Abstract
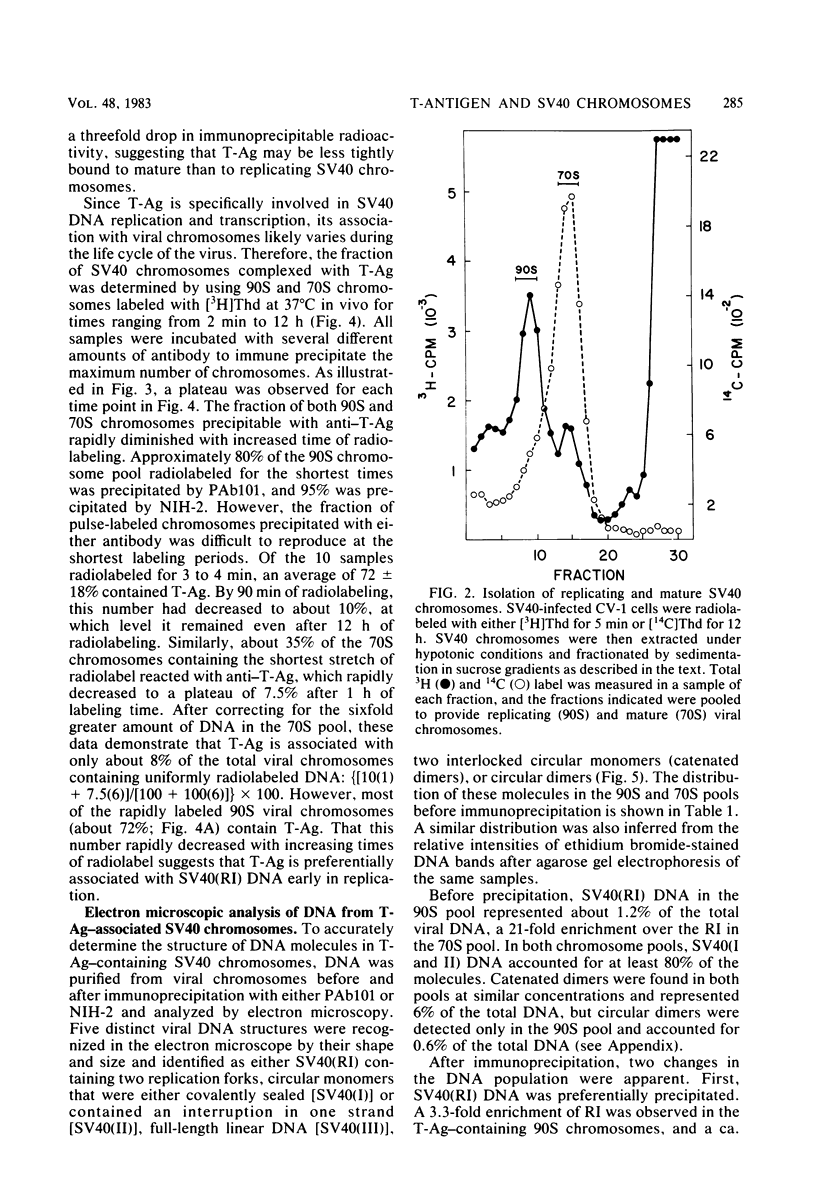
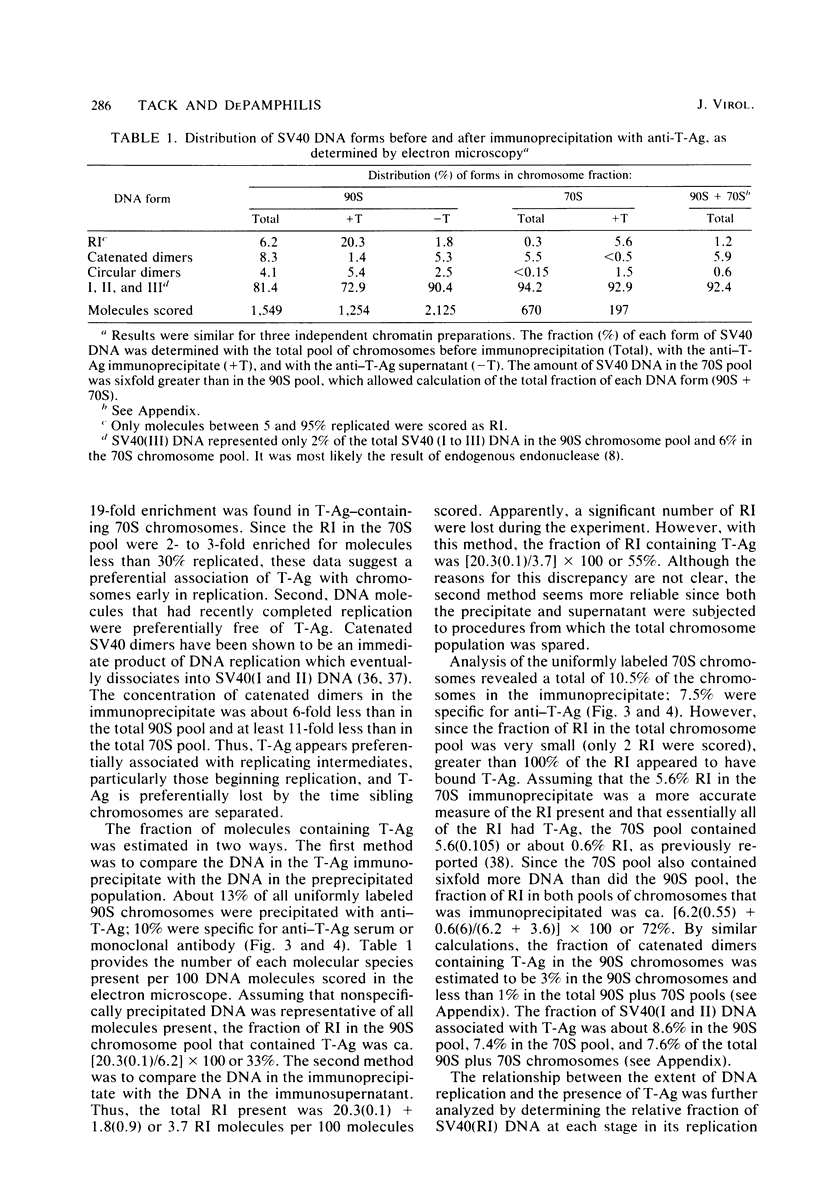
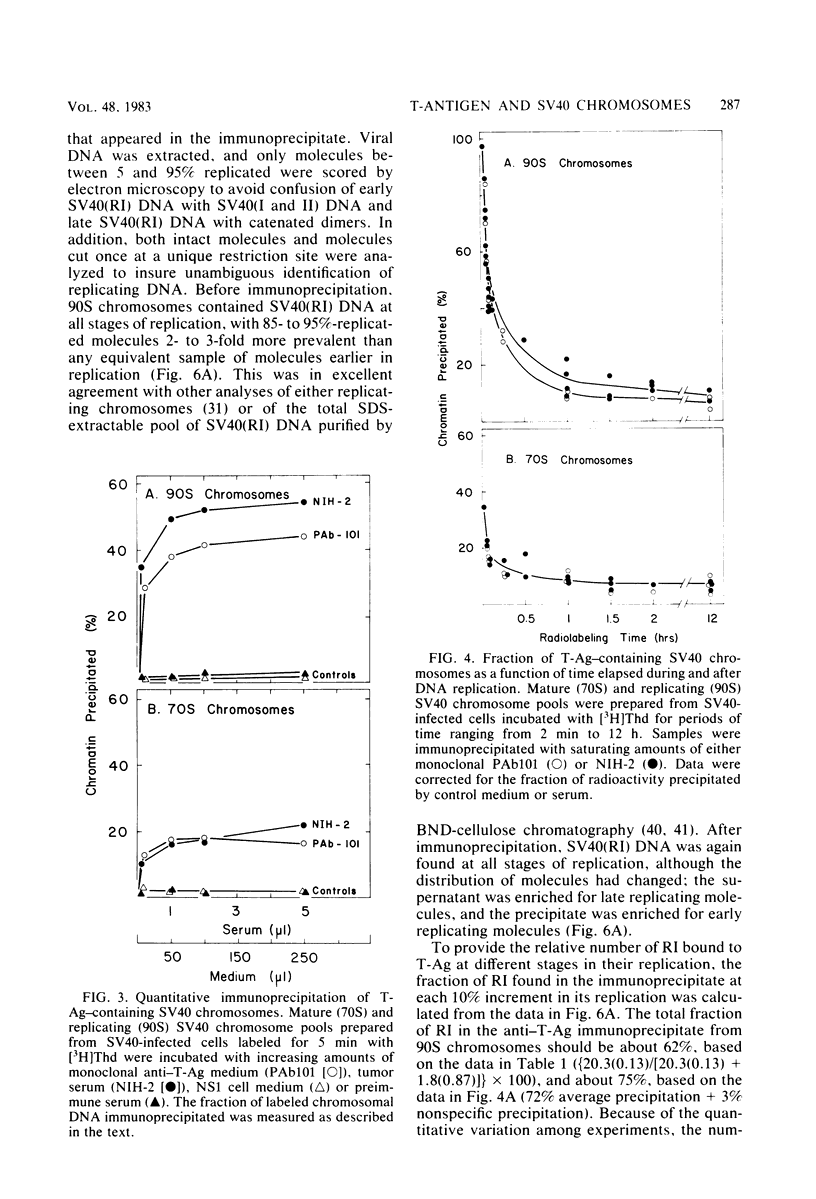
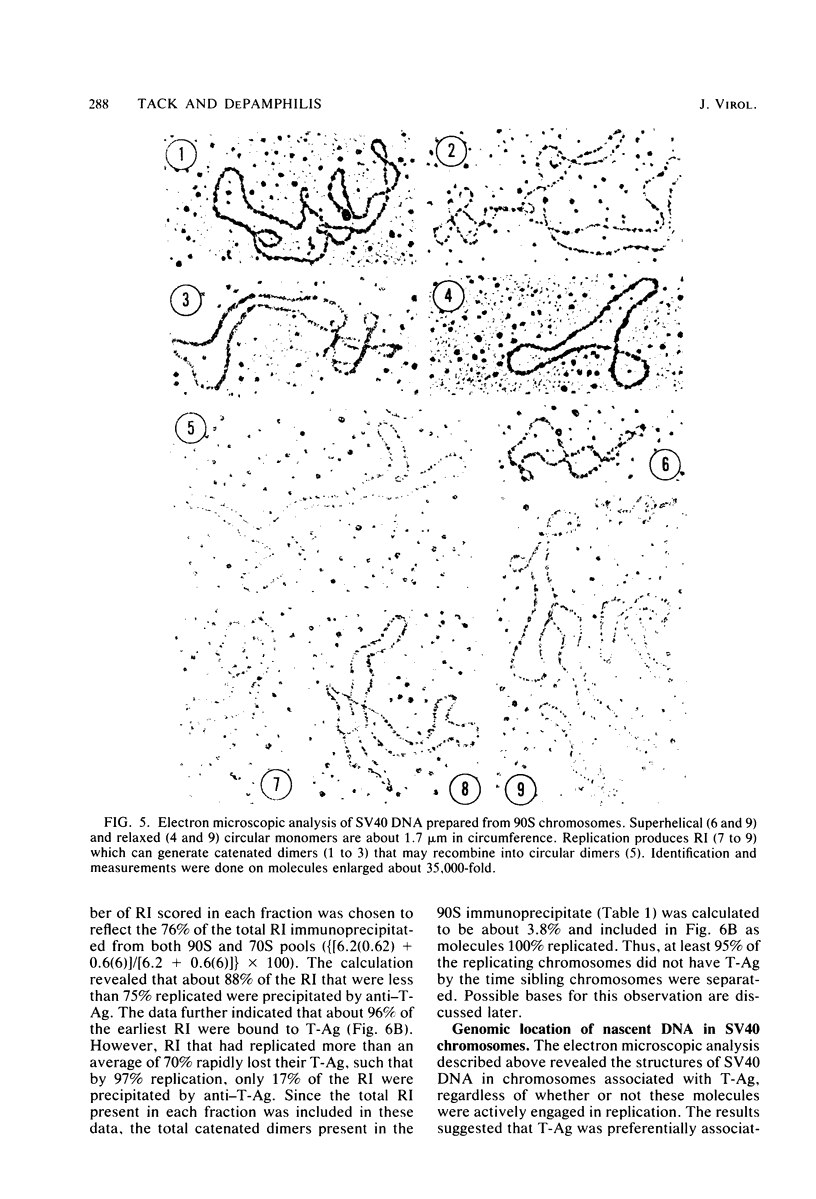
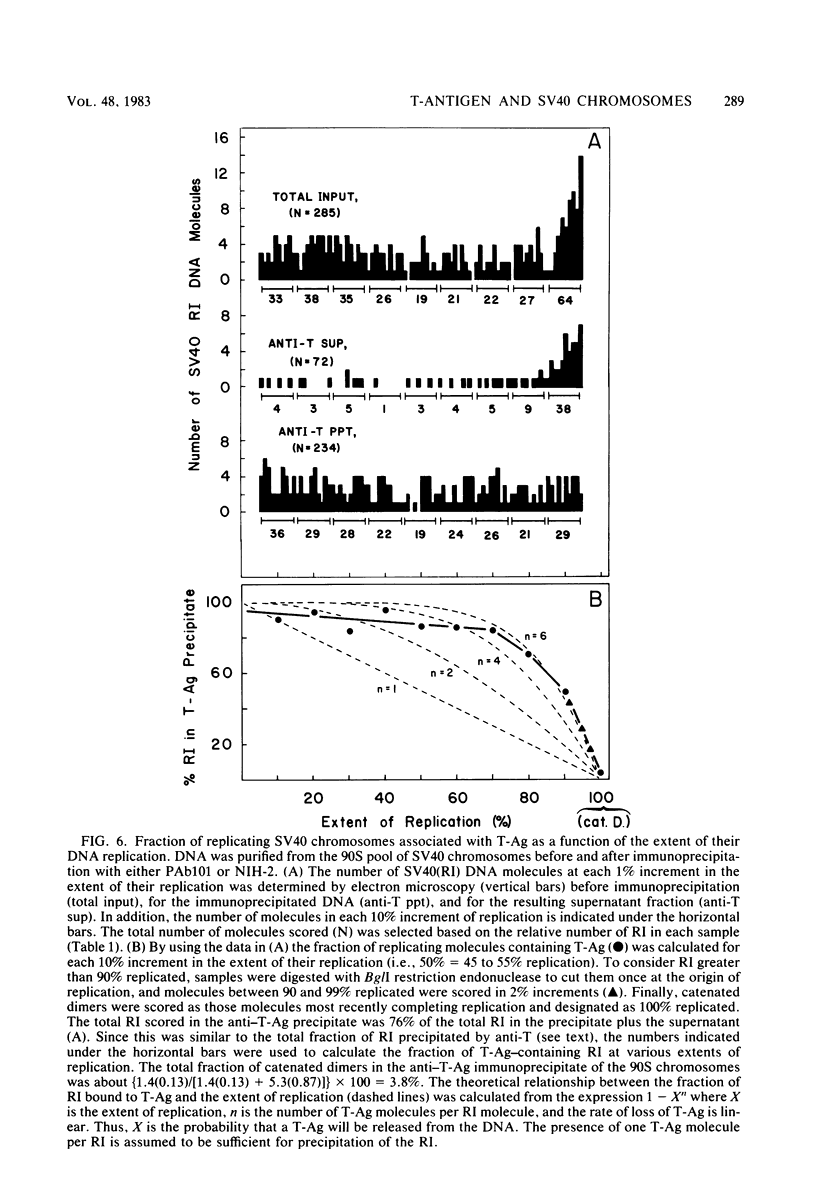
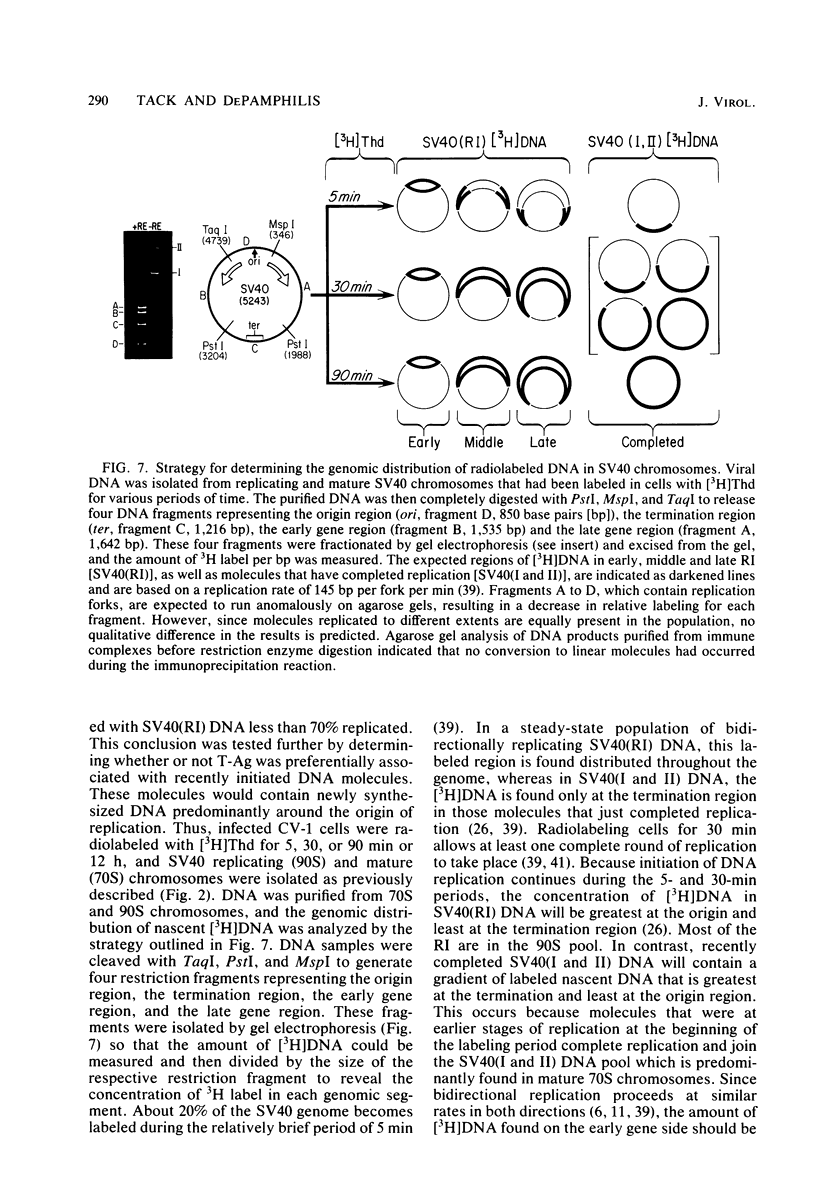
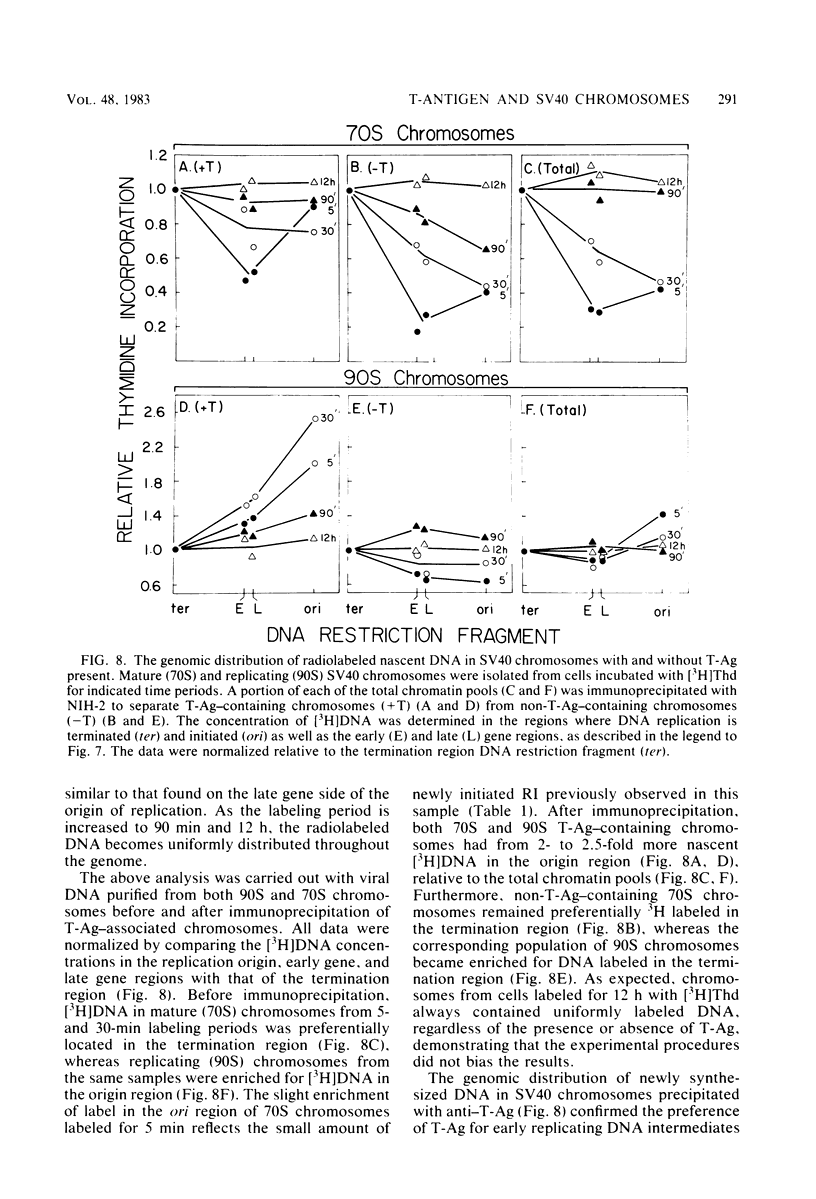
The fraction and DNA composition of simian virus 40 chromosomes that were complexed with large T-antigens (T-Ag) were determined at the peak of viral DNA replication. Simian virus 40 chromatin containing radiolabeled DNA was extracted by the hypotonic method of Su and DePamphilis (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73:3466-3470, 1976) and then fractionated by sucrose gradient sedimentation into replicating (90S) and mature (70S) chromosomes. Viral chromosomes containing T-Ag were isolated by immunoprecipitation with saturating amounts of either an anti-T-Ag monoclonal antibody or an anti—T-Ag hamster serum under conditions that specifically precipitated T-Ag protein from cytosol extracts. An average of 10% of the uniformly labeled DNA in the 90S pool and 7.5% in the 70S pool was specifically precipitated, demonstrating that under these conditions immunologically reactive T-Ag was tightly bound to only 8% of the total viral chromosomes. In contrast, simian virus 40 replicating intermediates (RI) represented only 1.2% of the viral DNA, but most of these molecules were associated with T-Ag. At the shortest pulse-labeling periods, an average of 72 ± 18% of the radiolabeled DNA in 90S chromosomes could be immunoprecipitated, and this value rapidly decreased as the