Abstract
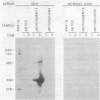
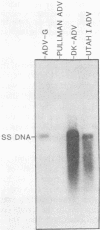
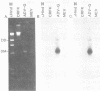
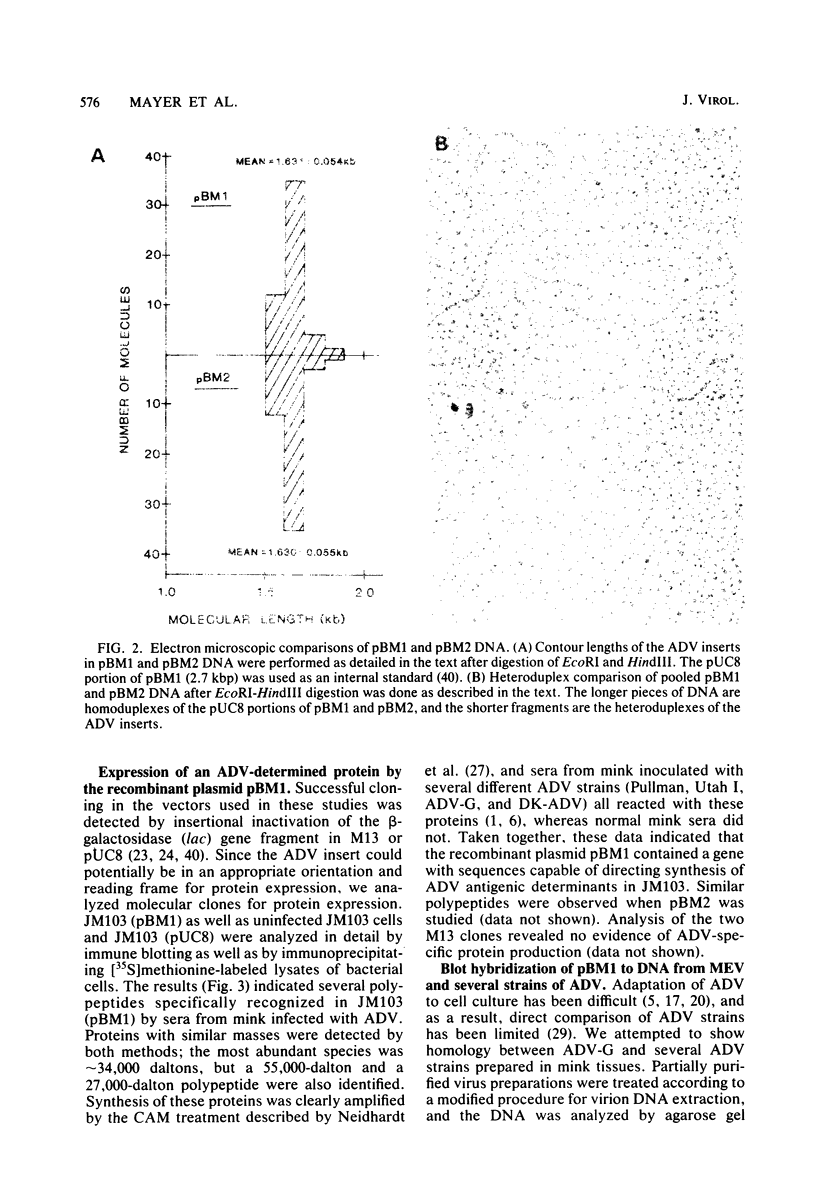
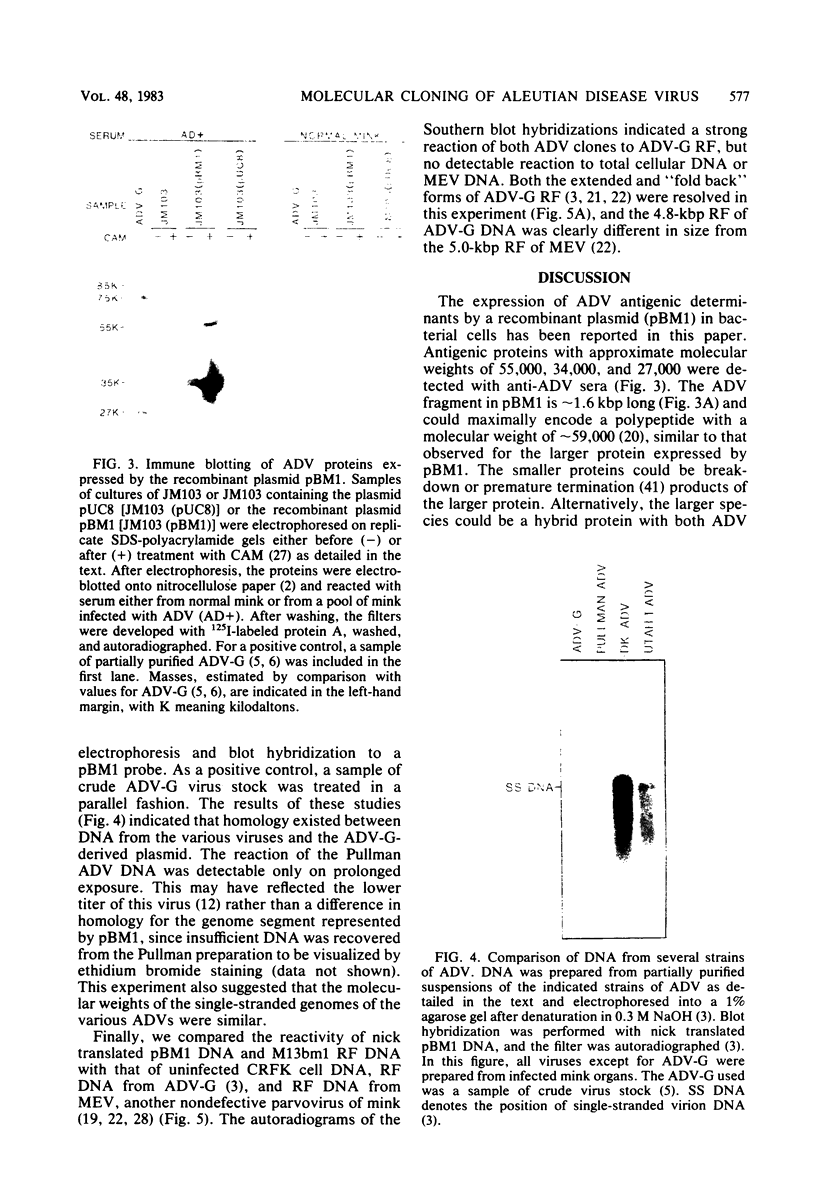
Three nonoverlapping segments representing approximately 80% of the 4.8-kilobase pair Aleutian disease virus (ADV-G) duplex genome were molecularly cloned into either bacteriophage M13mp9 (M13bm2 = 0.07 to 0.15 map unit; M13bm1 = 0.15 to 0.54 map unit) or plasmid pUC8 (pBM1 = 0.54 to 0.88 map units). In addition the 0.54- to 0.88-map unit segment of a Danish isolate of ADV (DK ADV) was also cloned into pUC8 (pBM2). The recombinant plasmids pBM1 and pBM2 induced expression of several polypeptides in Escherichia coli JM103 that were specifically recognized by sera from mink infected with ADV. The same three proteins with approximate molecular weights of 55,000, 34,000, and 27,000 were detected both by immune blotting and by immunoprecipitation of [35S]methionine-labeled JM103 (pBM1). None of these proteins were recognized in JM103 or JM103 (pUC8), nor were they detected by sera from normal mink. Purified pBM1 and pBM2 DNA appeared identical in size by gel analysis and contour length measurement, and electron microscopic heteroduplex mapping revealed no visible areas of heterology. However, restriction endonuclease mapping showed that pBM2 was different from pBM1, indicating that this segment of the ADV genome was similar but not identical for two strains of ADV (ADV-G and DK ADV). Furthermore, when cloned DNA from ADV-G was labeled with [32P]dCTP by nick translation, DNA relatedness to several field strains of ADV (Utah I, Pullman, and DK), but not to mink enteritis virus or cellular DNA, was shown by Southern blot hybridization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B. Purification and characterization of Aleutian disease virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Dec;88(6):323–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Mayer L. W., Garon C. F. Characterization of the Aleutian disease virus genome and its intracellular forms. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):977–984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.977-984.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Hadlow W. J., Chesebro B. Aleutian disease of mink: the antibody response of sapphire and pastel mink to Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1034–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Characterization of Aleutian disease virus as a parvovirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.836-843.