Abstract
A microtechnique is described for the determination of vibriocidal antibodies to Vibrio cholerae, using 0.025 ml of fingertip blood or venous serum per test. This test could be used in epidemiological surveys, or as a routine test on patients admitted to hospital.
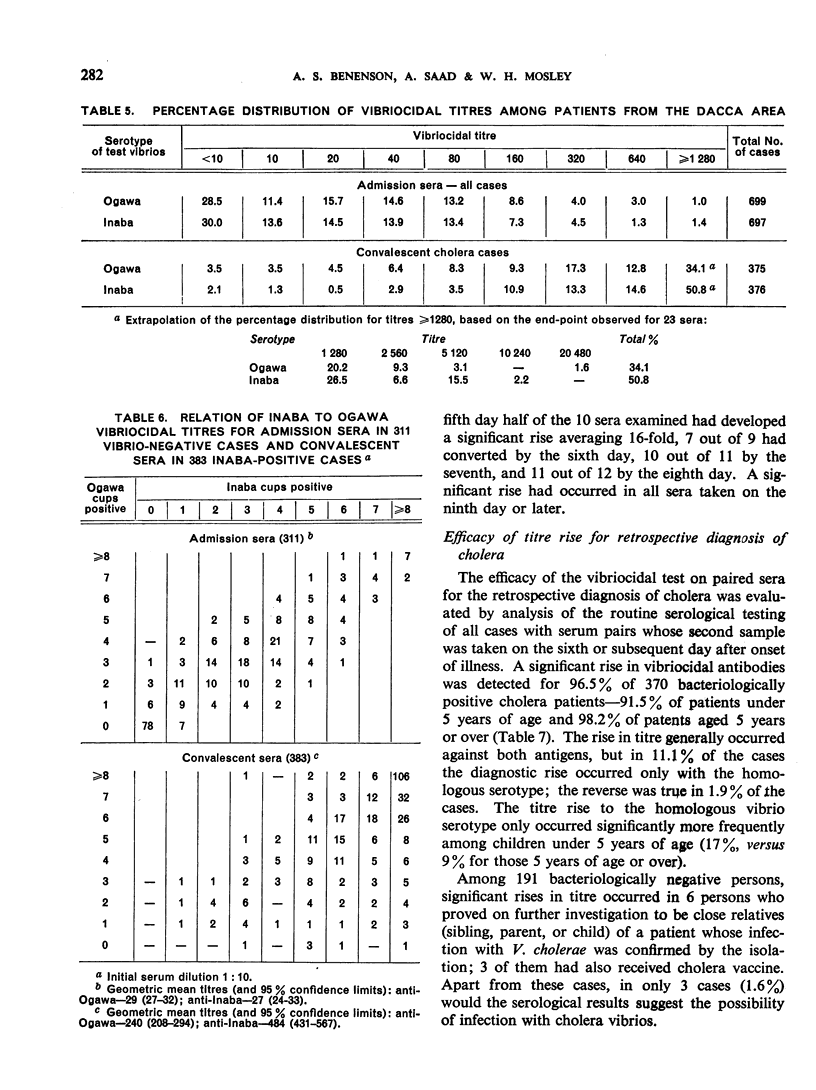
Fourfold or greater rises in vibriocidal titre were noted for 96.5% of 370 bacteriologically confirmed cholera patients in an endemic area of East Pakistan (91.5% for the 94 children under 5 years in the study group). It is necessary to test sera against both Ogawa and Inaba serotypes of V. cholerae, as a significant titre rise was found against the homologous serotype only in 11% of the cases, and against the heterologous serotype only in 2%.
Six serologically positive but bacteriologically negative persons were found to be household contacts of confirmed cholera patients (and 3 of the contacts had been vaccinated against cholera within 1 week before testing); 3 other cases (1.6%) were considered to be false positives.
The vibriocidal test using fingertip blood was compared with daily rectal swabbing for the detection of cholera carriers among 153 household contacts of cholera patients, who had not received cholera vaccine within 2 weeks before testing; 16% gave a positive vibriocidal titre, while V. cholerae was isolated from 13% only.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benenson A. S., Saad A., Paul M. Serological studies in cholera. I. Vibrio agglutinin response of cholera patients determined by a microtechnique. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(2):267–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSIZMAS L. Preparation of formalinized erythrocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Jan;103:157–160. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., FEELEY J. C. PASSIVE SERUM PROTECTION OF THE INFANT RABBIT AGAINST EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA. J Infect Dis. 1964 Dec;114:468–475. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.5.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., TREFFERS H. P. Quantitative studies on the bactericidal actions of serum and complement. I. A rapid photometric growth assay for bactericidal activity. J Immunol. 1956 Jan;76(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Barua D., Saxena R., Carpenter C. C. Vibriocidal and agglutinating antibody patterns in cholera patients. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):630–640. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



