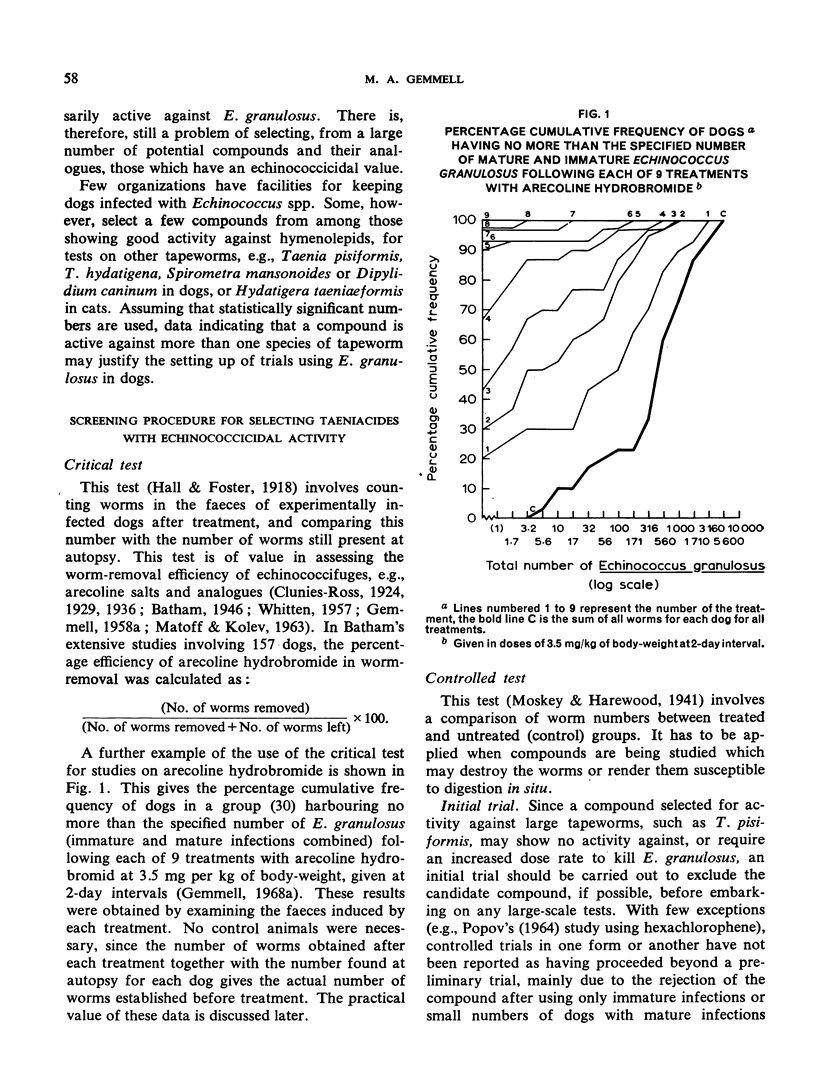
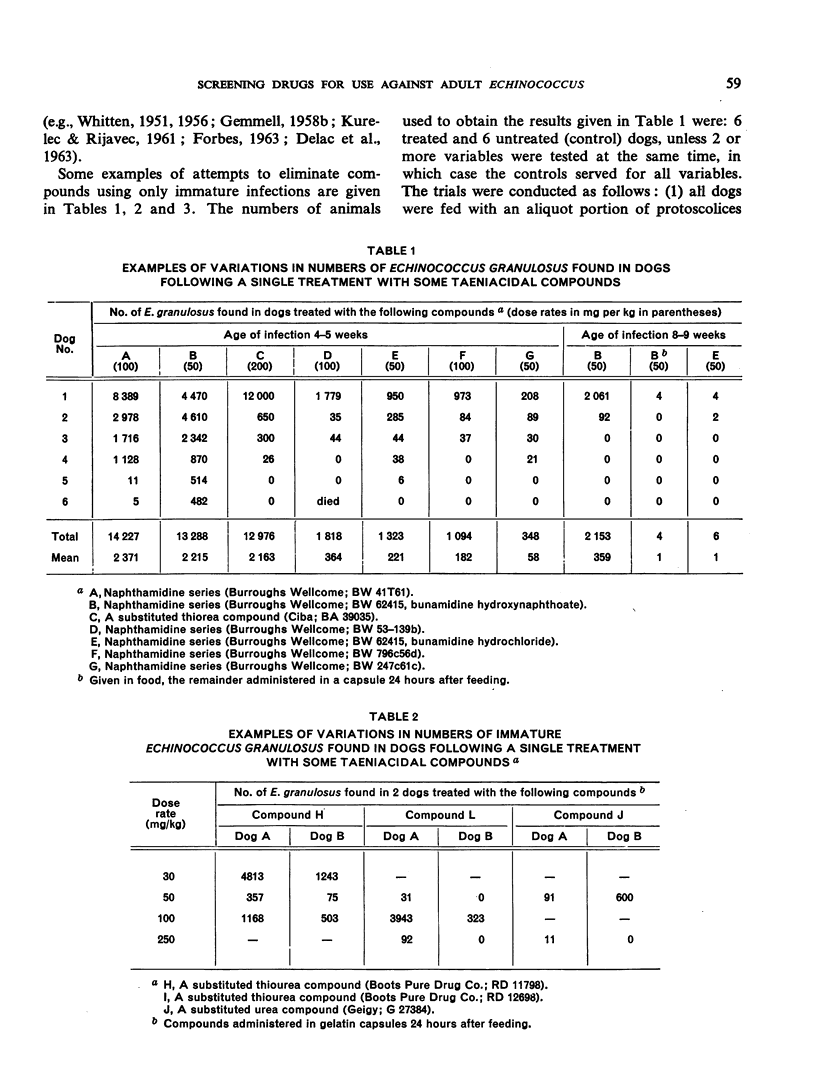
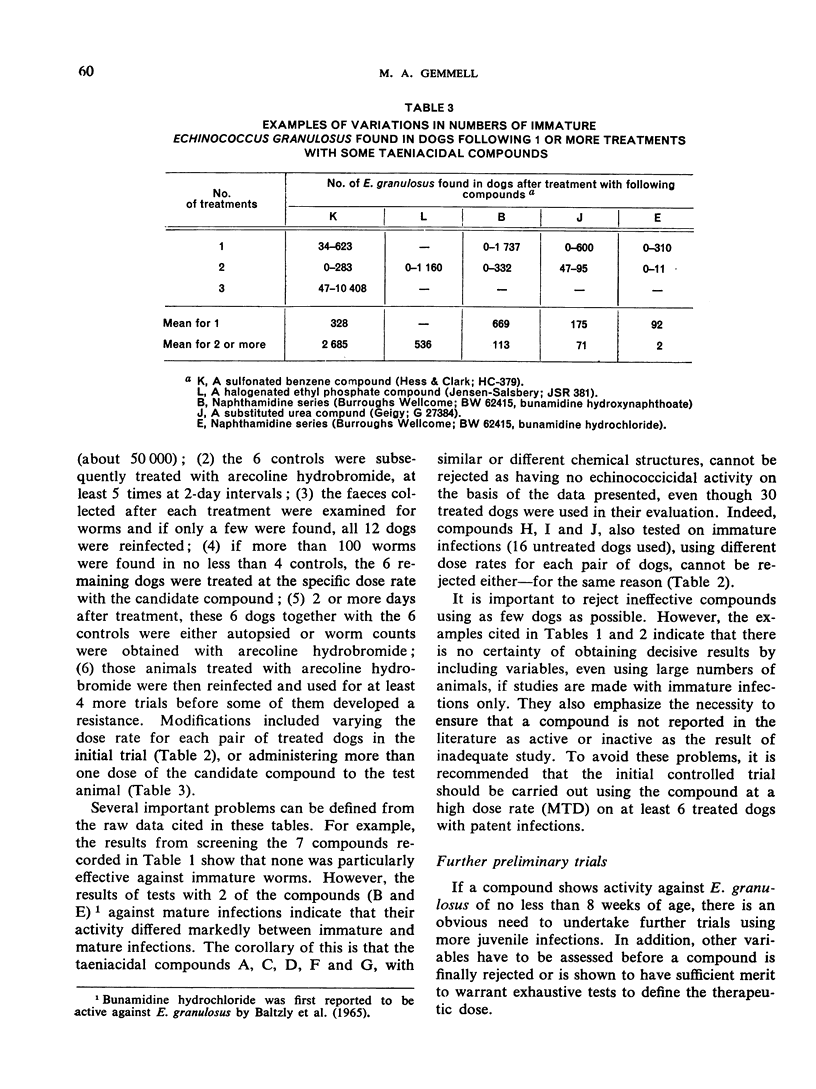
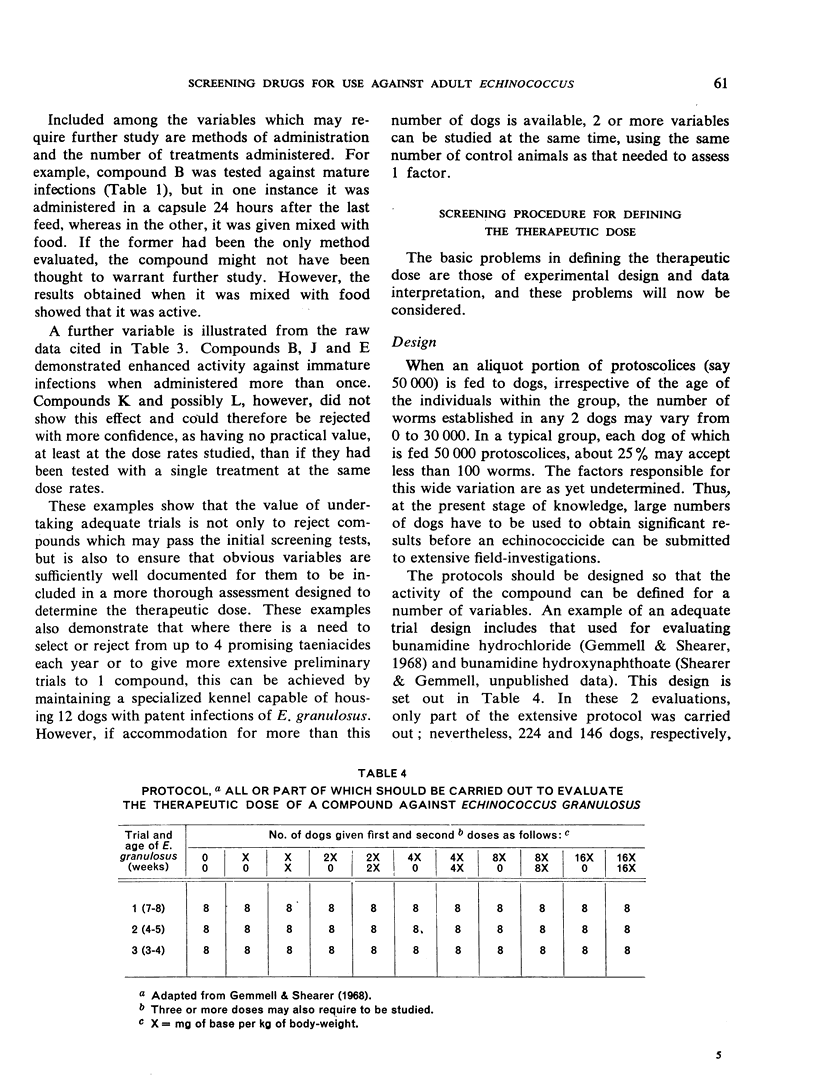
Abstract
From time to time, reports of anthelmintic trials are published indicating that a compound is, or is not, effective against Echinococcus granulosus in dogs. In some of these reports, an attempt is made to assess the efficacy of the compound from inadequate data. This paper reviews the problems associated with selecting, screening and defining the therapeutic dose-rate of a compound against E. granulosus. From this evaluation, a programme is defined, which, if followed, should result in the selection of promising compounds and the rejection of unsuccessful compounds at specific stages during the programme.
