Abstract
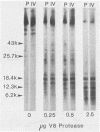
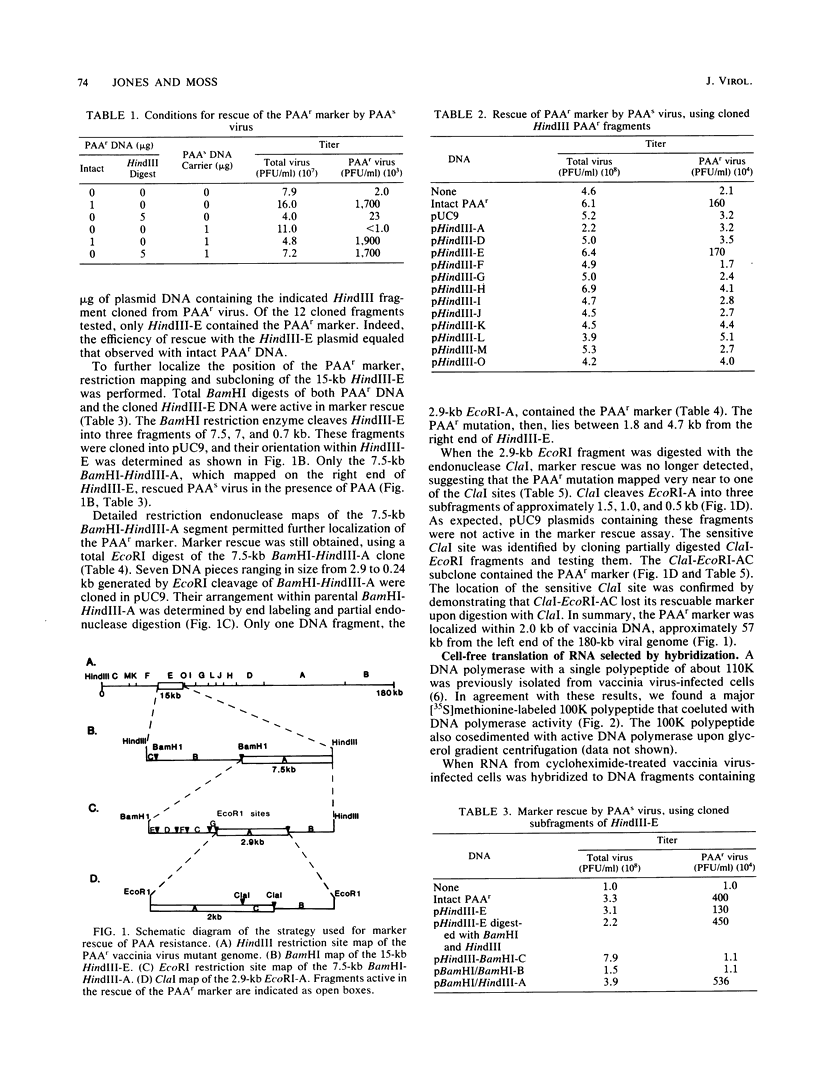
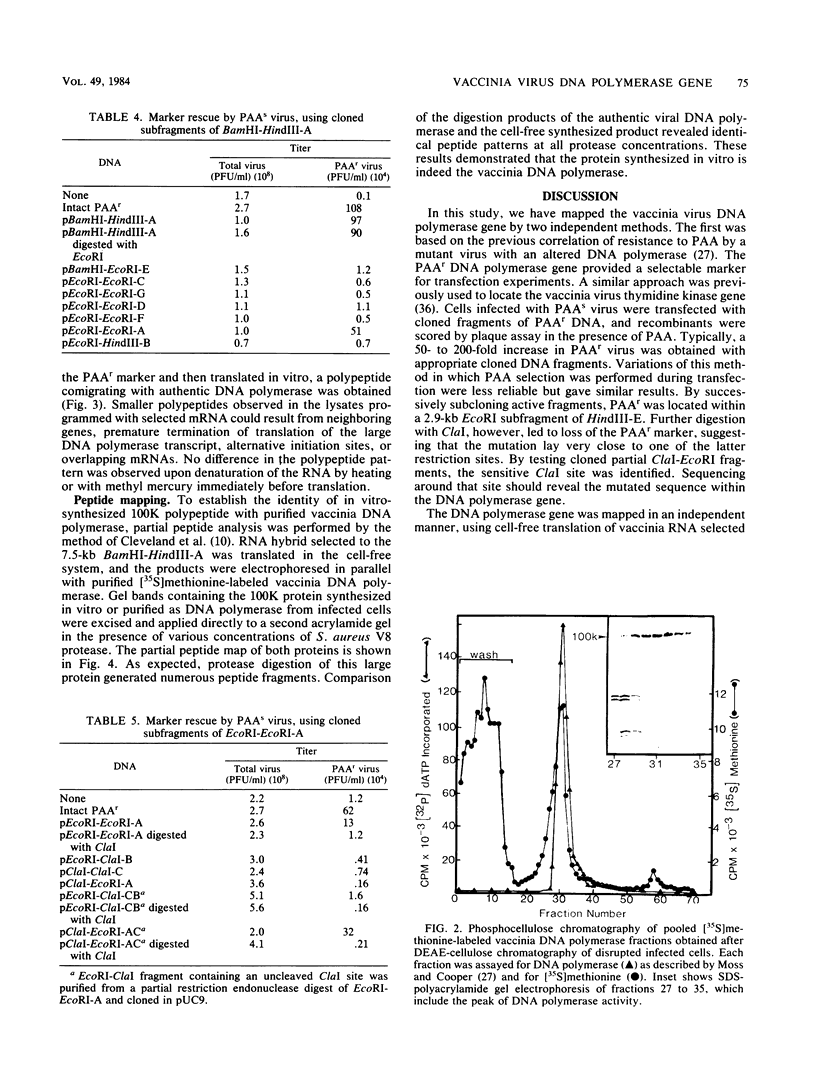
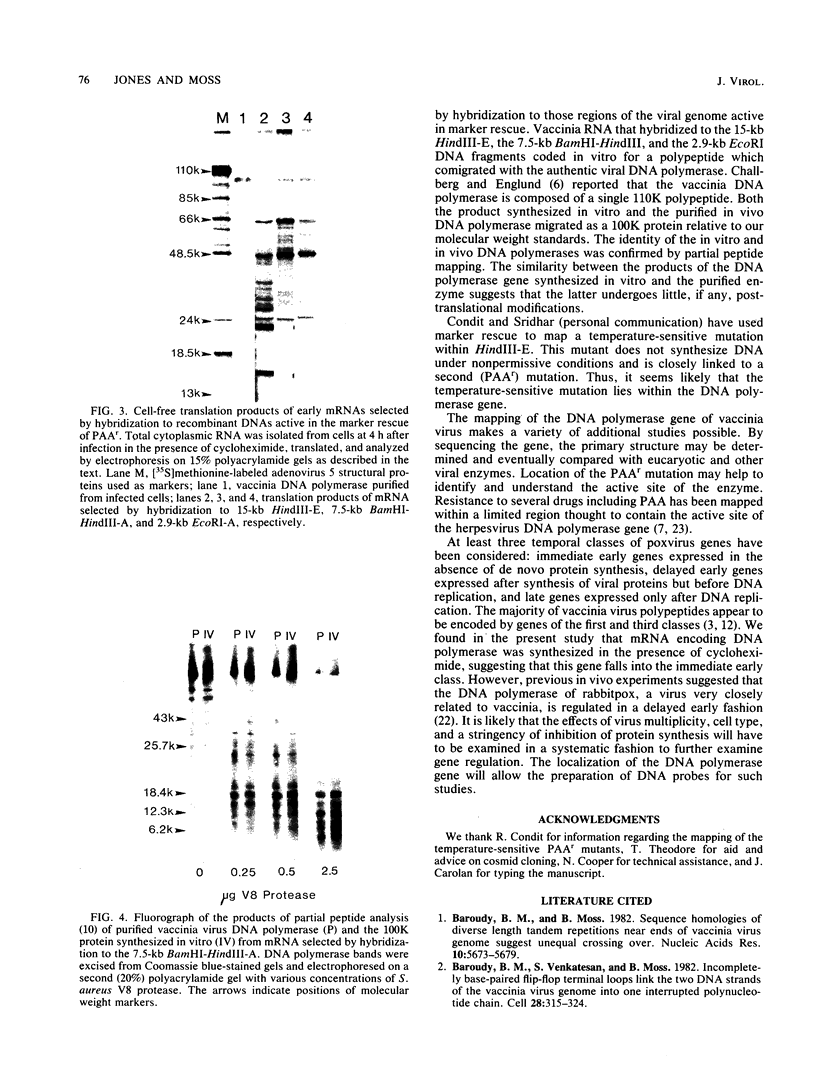
The previous demonstration that a phosphonoacetate (PAA)-resistant (PAAr) vaccinia virus mutant synthesized an altered DNA polymerase provided the key to mapping this gene. Marker rescue was performed in cells infected with wild-type PAA-sensitive (PAAs) vaccinia by transfecting with calcium phosphate-precipitated DNA from a PAAr mutant virus. Formation of PAAr recombinants was measured by plaque assay in the presence of PAA. Of the 12 HindIII fragments cloned in plasmid or cosmid vectors, only fragment E conferred the PAAr phenotype. Successive subcloning of the 15-kilobase HindIII fragment E localized the marker within a 7.5-kilobase BamHI-HindIII fragment and then within a 2.9-kilobase EcoRI fragment. When the latter was digested with ClaI, marker rescue was not detected, suggesting that the PAAr mutation mapped near a ClaI site. The sensitive ClaI site was identified by cloning partial ClaI-EcoRI fragments and testing them in the marker rescue assay. The location of the DNA polymerase gene, about 57 kilobases from the left end of the genome, was confirmed by cell-free translation of mRNA selected by hybridization to plasmids containing regions of PAAr vaccinia DNA active in marker rescue. A 100,000-dalton polypeptide that comigrated with authentic DNA polymerase was synthesized. Correspondence of the in vitro translation product with purified vaccinia DNA polymerase was established by peptide mapping.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Sequence homologies of diverse length tandem repetitions near ends of vaccinia virus genome suggest unequal crossing over. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5673–5679. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Incompletely base-paired flip-flop terminal loops link the two DNA strands of the vaccinia virus genome into one uninterrupted polynucleotide chain. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Aucker J., Weissbach A. Synthesis of herpes simplex virus, vaccinia virus, and adenovirus DNA in isolated HeLa cell nuclei. I. Effect of viral-specific antisera and phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1584–1592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1584-1592.