Abstract
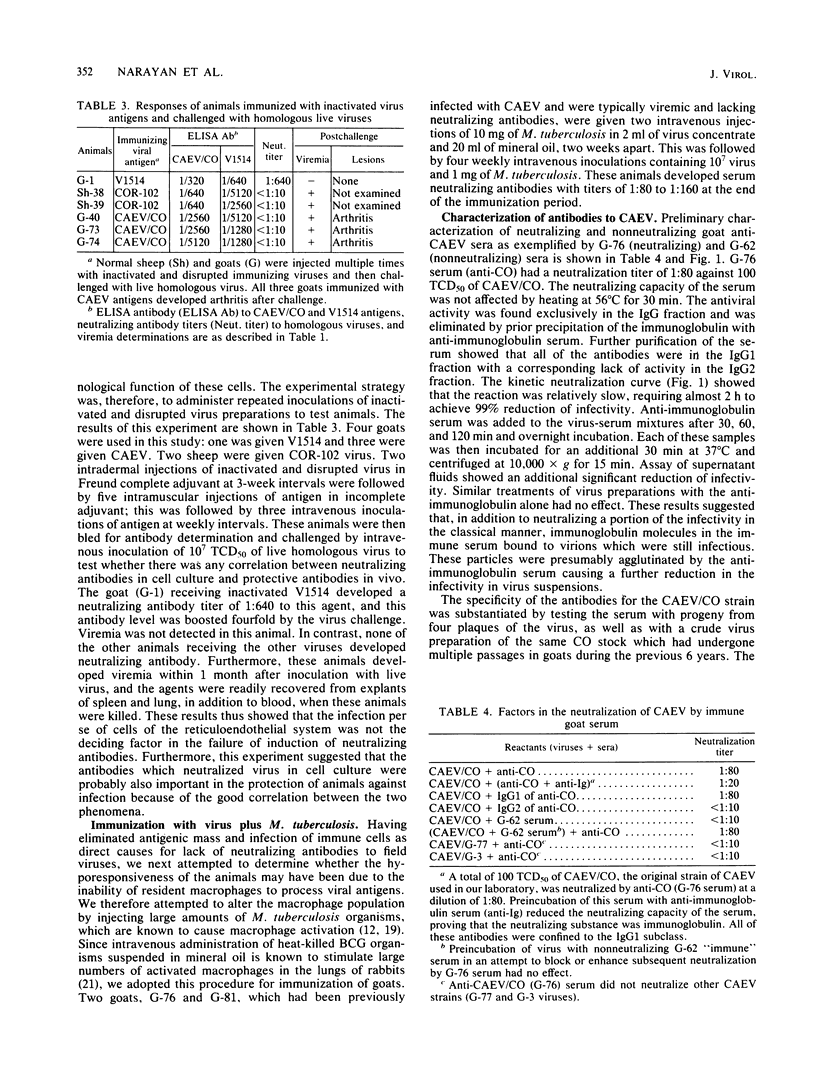
The pathogenesis of the persistent progressive diseases of sheep (visna-maedi) and goats (arthritis-encephalitis) is dependent on continuous replication of the causative lentiviruses. One subgroup of these viruses, Icelandic visna virus, accomplishes this form of replication by undergoing antigenic mutation. Mutant viruses arising late in the infection escape neutralization by antibodies directed to the parental virus. In contrast, we show here that viruses obtained from persistently infected sheep and goats with natural disease in this country do not induce virus-neutralizing antibodies, although antibodies to virus core proteins were produced. The lack of neutralizing antibodies was not overcome by hyperimmunization of animals with concentrated preparations of live or inactivated virus. Thus, failure to produce these specific antibodies was not due to lack of sufficient antigen or interference with the immune response because of the ability of these viruses to infect macrophages. The hyporesponsive state, however, was overcome by immunization of animals with virus and large amounts of inactivated Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Induction of agglutinating and neutralizing antibodies by this method was probably due to a unique form of antigen processing by macrophages activated by M. tuberculosis. Neutralizing antibodies were produced for the first time against the caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus by this method. These antibodies have similar biological properties to those induced by Icelandic visna virus. They belong to the immunoglobulin G1 subclass, they are effective against a narrow range of caprine arthritis-encephalitis viruses, and they identify (for the first time) antigenic variants among these caprine agents.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. S., Crawford T. B., Banks K. L., McGuire T. C., Perryman L. E. Immune responses of goats persistently infected with caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.421-427.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Studies of the macrophage complement receptor. Alteration of receptor function upon macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1278–1290. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Stowring L., Ventura P., Haase A. T. Gene expression in visna virus infection in sheep. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):240–242. doi: 10.1038/292240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan A. M. Atypical colony-like structures developing in control media and in clinical L-form cultures containing serum. Vet Microbiol. 1982 Mar;7(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(82)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., D'Antonio N., Narayan O. Genomic changes associated with antigenic variation of visna virus. II. Common nucleotide sequence changes detected in variants from independent isolations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):415–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. E., Narayan O., Cork L. C. Biochemical characterization of the virus causing leukoencephalitis and arthritis in goats. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):423–427. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggins L. African swine fever virus. Pathogenesis. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):48–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Hadlow W. J., Crawford T. B., Gorham J. R., Piper R. C. Infectious leukoencephalomyelitis of young goats. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):134–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Narayan O. The pathogenesis of viral leukoencephalomyelitis-arthritis of goats. I. Persistent viral infection with progressive pathologic changes. Lab Invest. 1980 Jun;42(6):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford T. B., Adams D. S., Cheevers W. P., Cork L. C. Chronic arthritis in goats caused by a retrovirus. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):997–999. doi: 10.1126/science.6153243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer G. F. Zwoegerziekte virus, the causative agent for progressive interstitial pneumonia (maedi) and meningo-leucoencephalitis (visna) in sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1975 Jan;18(1):15–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Erbs C. Biochemical and functional characteristics of the plasma membrane of macrophages from BCG-infected mice. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1532–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Baringer J. R. The structural polypeptides of RNA slow viruses. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Stowring L., Narayan P., Griffin D., Price D. Slow persistent infection caused by visna virus: role of host restriction. Science. 1977 Jan 14;195(4274):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.188133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. Elimination of Leishmania donovani amastigotes by activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):918–926. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.918-926.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevjer-Anderson P., McGuire T. C. Neutralizing antibody response of rabbits and goats to caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.455-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Ewalt L. C. Induction of enhanced resistance against encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mice by nonviable Mycobacterium tuberculosis: mechanisms of protection. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):740–745. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.740-745.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q. N., LEAKE E. S., OSHIMA S. A study of macrophages and epitheloid-like cells from granulomatous (BCG-induced) lungs of rabbits. J Immunol. 1962 Nov;89:745–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. D., Thormar H. Comparative studies of Visna and Maedi viruses as antigens. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.829-834.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Virus mutation during 'slow infection': temporal development and characterization of mutants of visna virus recovered from sheep. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):343–352. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Virus mutation during 'slow infection': temporal development and characterization of mutants of visna virus recovered from sheep. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):343–352. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Sheffer D., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Activation of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus expression during maturation of monocytes to macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.67-73.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Wolinsky J. S., Clements J. E., Strandberg J. D., Griffin D. E., Cork L. C. Slow virus replication: the role of macrophages in the persistence and expression of visna viruses of sheep and goats. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):345–356. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Stowring L., Haase A. T., Narayan O., Vigne R. Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



