Abstract
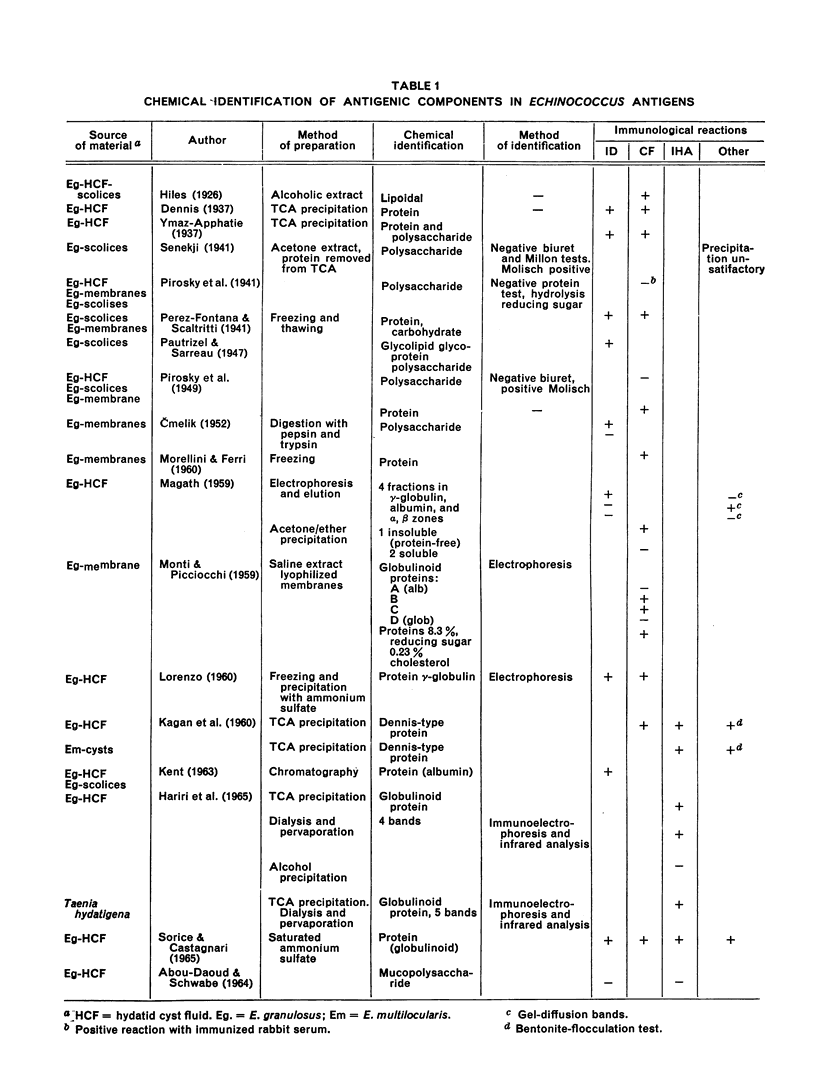
Much of the work on immunology of hydatidosis has so far been devoted to the development of suitable methods for serological diagnosis. The precise nature of hydatid antigens and their chemical characterization has still not been worked out, largely because of the complex life-history of the parasite and the difficulties of in vitro cultivation. The most widely used antigen for routine serological testing in hydatidosis caused by Echinococcus granulosus is fluid taken from the cyst. This fluid is, however, a complex mixture of substances and contains several protein and carbohydrate fractions as well as end-products of carbohydrate and protein metabolism. The cyst fluid from different sources is variable in its antigenic properties, and the fluid from sterile cysts is especially lacking in antigenic activity. Antigens from tissue extracts of hydatid cysts appear to have greater specificity. Cyst extracts of E. multilocularis, the cysts of which contain relatively little fluid, have also been used but are poor antigens, and contain measurable amounts of host protein. Antigens prepared from other cestodes and metabolic antigens are also reviewed.
