Abstract
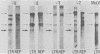
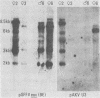
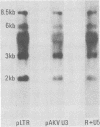
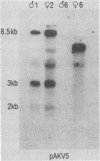
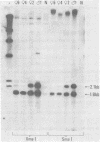
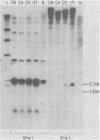
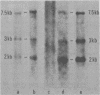
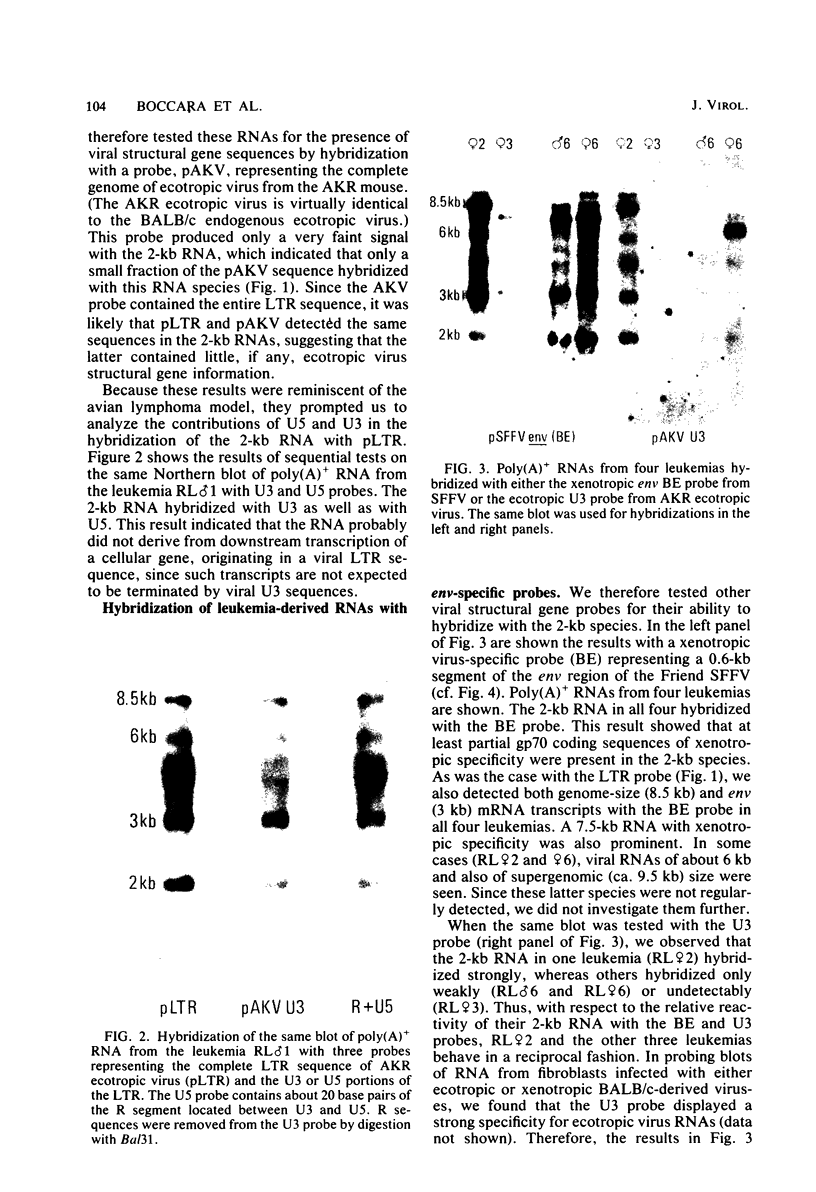
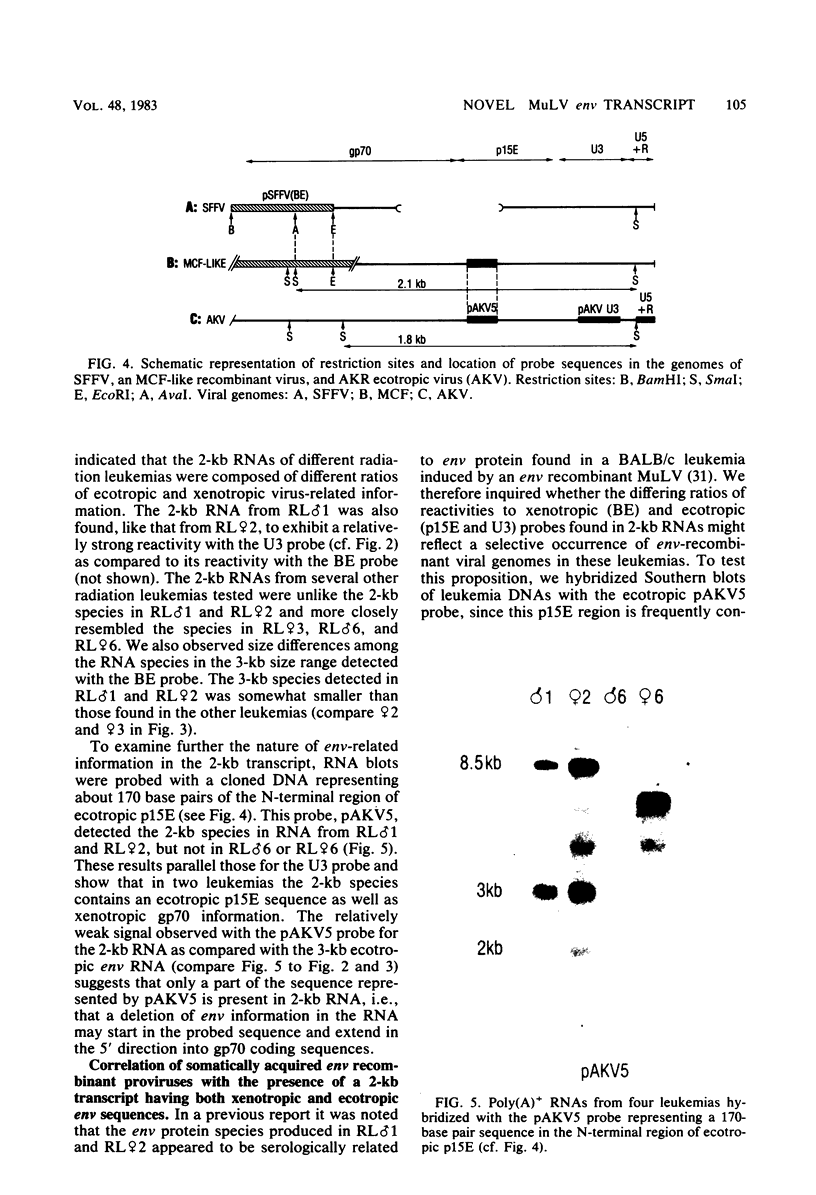
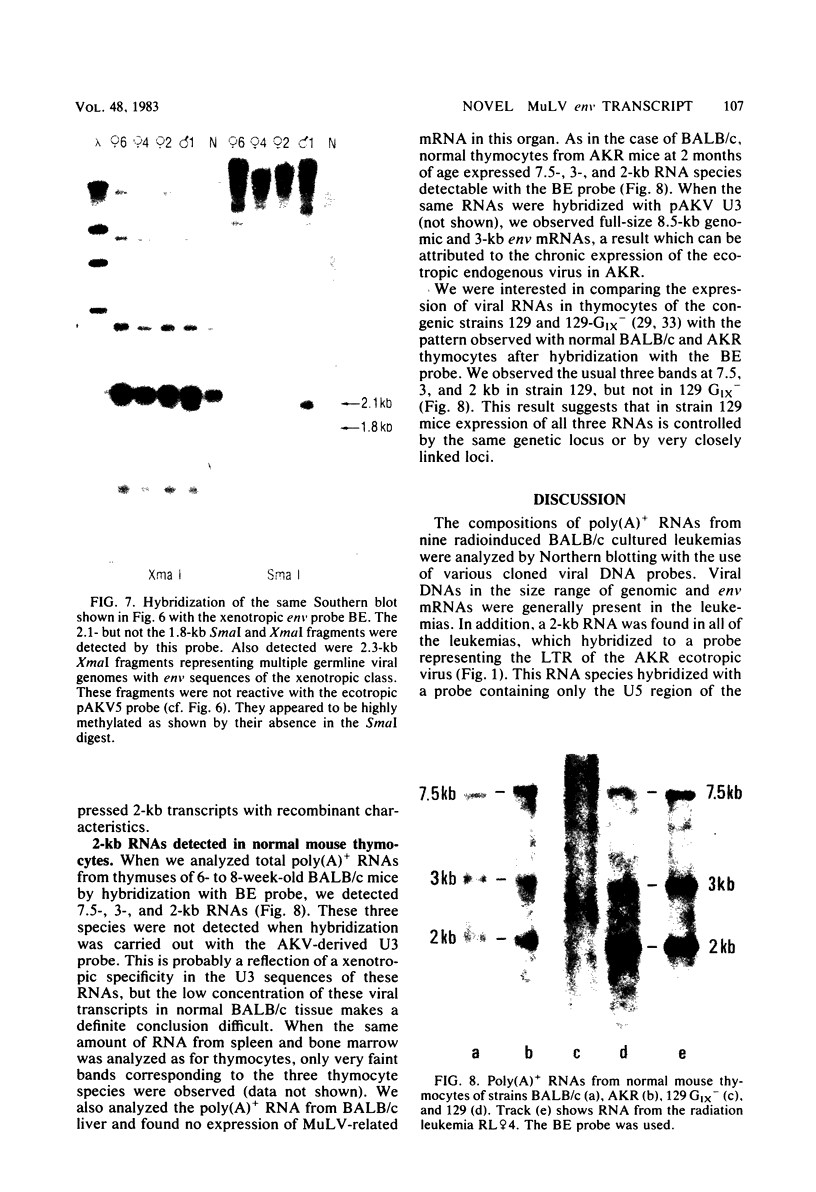
Murine leukemia virus-related RNA species were examined in a set of radiation-induced T-cell leukemias from BALB/c mice. No evidence was found for linkage of viral long terminal repeat-derived (U5) sequences to information of host origin. A novel class of 2-kilobase (kb) env-related transcripts, about 1kb shorter than normal viral env messenger, was found in all the leukemias. All of the 2-kb transcripts contained sequences homologous to the xenotropic virus-related env sequences in the Friend spleen focus-forming virus, representing the N-terminal portion of gp70. In two of the leukemias, these transcripts were found to contain both ecotropic p15E and U3 sequences in addition to the xenotropic gp70-related sequence. These two leukemias, but not others in which ecotropic sequences were absent from the 2-kb RNA, harbored several copies of a specific class of env recombinant proviruses. These proviruses possessed full-size env genes and were submethylated, as shown by SmaI and XmaI digests of proviral DNA. Low levels of 2-kb RNA were found in normal thymocytes from strains BALB/c, AKR, and 129 but not from congenic 129 GIX- mice. It is possible that the 2-kb RNA may originate by a novel splicing step that removes portions of the gp70 and p15E sequences from full-length env transcripts.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Hopkins N., Fleissner E. Biochemical analysis of murine leukemia viruses isolated from radiation-induced leukemias of strain BALB/c. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):661–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.661-670.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Stockert E., Fleissner E. Association of endogenous retroviruses with radiation-induced leukemias of BALB/c mice. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):652–660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.652-660.