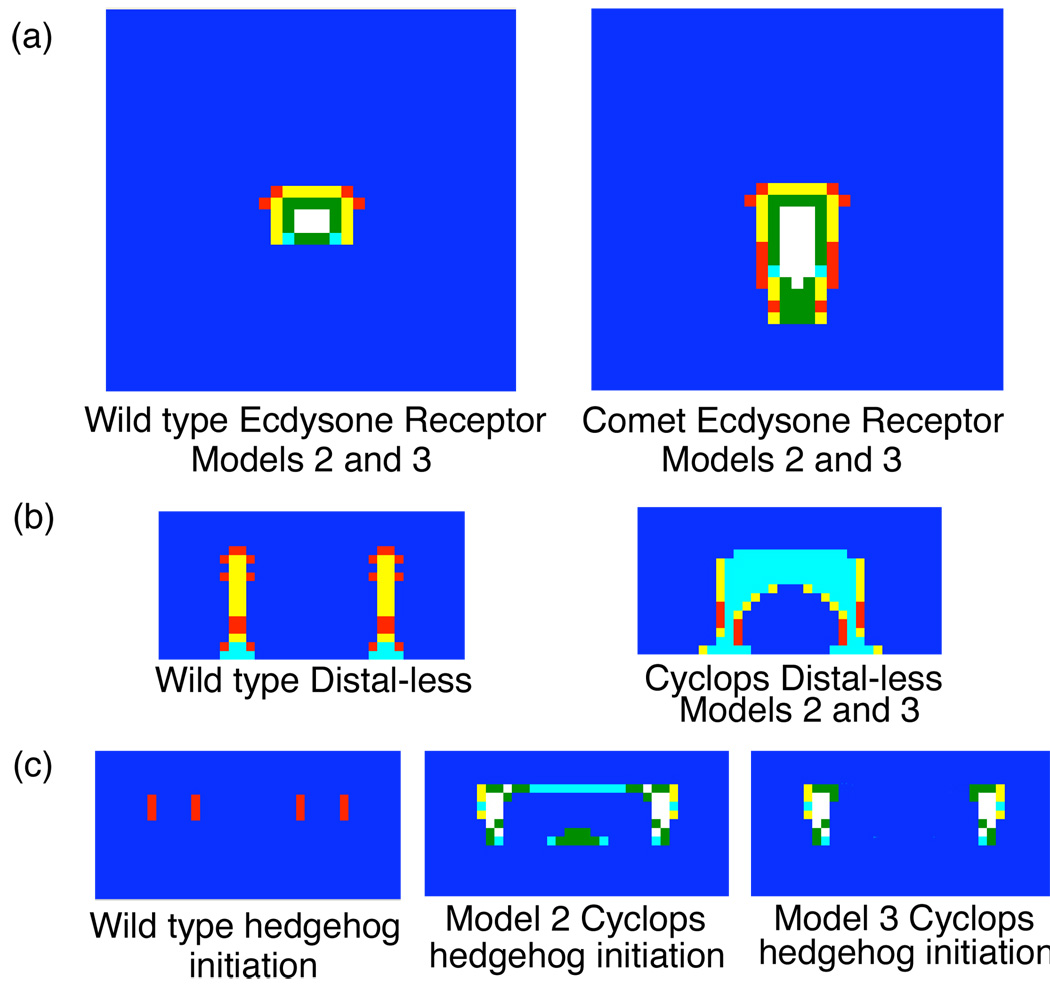
Fig. 3.
Simulated gene expression patterns of (a) Ecdysone Receptor in one wing-cell models. This gene product appears to be the last gene product in the regulatory network before the focal signal is released and the shape of the expression pattern corresponds to the shape of the eyespot focus. Comet mutants have enlarged eyespot foci that are tear-drop shaped instead of the circles as is typical of wild-type animals. The narrow end of the tear-drop is oriented towards the wing margin, the bottom of the field in these simulations. The expression of Distal-less (b) in two wing-cell models matches known expression patterns in both wild type and Cyclops mutant genotypes (Brakefield, et al., 1996). To date, no additional expression patterns have been published for Cyclops mutants. Models 2 and 3 produce similar results for all gene products in the regulatory network in Cyclops except for hedgehog (c), which shows radically different patterns of expression. This suggests that examining hedgehog expression in Cyclops mutants is a critical experiment for differentiating between Models 2 and 3.