Abstract
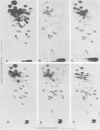
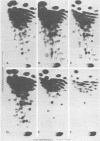
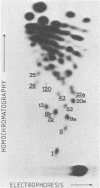
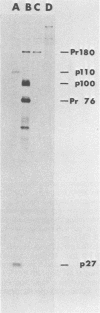
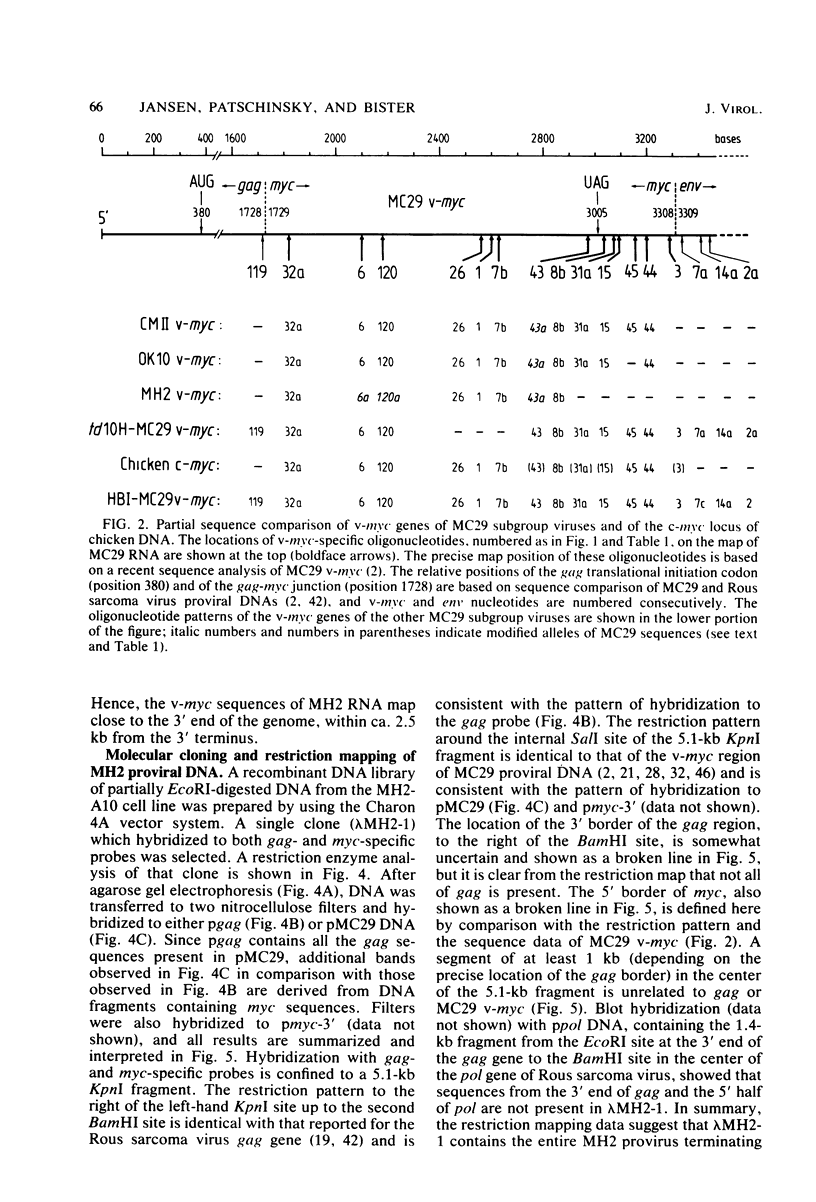
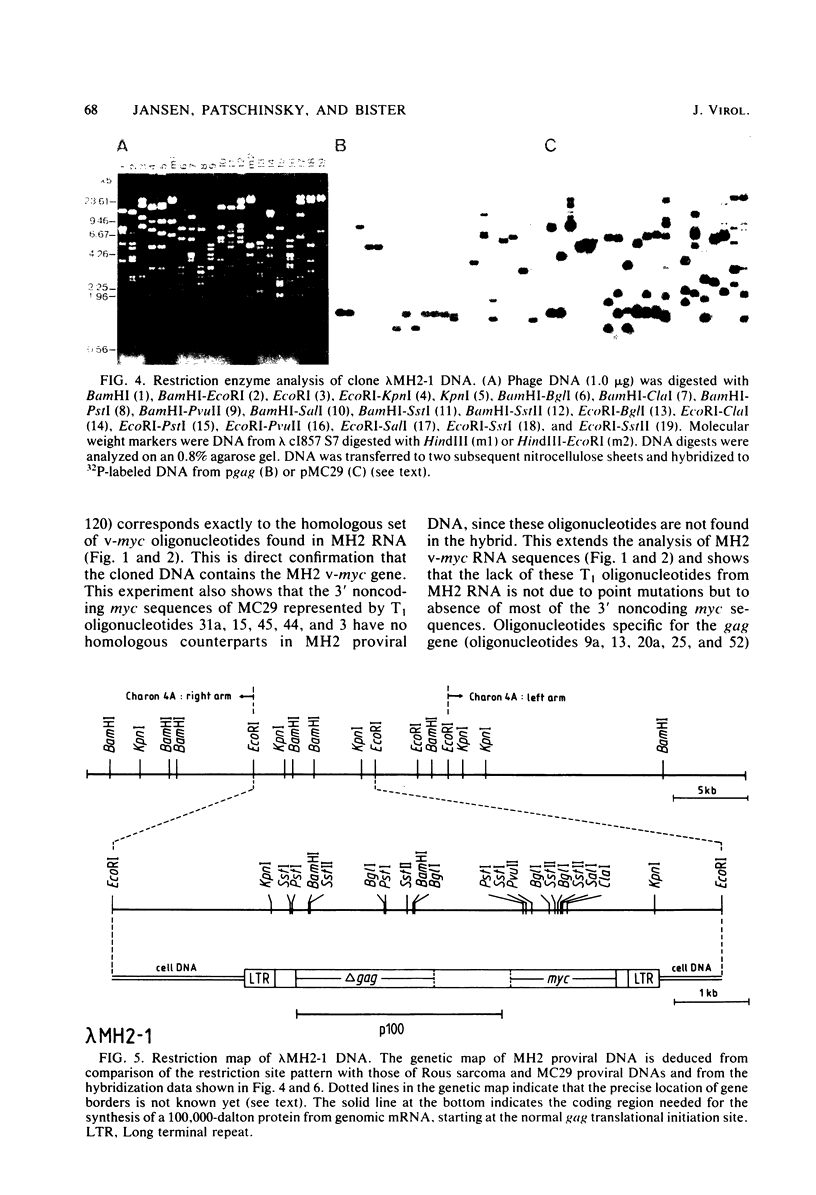
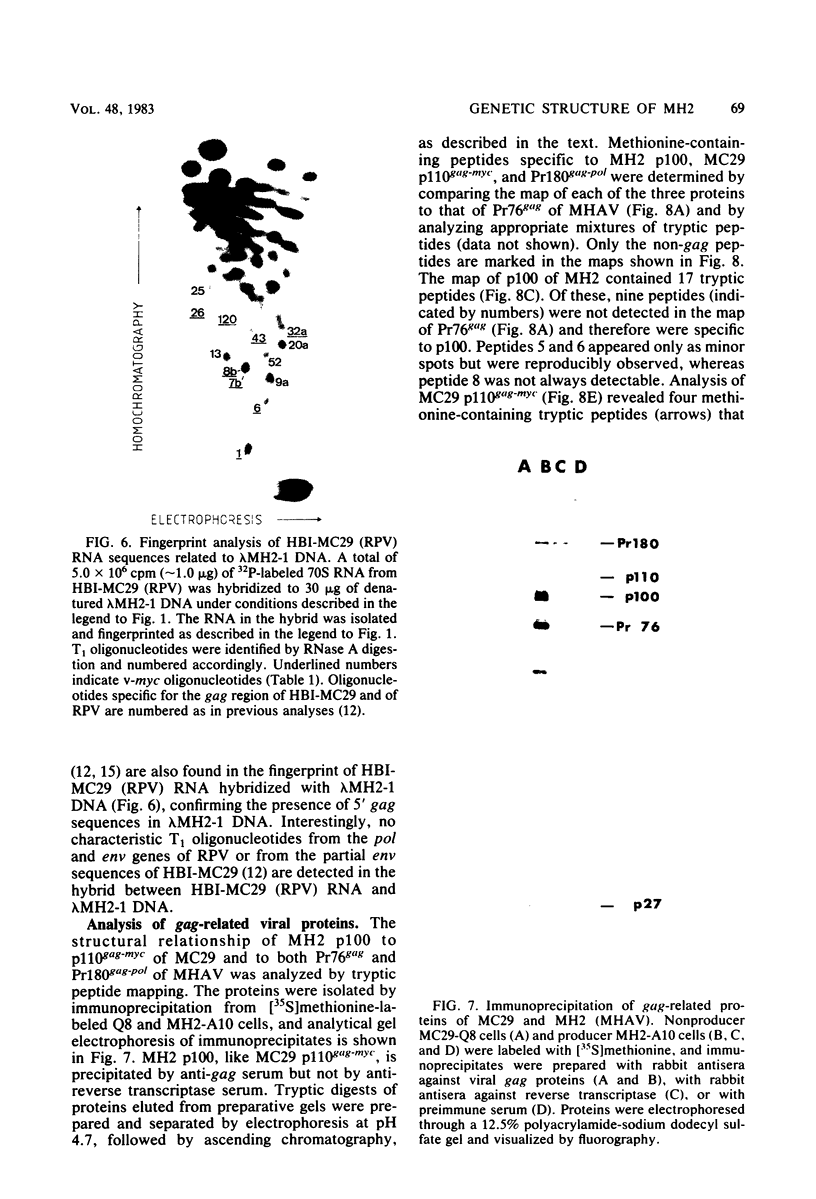
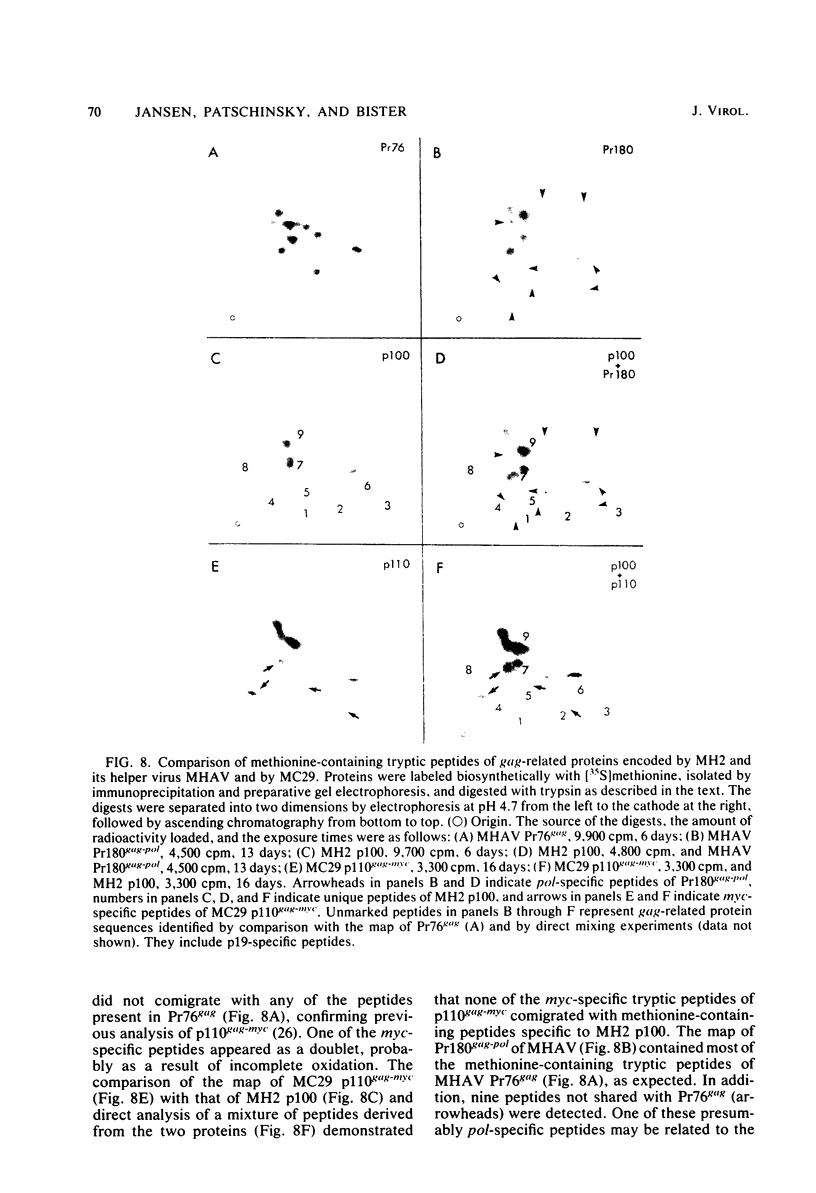
Viral RNA, molecularly cloned proviral DNA, and virus-specific protein of avian retrovirus MH2 were analyzed. The complexity and sequence conservation of the transformation-specific v-myc sequences of MH2 RNA were compared with those of the other members of the MC29 subgroup of acute leukemia viruses, MC29, CMII, and OK10, and with chicken cellular c-myc sequences. All T1 oligonucleotides mapping within the 1.3-kilobase coding region of MC29 v-myc have homologous counterparts in the RNAs of all MC29 subgroup viruses and in c-myc. These counterparts are either identical in composition or altered by single point mutations. Hence, the 47,000-dalton carboxy-terminal sequences of the transforming proteins of these viruses and of the cellular gene product are probably highly conserved but may contain single amino acid substitutions. T1 oligonucleotide mapping of MH2 RNA indicated that the MH2 v-myc sequences map close to the 3' end of viral RNA. A genomic library of an MH2-transformed quail cell line was prepared by using the Charon 4A vector system. By screening with an myc-specific probe, a clone containing the entire MH2 provirus (lambda MH2-1) was isolated. Digestion of cloned DNA with KpnI yielded a 5.1-kilobase fragment hybridizing to both gag- and myc-specific probes. Further restriction mapping of lambda MH2-1 DNA showed that about 1.6 kilobases of the gag gene are present near the 5' end of proviral DNA, and the conserved part of v-myc, i.e., 1.3 kilobases, is present near the 3' end of proviral DNA. These two domains are separated by a segment of at least 1 kilobase of different genetic origin, including additional unique sequences unrelated to virion genes. Tryptic peptide analysis of the gag-related