labeling period was increased. Electron microscopic analysis of the DNA before and after precipitation revealed that about 55% of the 90S chromosomal RI and 72% of the total RI from both pools were specifically bound to T-Ag. Comparison of the extent of replication with the fraction of RI precipitated revealed a strong selection for early replicating DNA intermediates. Essentially all of the RI in the 70S chromosomes were less than 30% replicated and were precipitated with anti—T-Ag monoclonal antibody or hamster antiserum. An average of 88% of the 90S chromosomal RI which were from 5 to 75% replicated were immunoprecipitated, but the proportion of RI associated with T-Ag rapidly decreased as replication proceeded beyond 70% completion. By the time sibling chromosomes had separated, only 3% of the newly replicated catenated dimers in the 90S pool (<1% of the dimers in both pools) were associated with T-Ag. Measurements of the fraction of radiolabeled DNA in each quarter of the genome confirmed that T-Ag was preferentially associated with newly initiated molecules in which the nascent DNA was nearest the origin of replication. These results are consistent with a specific requirement for the binding of T-Ag to viral chromosomes to initiate DNA replication, and they also demonstrate that T-Ag does not immediately dissociate from chromosomes once replication begins. The biphasic relationship between the fraction of T-Ag—containing RI and the extent of DNA replication suggests either that 1 or 2 molecules of T-Ag remain stably bound until replication is about 70% completed or that 4 to 6 molecules of T-Ag are randomly released from each RI at a uniform rate throughout replication.