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Identification of a nonvirion protein of Aleutian disease virus: mink with Aleutian disease have antibody to both virion and nonvirion proteins. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):608–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.608-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Rose J. A. Transcription of adenovirus-associated virus RNA in isolated KB cell nuclei. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):118–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. H., Scott F. W., Duncan J. R. Feline Panleukopenia. I. Pathogenesis in germfree and specific pathogen-free cats. Vet Pathol. 1977 Jan;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1177/030098587701400110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ingram D. G. The antigen and virus of Aleutian disease in mink. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Mar;4(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Fabricant C. G., Nelson-Rees W. A. Development, characterization, and viral susceptibility of a feline (Felis catus) renal cell line (CRFK). In Vitro. 1973 Nov-Dec;9(3):176–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02618435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Vovis G. F., Zinder N. D. Genetic studies with heteroduplex DNA of bacteriophage fl. Asymmetric segregation, base correction and implications for the mechanism of genetic recombination. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 15;96(3):495–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F. Electron microscopy of nucleic acids. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:573–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. R., Colot H. V., Guarente L., Rosbash M. Open reading frame cloning: identification, cloning, and expression of open reading frame DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E. C., Ramos L., Kenyon A. J. Expression of Aleutian mink disease antigen in cell culture. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.204-211.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Siegl G., Gautschi M. Characteristics of feline panleucopaenia virus strains enabling definitive classification as parvoviruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;46(3-4):315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF01240073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Tratschin J. D., Siegl G. Comparison of canine parvovirus with mink enteritis virus by restriction site mapping. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):368–371. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.368-371.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. L., Alberts J. O., Brandly C. A. Certain Characteristics Of The Virus Of Infectious Enteritis Of Mink And Observations On Pathogenesis Of The Disease - Preliminary Report. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1959 Sep;23(9):282–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Wirth R., Smith M. W., Van Bogelen R. Selective synthesis of plasmid-coded proteins by Escherichia coli during recovery from chloramphenicol treatment. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):535–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.535-537.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER D. D., DIXON F. J., LARSEN A. E. METABOLISM AND FUNCTION OF GAMMA GLOBULIN IN ALEUTIAN DISEASE OF MINK. J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:889–900. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Carmichael L. E., Antczak D. F. Antigenic relationships between canine parvovirus type 2, feline panleukopenia virus and mink enteritis virus using conventional antisera and monoclonal antibodies. Arch Virol. 1982;72(4):267–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01315223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Cox N. A., Porter H. G., Suffin S. C. Isolation of Aleutian disease virus of mink in cell culture. Intervirology. 1977;8(3):129–144. doi: 10.1159/000148888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. 3. Immune complex arteritis. Am J Pathol. 1973 May;71(2):331–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. II. Enhancement of tissue lesions following the administration of a killed virus vaccine or passive antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Klaassen B. DNA sequence of the 5' terminus containing the replication origin of parvovirus replicative form DNA. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):990–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.990-999.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Paradiso P. R. Parvovirus genome: nucleotide sequence of H-1 and mapping of its genes by hybrid-arrested translation. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.173-184.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]