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Englund P. T. Purification and properties of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase induced by vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7812–7819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipchase M., Schwendimann F., Wyler R. A map of the late proteins of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citarella R. V., Muller R., Schlabach A., Weissbach A. Studies on vaccinia virus-directed deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):721–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.721-729.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. In vitro translation of immediate early, early, and late classes of RNA from vaccinia virus-infected cells. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus mRNA coupled to translation in vitro. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Wittek R., Moss B. Hybridization selection and cell-free translation of mRNA's encoded within the inverted terminal repetition of the vaccinia virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):284–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.284-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFilippes F. M. Restriction enzyme mapping of vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):136–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.136-149.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Barbosa E., Moss B. Visualization of an inverted terminal repetition in vaccinia virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4863–4867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geshelin P., Berns K. I. Characterization and localization of the naturally occurring cross-links in vaccinia virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):785–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Mapping and identification of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):403–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.403-409.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isle H. B., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Cell-free translation of early and late mRNAs selected by hybridization to cloned DNA fragments derived from the left 14 million to 72 million daltons of the vaccinia virus genome. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90636-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Messenger RNA synthesis by a "coated" viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):314–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W., Kaufman E. R., Crumpacker C. Physical mapping of drug resistance mutations defines an active center of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase enzyme. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):746–757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.746-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Cooper N. Genetic evidence for vaccinia virus-encoded DNA polymerase: isolation of phosphonoacetate-resistant enzyme from the cytoplasm of cells infected with mutant virus. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):673–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.673-678.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Winters E., Cooper J. A. Deletion of a 9,000-base-pair segment of the vaccinia virus genome that encodes nonessential polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):387–395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.387-395.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano E., Panicali D., Paoletti E. Molecular genetics of vaccinia virus: demonstration of marker rescue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1593–1596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overby L. R., Duff R. G., Mao J. C. Antiviral potential of phosphonoacetic acid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:310–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Davis S. W., Mercer S. R., Paoletti E. Two major DNA variants present in serially propagated stocks of the WR strain of vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1000–1010. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1000-1010.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bajszár G., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene by marker rescue and by cell-free translation of selected mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Hammarskjöld M. L. Isolation of DNA from agarose gels using DEAE-paper. Application to restriction site mapping of adenovirus type 16 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):253–264. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Menna A., Müller H. K., Schümperli D., Boseley P. G., Wyler R. Inverted terminal repeats in rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):171–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.171-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Menna A., Schümperli D., Stoffel S., Müller H. K., Wyler R. HindIII and Sst I restriction sites mapped on rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):669–678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.669-678.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Moss B. Tandem repeats within the inverted terminal repetition of vaccinia virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]