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G. Murine leukemia viruses with recombinant env genes: a discussion of their role in leukemogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;103:75–108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68943-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Thiel H. J., Ihle J. N., Lee J. C., Elder J. H. Detection of a recombinant murine leukemia virus-related glycoprotein on virus-negative thymoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1920–1924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleissner E., Snyder H. W., Jr Oncoviral proteins as cellular antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;98:37–80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68369-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. W., Steffen D., Gusella J., Tabin C., Bird S., Cowing D., Weinberg R. A. DNA methylation affecting the expression of murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):144–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.144-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P., Gattoni-Celli S., Dina D., Weinstein I. B. Carcinogen- and radiation-transformed C3H 10T1/2 cells contain RNAs homologous to the long terminal repeat sequence of a murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2773–2777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lerner R. A., Wilson M. C. A genetic locus regulates the expression of tissue-specific mRNAs from multiple transcription units. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5823–5827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Ruscetti S. K., Evans L. H., Scolnick E. M. Envelope gene sequences which encode the gp52 protein of spleen focus-forming virus are required for the induction of erythroid cell proliferation. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):223–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.223-233.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Montandon F., Fan H. Methylation state and DNase I sensitivity of chromatin containing Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA in exogenously infected mouse cells. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.475-486.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Hayward W. S., Robinson H. L., Fang J., Astrin S. M. Avian leukosis virus-induced tumors have common proviral integration sites and synthesize discrete new RNAs: oncogenesis by promoter insertion. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E. Immunogenetics of cell surface antigens of mouse leukemia. