Abstract
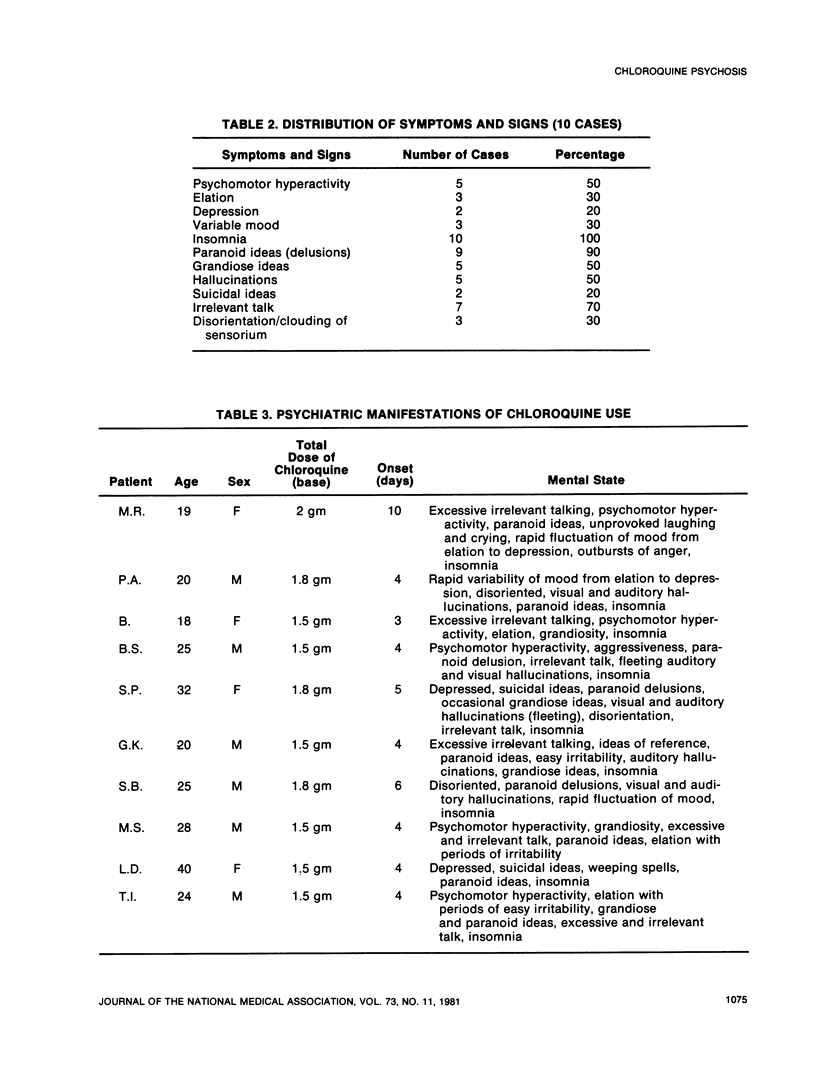
Psychotic states are mimicked by the use of many drugs including amphetamines, cannabis, lysergic acid diethylamide, psilocybin, mescaline, isoniazid, and L-dopa. A paranoid psychotic picture in a clear sensorium is characteristic of amphetamine psychosis. In developing countries, malaria among other diseases is a frequent indicator of chloroquine administration. The present communication reports a series of chloroquine-induced psychosis in a clear sensorium simulating affective illness, such as mania, mixed affective states, or depression. The psychosis disappeared after cessation of the drug, combined with or without the use of low dosage phenothiazines in excited patients. From our cases, two types of presentation of chloroquine psychosis could be seen: (1) psychic with clear sensorium, mood changes, alteration in motor activity, delusions, and hallucinations; and (2) psycho-organic with clouded sensorium, disorientation, and fleeting hallucinations. The precise nature of the mechanism of the psychosis is not clear because of the limited number of reported cases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving A. S., Eichelberger L., Craige B., Jones R., Whorton C. M., Pullman T. N. STUDIES ON THE CHRONIC TOXICITY OF CHLOROQUINE (SN-7618). J Clin Invest. 1948 May;27(3 Pt 2):60–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI101974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURRELL Z. L., Jr, MARTINEZ A. C. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. N Engl J Med. 1958 Apr 17;258(16):798–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195804172581608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes D. B. Chloroquine psychosis. Br Med J. 1966 Apr 16;1(5493):983–983. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5493.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANN H. M., VERHULST H. L. Fatal acute chloroquine poisoning in children. Pediatrics. 1961 Jan;27:95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantin B., Charmot G. Intoxications volontaires par la chloroquine. A propos de 20 observations. Therapie. 1966 Mar-Apr;21(2):387–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS E. L. Systemic lupus erythematosus: recent advances in its diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1956 Aug;45(2):163–184. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-45-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. I., Shader R. I. Behavioral toxicity and equivocal suicide associated with chloroquine and its derivatives. Am J Psychiatry. 1977 Jul;134(7):798–601. doi: 10.1176/ajp.134.7.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIEL F. W. CHLOROQUINE SUICIDE. JAMA. 1964 Oct 26;190:398–400. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070170139030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. M. Chloroquine psychosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(4):549–549. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(69)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSTAKALLIO K. K., PUTKONEN T., PIHKANEN T. A. Chloroquine psychosis? Lancet. 1962 Dec 29;2(7270):1387–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEFF L. DRUG REACTIONS IN ADOLESCENCE. GP. 1964 Jan;29:112–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAB S. M. Two cases of chloroquine psychosis. Br Med J. 1963 May 11;1(5340):1275–1275. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5340.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN M., BERNSTEIN H. N., ZVAIFLER N. J. STUDIES ON THE PHARMACOLOGY OF CHLOROQUINE. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHLOROQUINE RETINOPATHY. Arch Ophthalmol. 1963 Oct;70:474–481. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1963.00960050476009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPP O. L., 3rd TOXIC PSYCHOSIS DUE TO QUINARCRINE AND CHLOROQUINE. JAMA. 1964 Feb 1;187:373–375. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060180059026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermeyer J. A comparison of amok and other homicide in Laos. Am J Psychiatry. 1972 Dec;129(6):703–709. doi: 10.1176/ajp.129.6.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