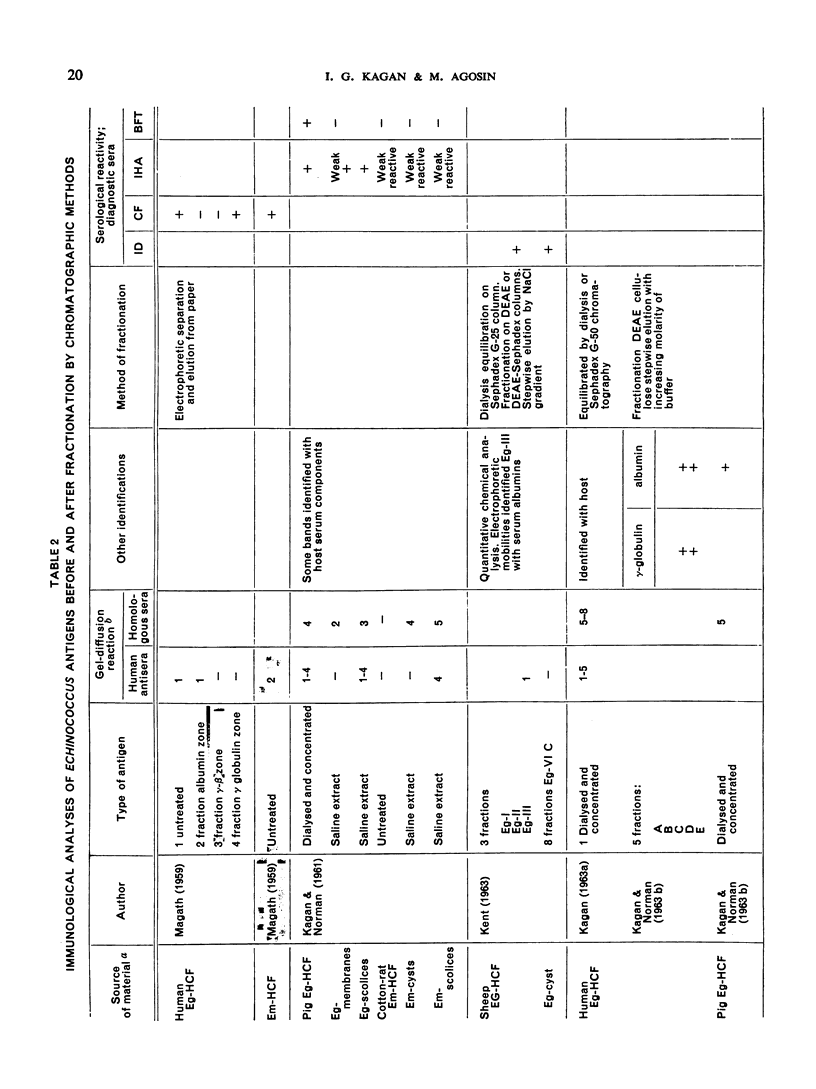
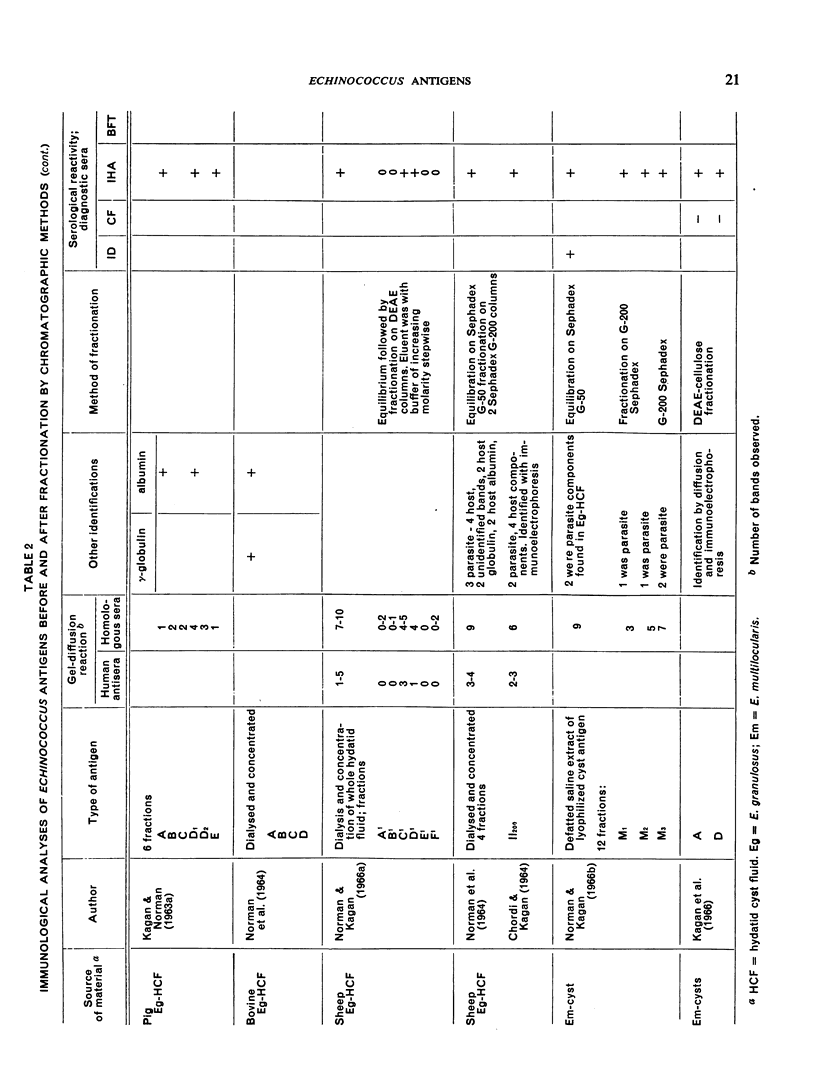
Biochemical analysis of Echinococcus antigens covering polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and blood-group substances is considered, together with the characterization of antigens by electrophoresis, column chromatography and gel-diffusion methods. The problems associated with the standardization of antigens are discussed. Recent data on the character and reactivity of antigens employed in Echinococcus studies are summarized.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELSON N. M., RAWSON A. J. [Studies of blood group antibodies. I. Fractionation of anti-A and anti-B Isohemagglutinins by anioncation cellulose exchange chromatography]. J Immunol. 1959 May;82(5):435–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABOU-DAOUD K., SCHWABE C. W. EPIDEMIOLOGY OF ECHINOCOCCOSIS IN THE MIDDLE EAST. 3. A STUDY OF HYDATID DISEASE PATIENTS FROM THE CITY OF BEIRUT. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Sep;13:681–685. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M., ARAVENA L. Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. III. Glycolysis, with special reference to hexokinases and related glycolytic enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:90–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M., ARAVENA L. Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. IV. Enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway. Exp Parasitol. 1960 Sep;10:28–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(60)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M., ARAVENA L. Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. V. The phosphopentose isomerase of hydatid cyst scolices. Enzymologia. 1960 Dec 31;22:281–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M., REPETTO Y. STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS. VII. REACTIONS OF THE TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE IN E. GRANULOSUS SCOLICES. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1963 Mar;9:245–261. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(63)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M. Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. II. Some observations on the carbohydrate metabolism of hydatid cyst scolices. Exp Parasitol. 1957 Nov;6(6):586–593. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(57)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AGOSIN M., VON BRAND T., RIVERA G. F., MCMAHON P. Studies on the metabolism of Echinococcus granulosus. I. General chemical composition and respiratory reactions. Exp Parasitol. 1957 Jan;6(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(57)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARABATZIS G., PAPAPANAGIOTOU J. Laboratory tests in hydatid disease: a comparison of the indirect haemagglutination, complement-fixation and intradermal tests. Bull World Health Organ. 1963;28(2):266–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSTED H. J., ATKINSON J. D. Hydatid disease; serological reactions with standardised reagents. Lancet. 1953 Feb 7;1(6754):265–268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90937-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUEDING E., HAWKINS J. T. ENZYMIC DEGRADATION AND MICRODETERMINATION OF GLYCOGEN. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:26–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMERON G. L., STAVELEY J. M. Blood group P substance in hydatid cyst fluids. Nature. 1957 Jan 19;179(4551):147–148. doi: 10.1038/179147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARBONE G., LORENZETTI L. Osservazioni in tema di idatidosi. I. Studio della composizione del liquido cistico in relazione al diverso stato biologico dell'idatide. Rass Med Sarda. 1957 Sep-Oct;59(5):519–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHORDI A., KAGAN I. G. ANALYSIS OF NORMAL SHEEP SERUM BY IMMUNOELECTROPHORESIS. J Immunol. 1964 Sep;93:439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHORDI A., KAGAN I. G. IDENTIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ANTIGENIC COMPONENTS OF SHEEP HYDATID FLUID BY IMMUNOELECTROPHORESIS. J Parasitol. 1965 Feb;51:63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CMELIK S. Ein antigenes Polysaccharid aus den Echinococcuscysten. Biochem Z. 1952 May;322(6):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CMELKI S., BRISKI B. Untersuchungen über Eiweissfraktionen von Taenia echinococcus. Biochem Z. 1953;324(2):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHMAN A. REACTIVITY OF LATEX AND COMPLEMENT FIXATION TESTS IN HYDATID DISEASE. J Parasitol. 1965 Aug;51:497–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODCHILD C. G., KAGAN I. G. Comparison of proteins in hydatid fluid and serum by means of electrophoresis. J Parasitol. 1961 Apr;47:175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALBERT S. P. Naturally occurring human antibodies to streptococcal enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 8;103:1027–1051. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIDELBERGER M., AISENBERG A. C., HASSID W. Z. Glycogen, an immunologically specific polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1954 Apr 1;99(4):343–353. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.4.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., GOODCHILD C. G. Paper electrophoresis of sera from man and experimental animals infected with various helminths. J Parasitol. 1961 Jun;47:373–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., NORMAN L. ANALYSIS OF HELMINTH ANTIGENS (ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS AND SCHISTOSOMA MANSONI) BY AGAR GEL METHODS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;113:130–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb40663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., NORMAN L. Antigenic analysis of Echinococcus antigens by agar diffusion techniques. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Sep;10:727–734. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1961.10.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN I. G., NORMAN L. THE ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TWO HOST ANTIGENS IN HYDATID FLUID OF ECHINOCOCCUS GRANULOSUS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 May;12:346–357. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT N. H. Seminar on immunity to parasitic helminths. V. Antigens. Exp Parasitol. 