Abstract
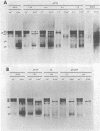
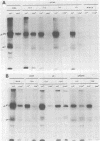
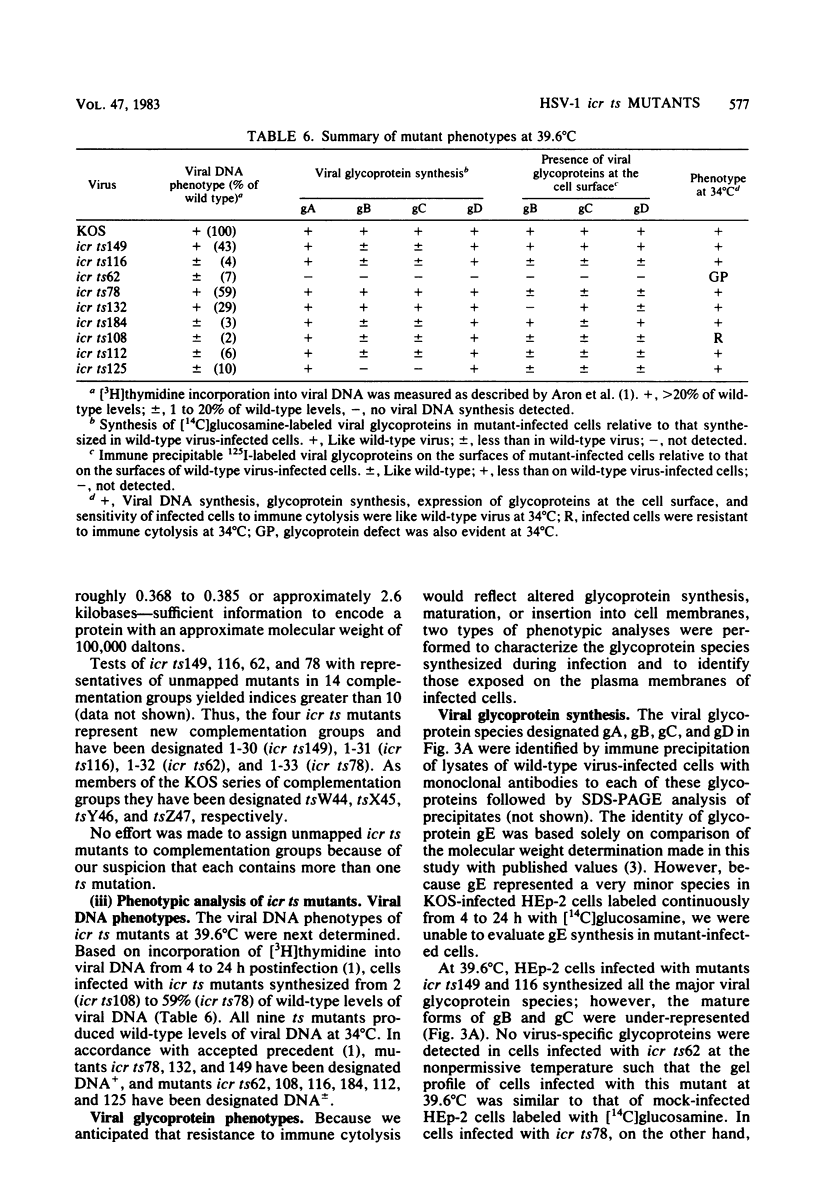
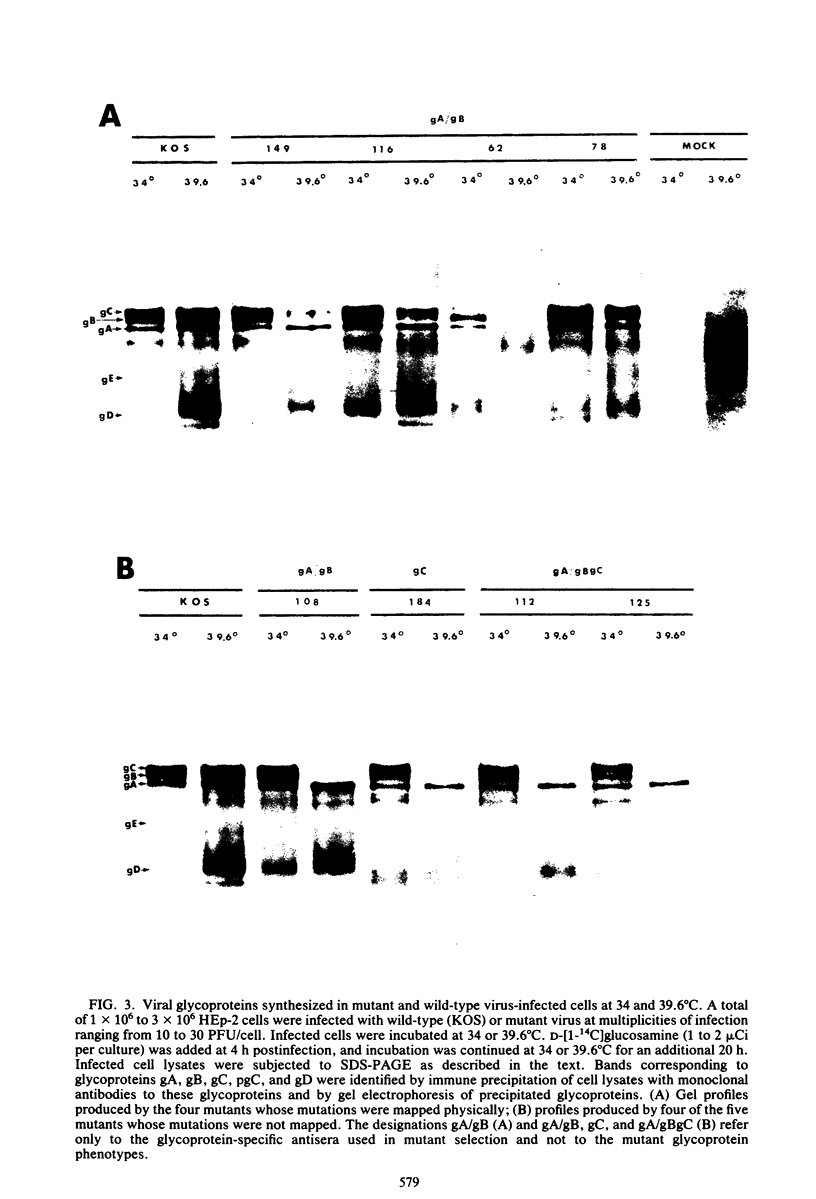
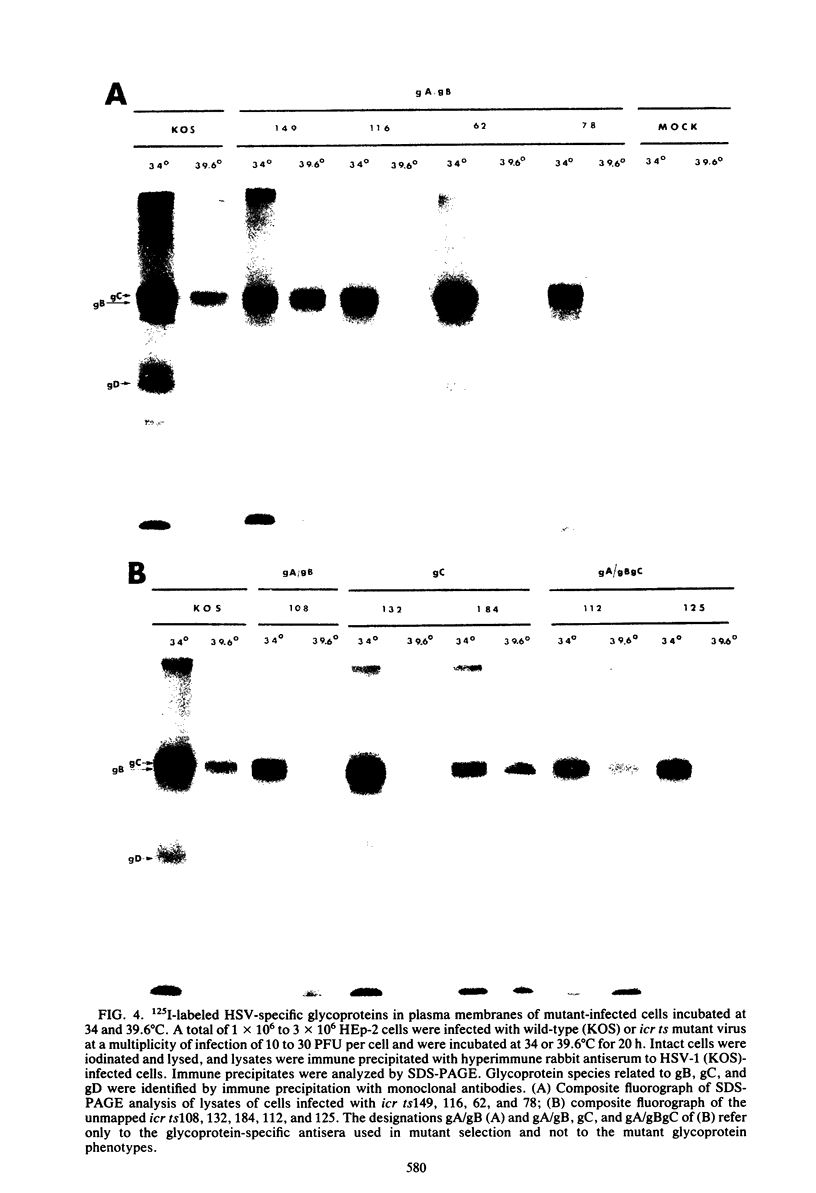
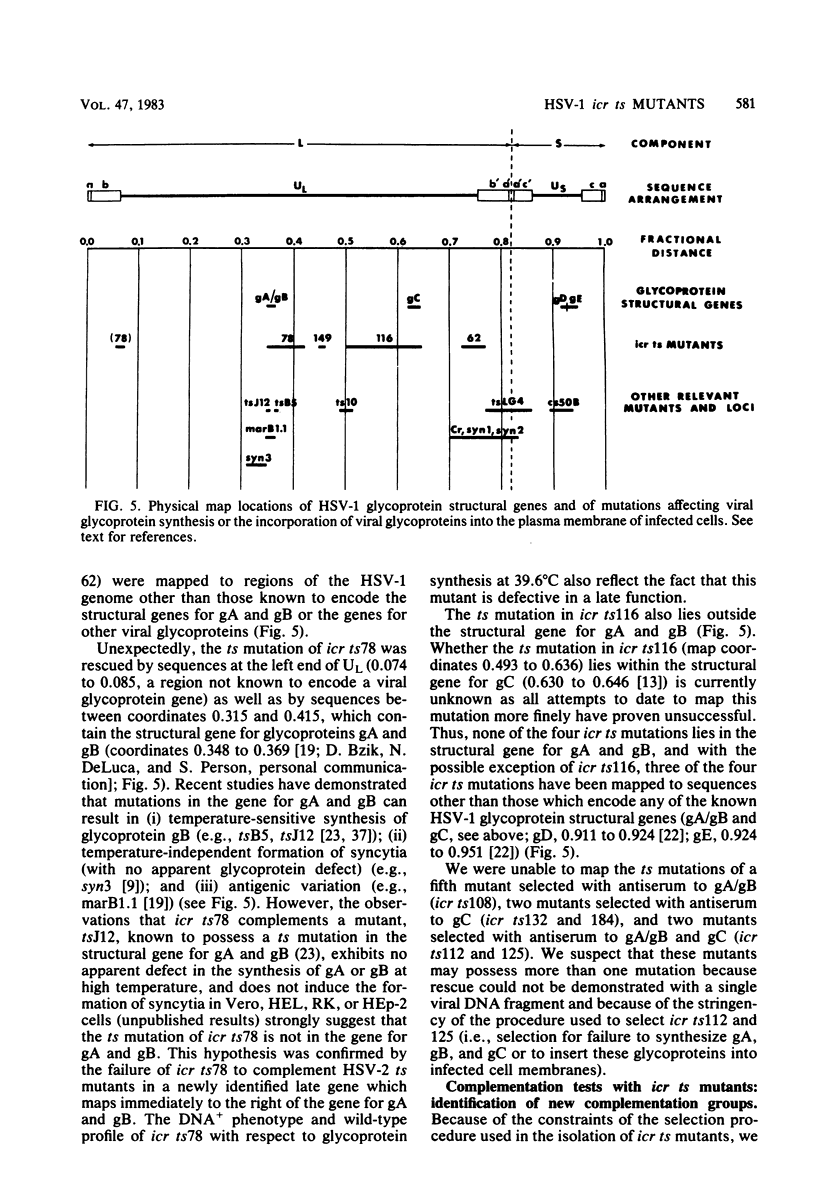
Nine temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 selected for their inability to render cells susceptible to immune cytolysis after infection at the nonpermissive temperature have been characterized genetically and phenotypically. The mutations in four mutants were mapped physically by marker rescue and assigned to functional groups by complementation analysis. In an effort to determine the molecular basis for cytolysis resistance, cells infected with each of the nine mutants were monitored for the synthesis of viral glycoprotein in total cell extracts and for the presence of these glycoproteins in plasma membranes. The four mutants whose ts mutations were mapped were selected with polypeptide-specific antiserum to glycoproteins gA and gB; however, three of the four mutations mapped to DNA sequences outside the limits of the structural gene specifying these glycoproteins. Combined complementation and phenotypic analysis indicates that the fourth mutation also lies elsewhere. The ts mutations in five additional cytolysis-resistant mutants could not be rescued with single cloned DNA fragments representing the entire herpes simplex virus type 1 genome, suggesting that these mutants may possess multiple mutations. Complementation tests with the four mutants whose ts lesions had been mapped physically demonstrated that each represents a new viral gene. Examination of mutant-infected cells at the nonpermissive temperature for the presence of viral glycoproteins in total cell extracts and in membranes at the cell surface demonstrated that (i) none of the five major viral glycoproteins was detected in extracts of cells infected with one mutant, suggesting that this mutant is defective in a very early function; (ii) cells infected with six of the nine mutants exhibited greatly reduced levels of all the major viral glycoproteins at the infected cell surface, indicating that these mutants possess defects in the synthesis or processing of viral glycoproteins; and (iii) in cells infected with one mutant, all viral glycoproteins were precipitable at the surface of the infected cell, despite the resistance of these cells to cytolysis. This mutant is most likely mutated in a gene affecting a late stage in glycoprotein processing, leading to altered presentation of glycoproteins at the plasma membrane. The finding that the synthesis of both gB and gC was affected coordinately in cells infected with six of the nine mutants suggests that synthesis of these two glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, or their insertion into plasma membranes is coordinately regulated.