Material
Synthesis and analytic data of 1, hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivatives 5 and 6, and tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8, experimental data for Job plot and 1H NMR titration experiments, and computational procedures and structures for 5, 6 and 7 obtained from modeling. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Acknowledgments
P.J.S. thanks the NIH (GM-057052) and the NSF (CHE-0306720) for financial support. B.H.N. thanks the NIH (GM-080820) for financial support. We thank Prof. Mei-Xiang Wang and Dr. Han-Yuan Gong for their help with the calculation of thermodynamic binding constants. D.C.M. and M.M.L thank NCSU Chemistry for generous financial support.
References
- 1.(a) Lehn JM. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1990;29:1304–1319. [Google Scholar]; (b) Philip D, Stoddart JF. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 1996;35:1155–1196. [Google Scholar]; (c) Whitesides GM, Grzybowski B. Science. 2002;295:2418–2421. doi: 10.1126/science.1070821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lehn JM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:4763–4768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.072065599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Hori A, Yamashita KI, Fujita M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2004;43:5016–5019. doi: 10.1002/anie.200460671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bassani DM, Lehn JM, Serroni S, Puntoriero F, Campagna S. Chem Eur J. 2003;9:5936–5946. doi: 10.1002/chem.200305441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Uppadine LH, Lehn JM. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2004;43:240–243. doi: 10.1002/anie.200352937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Uppadine LH, Gisselbrecht JP, Kyritsakas N, Nattinen K, Rissanen K, Lehn JM. Chem Eur J. 2005;11:2549–2565. doi: 10.1002/chem.200401224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Pollino JM, Stubbs LP, Week M. Polym Prepr. 2003;44:730–731. [Google Scholar]; (b) Pollino JM, Stubbs LP, Week M. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:563–567. doi: 10.1021/ja0372715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Hofineier H, El-ghayoury A, Schenning APHJ, Schubert US. Chem Commun. 2004:318–319. doi: 10.1039/b314459n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Hofineier H, Hoogenboom R, Wouters MEL, Schubert US. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:2913–2921. doi: 10.1021/ja042919e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kushner DJ. Bacterial Rev. 1969;33:302–345. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.302-345.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Sauvage J-P, Dietrich-Buchecker C, editors. Molecular Catenanes, Rotaxanes and Knots. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim, Germany: 1999. [Google Scholar]; (b) Raymo FM, Stoddart JF. Chem Rev. 1999;99:1643–1663. doi: 10.1021/cr970081q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Balzani V, Credi A, Raymo FM, Stoddart JF. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2000;39:3348–3391. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20001002)39:19<3348::aid-anie3348>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Collin JP, Dietrich-Buchecker C, Gaviòa P, Jimenez-Molero MC, Sauvage JP. Ace Chem Res. 2001;34:477–487. doi: 10.1021/ar0001766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Schalley CA, Beizai K, Vögtle F. Ace Chem Res. 2001;34:465–476. doi: 10.1021/ar000179i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Badjiæ JD, Balzani V, Credi A, Silvi S, Stoddart JF. Science. 2004;303:1845–1849. doi: 10.1126/science.1094791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Zhu XZ, Chen CF. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:13158–13159. doi: 10.1021/ja0546020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Huang F, Nagvekar DS, Slebodnick C, Gibson HW. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:484–485. doi: 10.1021/ja0438516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.(a) Stang PJ, Olenyuk B. Ace Chem Res. 1997;30:502–518. [Google Scholar]; (b) Leininger S, Olenyuk B, Stang PJ. Chem Rev. 2000;100:853–908. doi: 10.1021/cr9601324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Seidel SR, Stang PJ. Ace Chem Res. 2002;35:972–983. doi: 10.1021/ar010142d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Schwab PFH, Levin MD, Michl J. Chem Rev. 1999;99:1863–1934. doi: 10.1021/cr970070x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Holliday BJ, Mirkin CA. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:2022–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Cotton FA, Lin C, Murillo CA. Ace Chem Res. 2001;34:759–711. doi: 10.1021/ar010062+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Fujita M, Tominaga M, Hori A, Therrien B. Ace Chem Res. 2005;38:369–378. doi: 10.1021/ar040153h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Fiedler D, Leung DH, Bergman RG, Raymond KN. Ace Chem Res. 2005;38:349–360. doi: 10.1021/ar040152p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.(a) Gianneschi NC, Tiekink ERT, Rendina LM. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:8474–8479. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kim D, Paek JH, Jun MJ, Lee JY, Kang SO, Ko J. Inorg Chem. 2005;44:7886–7894. doi: 10.1021/ic0508369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Petitjean A, Kyritsakas N, Lehn JM. Chem Commun. 2004;24:1168–1169. [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Yang HB, Das N, Huang F, Hawkridge AM, Muddiman DC, Stang PJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:10014–10015. doi: 10.1021/ja063377z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Yang HB, Hawkridge AM, Huang SD, Das N, Bunge SD, Muddiman DC, Stang PJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:2120–2129. doi: 10.1021/ja066804h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Ashton PR, Campbell PJ, Chrystal EJT, Glink PT, Menzer S, Philip D, Spencer N, Stoddart JF, Tasker PA, Williams DJ. Angew Chemjnt Ed. 1995;34:1865–1869. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ashton PR, Campbell PJ, Chrystal EJT, Glink PT, Menzer S, Philip D, Spencer N, Stoddart JF, Tasker PA, Williams DJ. Angew Chemjnt Ed. 1995;34:1869–1871. [Google Scholar]; (c) Aricó F, Badjiæ JD, Cantrill SJ, Flood AH, Leung KCF, Liu Y, Stoddart JF. Top Curr Chem. 2005;279:203–259. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bourson J, Pouget J, Valeur B. J Phys Chem. 1993;97:4552–4557. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Upon stirring at 298 K for approximate 48 h, the 1H NMR of assemblies 7 and 8 do not show any significant change, demonstrating the stability of these novel supramolecular assemblies.
- 12.All attempts to grow X-ray quality single crystals of hexagonal hosts (5 and 6) and hexagonal cavity-cored tris[2]pseudorotaxanes (7 and 8) have so far proven unsuccessful.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Synthesis and analytic data of 1, hexagonal tris-DB24C8 derivatives 5 and 6, and tris[2]pseudorotaxanes 7 and 8, experimental data for Job plot and 1H NMR titration experiments, and computational procedures and structures for 5, 6 and 7 obtained from modeling. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.