1963 Feb;13:45–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(63)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERDE C., FUENFHAUSEN G., BRUNK R. [On the production of high titer anti-P-immune sera by immunization with echinococcal cyst fluid]. Z Immun exp ther. 1960 Feb;119:216–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILEJIAN A., SAUER K., SCHWABE C. W. Host-parasite relationships in echnoccosis. VIII. Infrared spectra and chemical composition of the hydatid cyst. Exp Parasitol. 1962 Oct;12:377–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(62)90049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILEJIAN A., SCHINAZI L. A., SCHWABE C. W. Host-parasite relationships in echinococcosis. V. Histochemical observations on Echinococcus granulosus. J Parasitol. 1961 Apr;47:181–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G., Osimani J. J., Varela J. C., Allain D. S. Evaluation of intradermal and serologic tests for the diagnosis of hydatid disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):172–179. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE P., CELANO M., STAVELEY J. M. The antigenicity of P substance in echinococcus cyst fluid coated on to tanned red cells. Vox Sang. 1958 Dec;3(6):434–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1958.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGATH T. B. The antigen of Echinococcus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jan;31(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/31.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURER P. H. Antigenicity of polypeptides (poly alpha amino acids). X. Studies with polymers of D amino acids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jul;113:553–557. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRITT M., HARDY J. Notes on a serum containing anti-P in high titre. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Nov;8(4):329–330. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.4.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTI G. F., PICCIOCCHI A. In tema di diagnosi sierologica dell'echinococcosi: la reazione con antigene estratto da membrana idatidea (secondo Morellini-Ferri-Romeo). Policlinico Chir. 1959 Apr;66(2):102–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORELLINI M., FERRI L., ROMEO V. Proposta di un nuovo antigene per le deviazione del complemento nella diagnosi sierologica dell'echinococcosi. Policlinico Prat. 1957 Aug 26;64(34):1117–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYA V., SANTAMARINA G. [Study of the Casoni test in the diagnosis of hydatidosis]. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1963 Jan-Mar;18:2–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBILI I., COSENTINO G., RIZZO G. CONTRIBUTO ALLA DIAGNOSI DELL' IDATIDOSI UMANA MEDIANTE LA FISSAZIONE DEL COMPLEMENTO CON ANTIGENE IDATIDEO CRIOLISATO ED ULTRACENTRIFUGATO. Riv Ist Sieroter Ital. 1963 Nov-Dec;38:296–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN L., KAGAN I. G., CHORDI A. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ANALYSIS OF SHEEP HYDATID FLUID BY AGAR GEL METHODS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Nov;13:816–821. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1964.13.