Full text
PDF
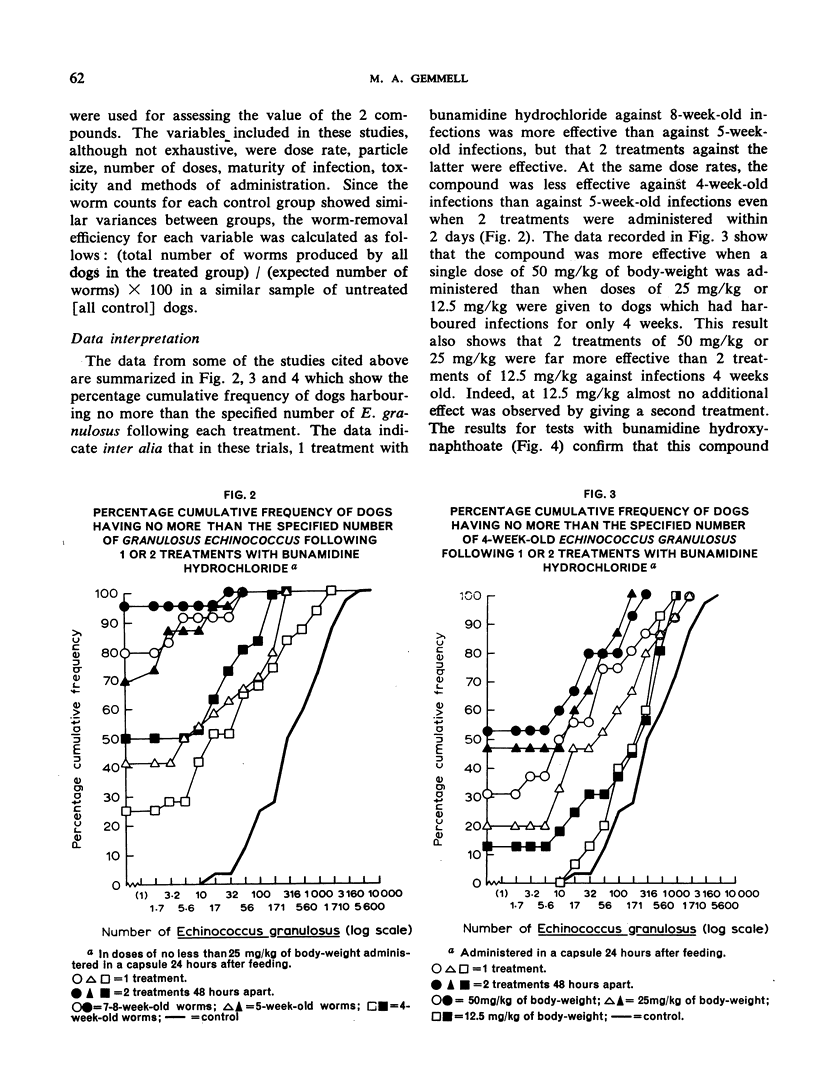
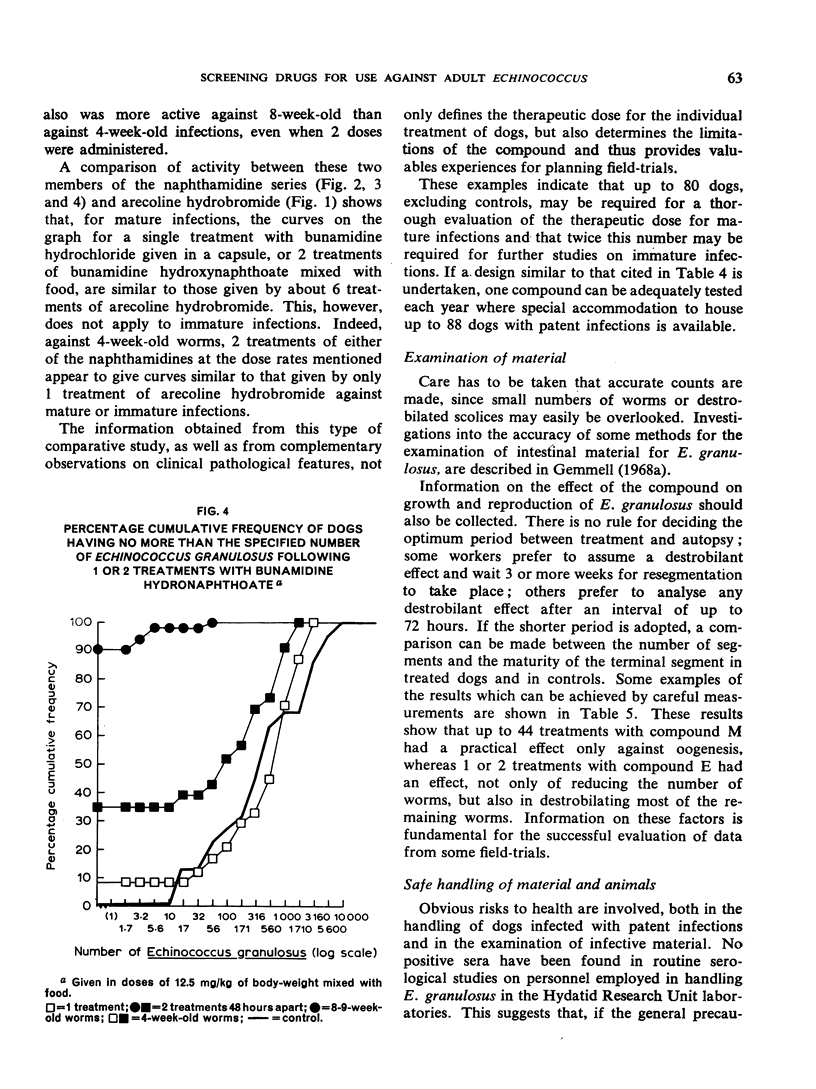
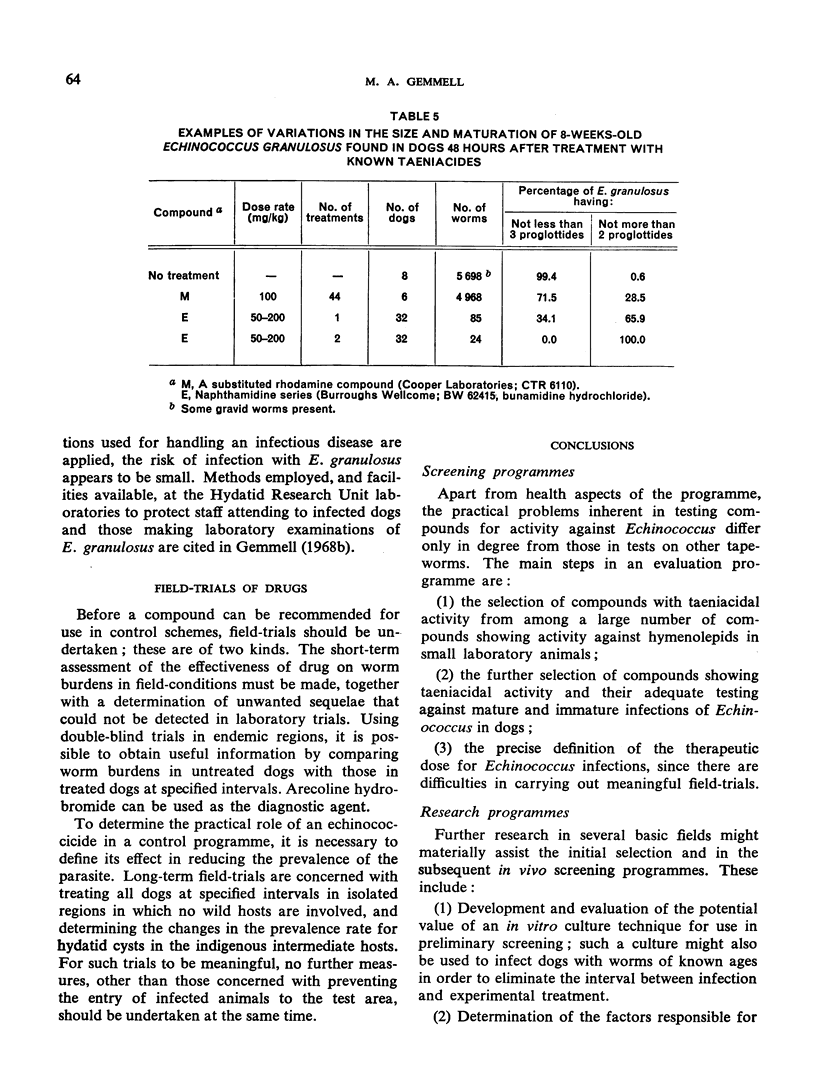

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltzly R., Burrows R. B., Harfenist M., Fuller K. A., Keeling J. E., Standen O. D., Hatton C. J., Nunns V. J., Rawes D. A., Blood B. D. A series of compounds active against cestodes. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):408–409. doi: 10.1038/206408b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE M. R. A., MANSOUR T. E. A kymographic study of the action of drugs on the liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1949 Mar;4(1):7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1949.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES G. B. NUTRITIONAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE WHOLE BODY COUNTER. Nutr Rev. 1963 Nov;21:321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1963.tb04688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell M. A. Safe handling of infected definitive hosts and eggs of Echinococcus spp. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(1):122–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell M. A. The Styx field-trial. A study on the application of control measures against hydatid disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(1):73–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