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Kaufman G., DePamphilis M. L. RNA primers in SV40 DNA replication: identification of transient RNA-DNA covalent linkages in replicating DNA. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4990–4998. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Nyfeler K. Transcription of Simian Virus 40 chromosomes in an extract of HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):9–14. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Gurney E. G. Time-dependent maturation of the simian virus 40 large T antigen-p53 complex studied by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):565–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.565-573.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Birkenmeier E., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 DNA replication: characterization of gaps in the termination region. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):614–621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.614-621.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Nathans D. Bidirectional replication of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 tumor antigens: analysis of antigenic binding sites, using adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):478–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.478-482.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Baumgartner I. Role of fast-sedimenting SV40 nucleoprotein complexes in virus assembly. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G. C., Garon G. F., Salzman N. P. Origin and direction of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):484–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.484-491.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Coca-Prados M., Hsu M. T. Intracellular forms of simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. I. Methods of isolation and characterization in CV-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):612–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.612-623.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Light S., Livingston D. M. Measurements of the molecular size of the simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):218–226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.218-226.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Tenen D. G., Livingston D. M., Sharp P. A. T antigen repression of SV40 early transcription from two promoters. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Aloni Y. Isolation and characterization of various forms of simian virus 40 DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss M. R., Benbow R. M. Polyoma virus minichromosomes: associated DNA molecules. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.815-825.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K., Hunter T. Association of simian virus 40 T antigen with simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):232–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.232-241.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Samulski R. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Rapid purification of covalently closed circular DNAs of bacterial plasmids and animal tumor viruses. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Defective simian virus 40 genomes: isolation and growth of individual clones. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milavetz B. I., Spotila L. D., Thomas R., Huberman J. A. Two-dimensional analysis of proteins sedimenting with simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):854–864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.854-864.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Danna K. J. Specific origin in SV40 DNA replication. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 19;236(68):200–202. doi: 10.1038/newbio236200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Renart J., Crawford L. V., Stark G. R. Specific association of simian virus 40 tumor antigen with simian virus 40 chromatin. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.78-87.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. Transforming genes and gene products of polyoma and SV40. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(3):215–286. doi: 10.3109/10409238209114230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Garon C. F., Salzman N. P. Superhelix density of replicating simian virus 40 DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa M., Sugano S., Yamaguchi N. Association of simian virus 40 T antigen with replicating nucleoprotein complexes of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):320–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.320-330.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Salzman N. P. Late replicative intermediates are accumulated during simian virus 40 DNA replication in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):600–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.600-609.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Kang J., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Chromatin assembly in isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):349–362. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Structure, spacing, and phasing of nucleosomes on isolated forms of mature simian virus 40 chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):771–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R. T., DePamphilis M. L. In vitro replication of simian virus 40 DNA in a nucleoprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3466–3470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R. T., DePamphilis M. L. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in isolated replicating viral chromosomes. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):53–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.53-65.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Arrest of segregation leads to accumulation of highly intertwined catenated dimers: dissection of the final stages of SV40 DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Terminal stages of SV40 DNA replication proceed via multiply intertwined catenated dimers. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Chromatin assembly. Relationship of chromatin structure to DNA sequence during simian virus 40 replication. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8821–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Distribution of replicating simian virus 40 DNA in intact cells and its maturation in isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):877–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.877-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Anderson S., DePamphilis M. L. Maturation of replicating simian virus 40 DNA molecules in isolated nuclei by continued bidirectional replication to the normal termination region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 22;565(1):84–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Discontinuous DNA replication: accumulation of Simian virus 40 DNA at specific stages in its replication. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 15;120(3):401–422. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Spaeren U., Mastromei G., Eliasson R., Reichard P. Replication of polyoma DNA in nuclear extracts and nucleoprotein complexes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):675–689. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. T., Roman A. Cessation of reentry of simian virus 40 DNA into replication and its simultaneous appearance in nucleoprotein complexes of the maturation pathway. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):255–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.255-262.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