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN L., KAGAN I. G. The maintenance of Echinococcus multilocularis in gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) by intraperitoneal inoculation. J Parasitol. 1961 Dec;47:870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN L., SADUN E. H., ALLAIN D. S. A bentonite flocculation test for the diagnosis of hydatid disease in man and animals. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Jan;8(1):46–50. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1959.8.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS T. J. BLOOD GROUP P: SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF ECHINOCOCCUS AND CARCINOMA. Med J Aust. 1965 May 29;1(22):792–794. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1965.tb72215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVOSELSKA-TEOHAROVA L. ON THE ANTIGENS OF THE ECHINOCOCCUS AND ITS INTERMEDIARY HOST. C R Acad Bulg Sci. 1964;17:163–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G., Allain D. S. Preparation and evaluation of antigens for use in the serologic diagnosis of human hydatid disease. II. Isolation and characterization from extracts of cysts of Echinococcus multilocularis of serologically reactive elements found in hydatid fluid of Echinococcus granulosus. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):822–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman L., Kagan I. G. Preparation and evaluation of antigens for use in the serologic diagnosis of human hydatid disease. I. Identification and partial purification of the reactive elements in Echinococcus granulosus antigen prepared from sheep hydatid fluid. J Immunol. 1966 May;96(5):814–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUTRIZEL R., BAILENGER J. [Immunological diagnosis of echinococcosis]. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1961 Mar-Apr;19:243–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROKOP O., OESTERLE P. Zur Frage der P-Antigenität von Echinokokkenflüssigkeit aus Schweinelebern. Blut. 1958 Jun;4(3):157–158. doi: 10.1007/BF01631739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWABE C. W., DAOUD K. A. Epidemiology of echinococcosis in the Middle East. I. Human infection in Lebanon, 1949 to 1959. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 May;10:374–381. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1961.10.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWABE C. W. Host-parasite relationships in echinococcosis. I. Observations on the permeability of the hydatid cyst wall. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Jan;8(1):20–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWABE C. W., KOUSSA M., ACRA A. N. Host-parasite relationships in echinococcosis--IV. Acetylcholinesterase and permeability regulation in the hydatid cyst wall. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1961 Mar;2:161–172. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(61)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVELEY J. M., CAMERON G. L. The inhibiting action of hydatid cyst fluid on anti-Tj a sera. Vox Sang. 1958 Mar;3(2):114–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1958.tb03602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


