Abstract
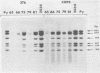
We constructed a series of deleted polyoma genomes by Bal 31 nuclease digestion from the unique Bg/I site at nucleotide 86 on the "early" side of the origin of DNA replication. The ability of the cloned deleted genomes to replicate was tested after transfection into mouse 3T6 fibroblasts or into the polyomatransformed C127 (COP5) mouse cell line (Tyndall et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 9:6231-6251, 1981). Deletions up to nucleotide 64-had no effect on the amount of replicated DNA accumulated, but larger deletions, extending up to nucleotide 42, decreased this amount 7- to 10-fold. By nucleotide 38, the quantity of detected DNA was down 100-fold, and by nucleotide 20, no replication could be detected. The minimum origin segment does not contain any known high-affinity, large tumor antigen binding site.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Landers T., Goff S. P., Manteuil-Brutlag S., Berg P. Physical and genetic characterization of deletion mutants of simian virus 40 constructed in vitro. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):277–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.277-294.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Cold-sensitive regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke B., Eckhart W. Polyoma gene function required for viral DNA synthesis. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Frisque R. J., Sambrook J. Origin-defective mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):293–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Sambrook J. F., Frisque R. J. Expression of early genes of origin-defective mutants of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutai M. W., Nathans D. Evolutionary variants of simian virus 40: Nucleotide sequence of a conserved SV40 DNA segment containing the origin of viral DNA replication as an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90362-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication in vivo: location and structure of 5' ends of DNA synthesized in the ori region. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):767–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M. Deletions of N-terminal sequences of polyoma virus T-antigens reduce but do not abolish transformation of rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Nilsson M. G., Magnusson G. Non-contiguous segments of the polyoma genome required in cis for DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):533–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Kleinberger T., Livingston D. M. Mapping of SV40 DNA replication origin region binding sites for the SV40 T antigen by protection against exonuclease III digestion. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Shenk T. Definition of the boundaries of the origin of DNA replication in simian virus 40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3635–3642. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]