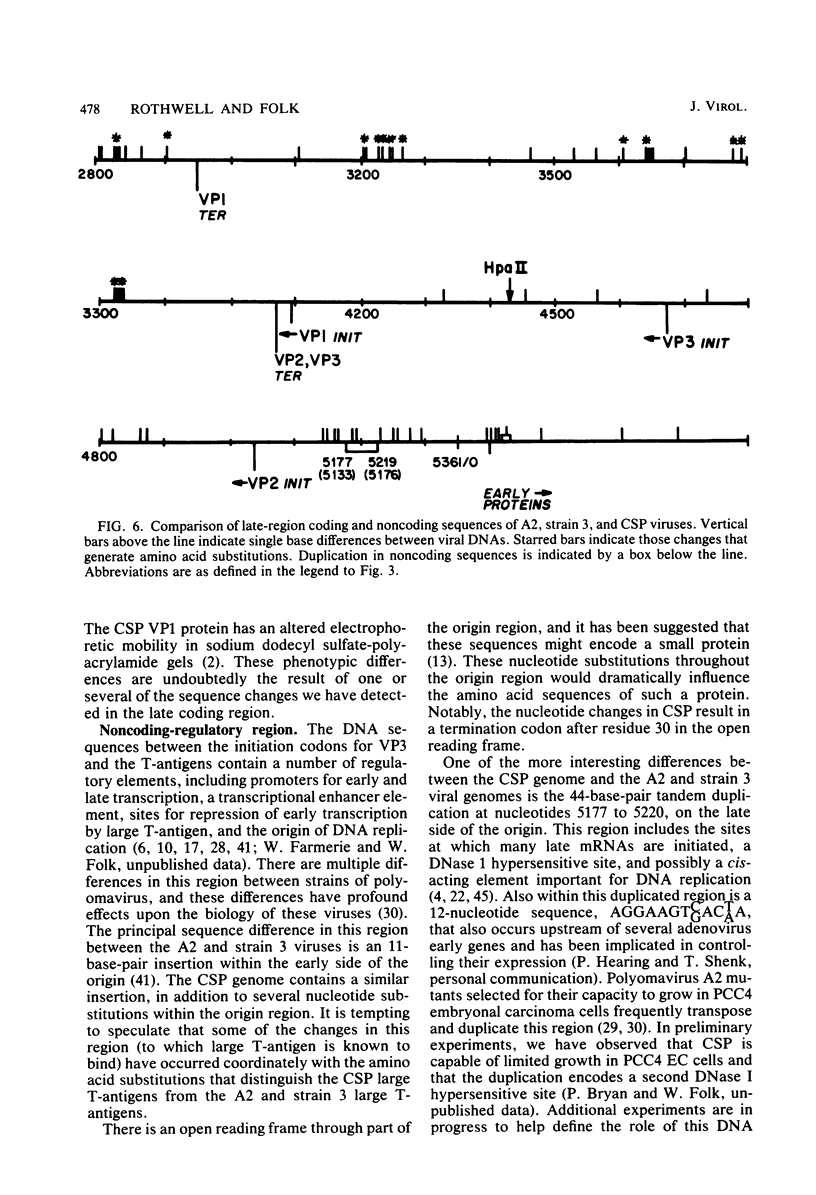
Abstract
The DNA sequence of two wild-type strains of polyomavirus (A2 and strain 3) are known. We have determined the majority of the DNA sequence of a third strain, the Crawford small-plaque virus. This virus has been noted for its capacity to induce readily detected tumor-specific transplantation antigen in hamster cells, a property that is most likely attributable to an altered middle T-antigen. A comparison of its DNA sequence with those of the A2 and strain 3 viruses reveals numerous nucleotide substitutions, insertions, and deletions throughout the genome. Most sequence changes in coding regions are silent mutations; however, variability in proteins can be predicted from these sequence data at 5 locations in middle T-antigen, 10 in large T-antigen, and 10 in VP1. The Crawford small-plaque virus noncoding regulatory region contains, in addition to nucleotide substitutions, a 44-base-pair tandem repeat of sequences on the late side of the origin of DNA replication.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrand J. R., Soeda E., Walsh J. E., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Polyoma virus DNA: Sequence from the late region that specifies the leader sequence for late mRNA and codes for VP2, VP3, and the N-terminus of VP1. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):606–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.606-618.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendig M. M., Thomas T., Folk W. R. Viable deletion mutant in the medium and large T-antigen-coding sequences of the polyoma virus genome. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1215–1220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1215-1220.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V. The adsorption of polyoma virus. Virology. 1962 Oct;18:177–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L., CRAWFORD L. V. SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF LARGE-PLAQUE AND SMALL-PLAQUE LINES OF POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:235–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalianis T., Magnusson G., Ito Y., Klein G. Immunization against the polyoma virus-induced tumor-specific transplantation antigen by early region mutants of the virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):772–777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.772-777.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., LaPorte P., Friedmann T. Nucleotide sequence changes in polyoma ts-a mutants: correlation with protein structure. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):871–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.871-875.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P., Esty A., LaPorte P., Friedmann T. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the polyoma late region: features common to the polyoma early region and SV40. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton R. G., Basilico C. Changes in the topography of early region transcription during polyoma virus lytic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7142–7146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Bancuk J. E. Polyoma genome in hamster BHK-21-C13 cells: integration into cellular DNA and induction of the viral replication. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):133–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.133-141.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Griffin B. E., Lund E., Robberson D. L. Polyoma virus--a study of wild-type, mutant and defective DNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):45–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Esty A., LaPorte P., Deininger P. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of the polyoma early region: extensive nucleotide and amino acid homology with SV40. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudray P., Tyndall C., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The high affinity binding site on polyoma virus DNA for the viral large-T protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5697–5710. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Maddock C. New classes of viable deletion mutants in the early region of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):645–656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.645-656.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare J. D. Transplant immunity to polyoma virus-induced tumor cells. IV. A polyoma strain defective in transplant antigen induction. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiser W. C., Eckhart W. Polyoma virus early and late mRNAs in productively infected mouse 3T6 cells. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):175–188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.175-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Saragosti S., Blangy D., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the origin-proximal DNAase I-hypersensitive region in wild-type and EC mutant polyoma. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):651–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Characterization of T antigens in polyoma-infected and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Martin M. A., Miyamura T., Takemoto K. K., Rifkin D., Pollack R. Phenotype of polyoma-induced hamster tumor cells lines. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):252–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.252-255.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett O. Different transplantation antigens in BHK21 cells transformed by four strains of polyoma virus. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):744–747. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J. Topography of the three late mRNA's of polyoma virus which encode the virion proteins. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):637–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.637-651.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Jat P., Treisman R., Favaloro J., Folk W. R. 5' termini of polyoma virus early region transcripts synthesized in vivo by wild-type virus and viable deletion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):189–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M., Vasseur M., Blangy D. Expression of polyoma early functions in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells depends on sequence rearrangements in the beginning of the late region. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90625-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The nature of the host range restriction of SV40 and polyoma viruses in embryonal carcinoma cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;101:1–30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68654-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Nilsson M. G., Dilworth S. M., Smolar N. Characterization of polyoma mutants with altered middle and large T-antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):673–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.673-683.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyoma viral middle T-antigen is required for transformation. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):621–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.621-629.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Fried M. Construction of infectious polyoma hybrid genomes in vitro. Nature. 1976 Feb 19;259(5544):598–601. doi: 10.1038/259598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Tyndall C., Magnusson G. Deletion mapping of a short polyoma virus middle T antigen segment important for transformation. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):284–287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.284-287.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E., Fried M. Sequence repeats in a polyoma virus DNA region important for gene expression. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.233-237.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Dorai H., Arakere G., Benjamin T. L. Polyoma virus middle T antigen: relationship to cell membranes and apparent lack of ATP-binding activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1187–1198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Ito Y. Differential subcellular localization of in vivo-phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated middle-sized tumor antigen of polyoma virus and its relationship to middle-sized tumor antigen phosphorylating activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6812–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., DePamphilis M. L. Preferred DNA sites are involved in the arrest and initiation of DNA synthesis during replication of SV40 DNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Vollmer P., Folk W. R. Nucleotide sequence changes in polyoma virus A gene mutants. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1094–1098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1094-1098.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Cowie A., Favaloro J., Jat P., Kamen R. The structures of the spliced mRNAs encoding polyoma virus early region proteins. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall C., La Mantia G., Thacker C. M., Favaloro J., Kamen R. A region of the polyoma virus genome between the replication origin and late protein coding sequences is required in cis for both early gene expression and viral DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6231–6250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R. Studies on cells rendered neoplastic by polyoma virus: the problem of the presence of virus-related materials. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:41–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