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:127–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roblin R., Young J. M., Mural R. J., Bell T. E., Ihle J. N. Molecular cloning and characterization of murine leukemia virus-related DNA sequences from C3H/HeN mouse DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):113–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.113-126.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Roussel M., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. Characterization of the oncogene (erb) of avian erythroblastosis virus and its cellular progenitor. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):409–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.409-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Diazotizable arylamine cellulose papers for the coupling and hybridization of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Mural R., Cowing D., Mielcarz J., Young J., Roblin R. Most of the murine leukemia virus sequences in the DNA of NIH/swiss mice consist of two closely related proviruses, each repeated several times. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.127-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Obata Y., Ikeda H., Sarkar N. H., Hoffman H. A. New mutant and congenic mouse stocks expressing the murine leukemia virus-associated thymocyte surface antigen GIX. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):512–517. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert E., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. The G-IX system. A cell surface allo-antigen associated with murine leukemia virus; implications regarding chromosomal integration of the viral genome. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1334–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tress E., Pierotti M., DeLeo A. B., O'Donnell P. V., Fleissner E. Endogenous murine leukemia virus-encoded proteins in radiation leukemias of BALB/c mice. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Yuan E., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent mink cell focus-inducing strains of Friend murine type-C virus: potential relationship to the origin of replication-defective spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):639–653. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Shen F. W., Viamontes G., Palladino M., Fleissner E. The same genetic locus directs differentiation-linked expression of endogenous retrovirus gp70 on thymocytes and spleen cells in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1982 Jan;15(1):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00375507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]