protein of MH2, p100, revealed gag-specific peptides and several unique methionine-containing peptides. One of the latter is possibly shared with the polymerase precursor protein Pr180gag-pol, but no myc-specific peptides, defined for the MC29 protein p110gag-myc, appear to be present in MH2 p100. The data on viral RNA, proviral DNA, and protein of MH2 reveal a unique genetic structure for this virus of the MC29 subgroup and suggest that its v-myc gene is not expressed as a gag-related protein.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. W., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. Avian oncovirus Mill Hill No. 2: pathogenicity in chickens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Feb;62(2):359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Bishop J. M., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Nucleotide sequence to the v-myc oncogene of avian retrovirus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Enemies within: the genesis of retrovirus oncogenes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Retroviruses and cancer genes. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;37:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Duesberg P. H. Genetic structure of avian acute leukemia viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):801–822. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Enrietto P., Graf T., Hayman M. The transforming gene of avian acute leukemia virus MC29. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1983;28:173–177. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68761-7_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Jansen H. W., Graf T., Enrietto P., Hayman M. J. Genome structure of HBI, a variant of acute leukemia virus MC29 with unique oncogenic properties. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):337–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.337-346.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Löliger H. C., Duesberg P. H. Oligoribonucleotide map and protein of CMII: detection of conserved and nonconserved genetic elements in avian acute leukemia viruses CMII, MC29, and MH2. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.208-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Ramsay G. M., Hayman M. J. Deletions within the transformation-specific RNA sequences of acute leukemia virus MC29 give rise to partially transformation-defective mutants. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):754–766. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.754-766.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Duesberg P. H. OK10, an avian acute leukemia virus of the MC 29 subgroup with a unique genetic structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7142–7146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Stedman J. D. Efficient fluorography of 3H and 14C on thin layers. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90747-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiswell D. J., Ramsay G., Hayman M. J. Two virus-specific rna species are present in cells transformed by defective leukemia virus OK10. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):301–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.301-304.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Avian acute leukemia viruses MC29 and MH2 share specific RNA sequences: evidence for a second class of transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1633–1637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enrietto P. J., Hayman M. J. Restriction enzyme analysis of partially transformation-defective mutants of acute leukemia virus MC29. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):711–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.711-715.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Stéhelin D. Avian leukemia viruses. Oncogenes and genome structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 28;651(4):245–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. The defectiveness of Mill Hill 2, a carcinoma-inducing avian oncovirus. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):162–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchener G., Hayman M. J. Comparative tryptic peptide mapping studies suggest a role in cell transformation for the gag-related protein of avian erythroblastosis virus and avian myelocytomatosis virus strains CMII and MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1637–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenberger J. A., Schulz R. A., Garon C. F., Tsichlis P. N., Papas T. S. Molecular cloning of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29) transforming sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M. Two retroviruses with similar transforming genes exhibit differences in transforming potential. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Pawson A., Bister K., Martin G. S., Duesberg P. H. Specific RNA sequences and gene products of MC29 avian acute leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5874–5878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Gasic G. P., Rogler C. E., Skalka A. M., Ju G., Hishinuma F., Papas T., Astrin S. M., Hayward W. S. Molecular analysis of the c-myc locus in normal tissue and in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):158–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.158-166.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Biegalke B., Linial M. RNA and protein encoded by MH2 virus: evidence for subgenomic expression of v-myc. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.133-139.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Sefton B. M. Evidence that there exist four classes of RNA tumor viruses which encode proteins with associated tyrosine protein kinase activities. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):104–114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.104-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G. M., Enrietto P. J., Graf T., Hayman M. J. Recovery of myc-specific sequences by a partially transformation-defective mutant of avian myelocytomatosis virus, MC29, correlates with the restoration of transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6885–6889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J. Analysis of cells transformed by defective leukemia virus OK10: production of noninfectious particles and synthesis of Pr76gag and an additional 200,000-dalton protein. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Bister K. Phosphorylation of specific sites in the gag-myc polyproteins encoded by MC29-type viruses correlates with their transforming ability. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1111–1116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins T., Bister K., Garon C., Papas T., Duesberg P. Structural relationship between a normal chicken DNA locus and the transforming gene of the avian acute leukemia virus MC29. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):635–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.635-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Sergeant A., Torpier G., Raes M. B., Pfeifer S., Stehelin D. Subgenomic mRNA in OK10 defective leukemia virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):71–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.71-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Beemon K., Hunter T. Comparison of the expression of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):957–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.957-971.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bister K., Moscovici C., Fanshier L., Gonda T., Bishop J. M. Avian retroviruses that cause carcinoma and leukemia: identification of nucleotide sequences associated with pathogenicity. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):962–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.962-968.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Moscovici C., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian myelocytomatosis virus genome and recovery of infectious virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.625-631.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]