Abstract
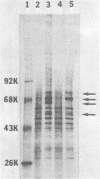
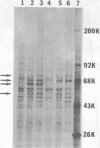
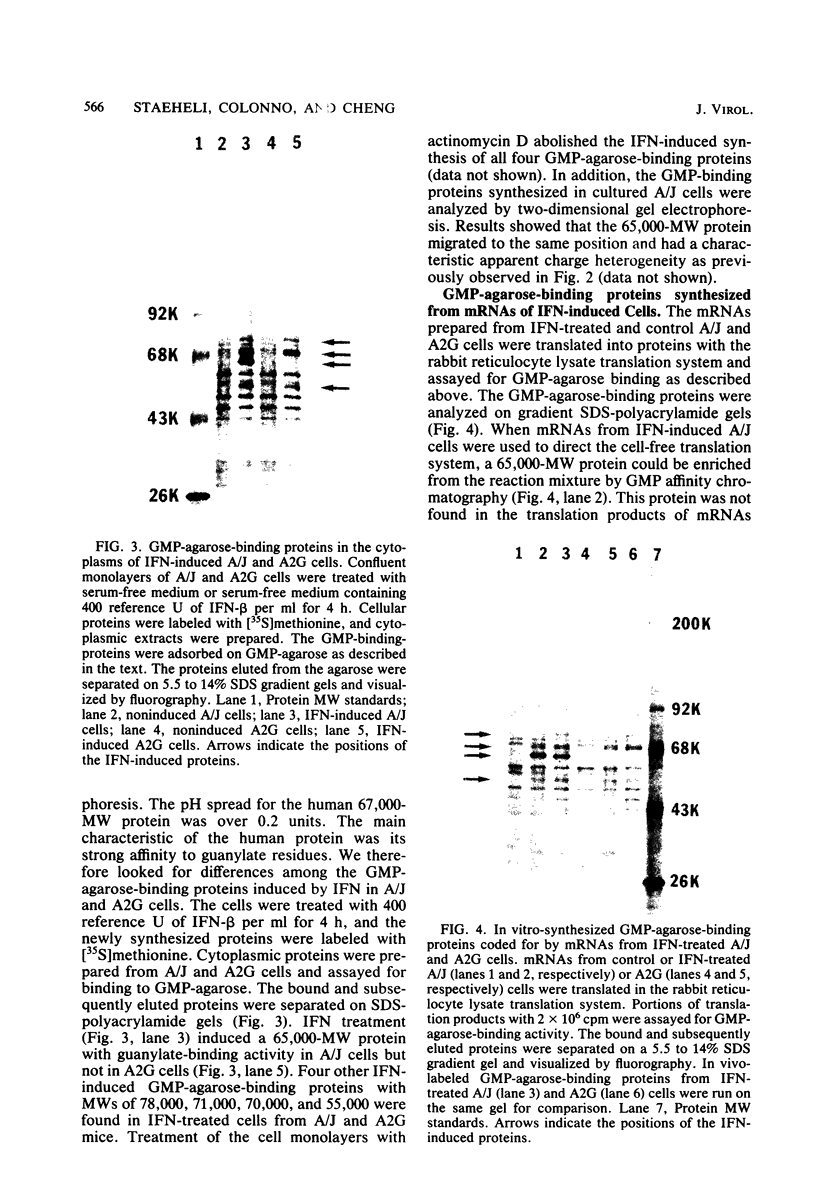
Treatment of cells from inbred mouse strains A/J and A2G with interferon resulted in the development of different antiviral states for influenza viruses. A2G mice-derived cells that carry the resistance gene Mx were efficiently protected by interferon against influenza viruses, whereas the interferon protection against the same viruses in wild-type A/J mice-derived cells was only marginal. The two cell types, however, were equally protected by interferon against vesicular stomatitis virus and other non-orthomyxoviruses. The interferon-induced mRNAs of mouse embryonic fibroblast cells that carried either homozygous wild-type alleles or homozygous Mx alleles were compared. The isolated polysome-bound mRNAs from A/J (+/+) and A2G (Mx/Mx) cells were translated in a cell-free translation system, and the translation products were analyzed after two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. New mRNAs coding for at least eight proteins with molecular weights (MW) ranging from 30,000 to 80,000 were found in interferon-treated cells but not in control cells. Differences in the interferon-induced mRNAs from A/J and A2G cells were also found. An mRNA coding for a 72,000-MW protein was found in interferon-treated A2G cells but not in interferon-treated A/J cells. Interferon-treated A/J cells, on the other hand, contained an mRNA coding for a 65,000-MW protein that was not found in interferon-treated A2G cells. The in vitro-synthesized 65,000-MW protein efficiently bound to GMP. Cytoplasmic extracts prepared from interferon-treated A/J cells also contained a GMP-binding 65,000-MW protein that was undetectable in similarly treated A2G cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Haller O. Mx gene control of interferon action: different kinetics of the antiviral state against influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):626–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.626-630.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Colonno R. J., Yin F. H. Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7746–7750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J. Accumulation of newly synthesized mRNAs in response to human fibroblast (beta) interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4763–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Pang R. H. Induction of unique mRNAs by human interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9234–9237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Rubin B. Y., Holmes S. L. Interferon action: induction of specific proteins in mouse and human cells by homologous interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4817–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O. Inborn resistance of ice to orthomyxoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:25–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Staeheli P., Haller O. Interferon induces a unique protein in mouse cells bearing a gene for resistance to influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1910–1914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Korant B. D. Fibroblast interferon induces synthesis of four proteins in human fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1824–1827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]