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron G. M., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A. DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):498–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.498-507.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Furlong D., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VIII. further characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in release of viral DNA and in other stages of the viral reproductive cycle. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):397–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.397-407.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Genetic studies with herpes simplex virus type 1. The isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants, their arrangement into complementation groups and recombination analysis leading to a linkage map. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):329–346. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Schaffer P. A., Tevethia S. S. The involvement of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins in cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1655–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. T., Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Farber F. E., Schaffer P. A. Hydroxylamine mutagenesis of HSV DNA and DNA fragments: introduction of mutations into selected regions of the viral genome. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):168–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A., Powell K. L. Synthesis of virus-specific polypaptides by temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):306–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N., Bzik D. J., Bond V. C., Person S., Snipes W. Nucleotide sequences of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) affecting virus entry, cell fusion, and production of glycoprotein gb (VP7). Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):411–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the genes for the major herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA-binding protein and a new late function. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):343–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.343-353.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza J., Benyesh-Melnick B., Schaffer P. A. Intertypic complementation and recombination between temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Levine M., Holland T. C., Szczesiul M. S. Mutant analysis of herpes simplex virus-induced cell surface antigens: resistance to complement-mediated immune cytolysis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):672–681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.672-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W. Intertypic recombinants of herpes simplex viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):1–23. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Randall R. E., Killington R. A., Watson D. H. Some properties of recombinants between type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):471–484. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Batterson W., Nosal C., Roizman B., Buchan A. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VI. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the expression of all early viral gene products. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):539–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.539-547.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Courtney R. J., Eberle R., Schaffer P. A., O'Hara M. K., Rouse B. T. Cell-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus: specificity of cytotoxic T cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):451–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.451-461.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Schaffer P. A. Expression of the syncytial (syn) phenotype in HSV-1, strain KOS: genetic and phenotypic studies of mutants in two syn loci. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):686–702. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machtiger N. A., Pancake B. A., Eberle R., Courtney R. J., Tevethia S. S., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: isolation of mutants resistant to immune cytolysis. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.336-346.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Buchman T. G., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. IX. Apparent exclusion of some parental DNA arrangements in the generation of intertypic (HSV-1 X HSV-2) recombinants. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):231–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.231-248.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and their expression on the cell surface. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.395-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Khanna B., Lycke E. Altered kinetic properties of sialyl and galactosyl transferases associated with herpes simplex virus infection of GMK and BHK cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Mar;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein gE of herpes simplex virus type 1: effects of anti-gE on virion infectivity and on virus-induced fc-binding receptors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.129-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Goldstein L., Spear P. G. Similarities and differences in the Fc-binding glycoprotein (gE) of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and tentative mapping of the viral gene for this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.137-144.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 ts mutants by marker rescue: correlation of the physical and genetic maps. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Coates J. A., Rixon F. J. Identification and characterization of a herpes simplex virus gene product required for encapsidation of virus DNA. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1056–1064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1056-1064.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Method for induction of mutations in physically defined regions of the herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.41-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Courtney R. J., McCombs R. M., Benyesh-Melnick M. A temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus defective in glycoprotein synthesis. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):356–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Summers W. C. Structure and function of herpesvirus genomes. II. EcoRl, Sbal, and HindIII endonuclease cleavage sites on herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):581–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spang A. E., Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 2 temperature-sensitive mutants whose lesions map in or near the coding sequences for the major DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):332–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.332-342.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognon M., Furlong D., Conley A. J., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. V. Characterization of a mutant defective in ability to form plaques at low temperatures and in a viral fraction which prevents accumulation of coreless capsids at nuclear pores late in infection. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.870-880.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]