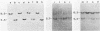Abstract
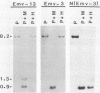
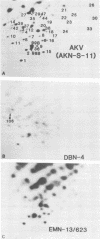
Endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus expression varies with inbred mouse strain and age. The mechanism(s) regulating virus expression is unknown, but expression is thought to be controlled at the transcriptional level by linkage to cis-acting cellular DNA sequences or DNA methylation or both. To begin to differentiate between these different control mechanisms, we molecularly cloned two endogenous ecotropic proviruses, Emv-3 and Emv-13, complete with flanking cellular DNA sequences. Both proviruses are poorly expressed in vivo and in vitro, although they appear to be structurally nondefective by restriction enzyme analysis. Cloned DNAs of both proviruses were poorly infectious in DNA transfection experiments, suggesting that methylation may not regulate the expression of these genes in vivo. Removal of their flanking cellular sequences did not increase their infectivity. However, these DNAs were highly infectious when mixed together, indicating that both proviruses carry mutations, that inhibit their expression and belong to different complementation groups. Marker rescue experiments suggested that Emv-3 is defective in the gag region and Emv-13 is defective in p15E-U3. The infectivity of Emv-3, but not of Emv-13, DNA was increased by the addition of AKR xenotropic murine leukemia virus DNA, consistent with known regions of homology between ecotropic and xenotropic proviruses. Recombination between defective endogenous viruses also appears to occur in vivo, suggesting that this may be a common mechanism controlling endogenous murine leukemia virus expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Independent segregation of loci for activation of biologically distinguishable RNA C-type viruses in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2055–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Scolnick E. M. Induction of murine C-type viruses from clonal lines of virus-free BALB-3T3 cells. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):157–159. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedigian H. G., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Salvatore K., Rodick S. Emv-13 (Akv-3): a noninducible endogenous ecotropic provirus of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):490–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.490-497.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabradilla C. D., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. Induction of mouse type-C virus by translational inhibitors: evidence for transcriptional derepression of a specific class of endogenous virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4541–4545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Tsichlis P. N., Conklin K. F., Senior A., Robinson H. L. Genomes of endogenous and exogenous avian retroviruses. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):51–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin K. F., Coffin J. M., Robinson H. L., Groudine M., Eisenman R. Role of methylation in the induced and spontaneous expression of the avian endogenous virus ev-1: DNA structure and gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):638–652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Cooper G. M. Transfection by exogenous and endogenous murine retrovirus DNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L., Sternberg N. In vitro packaging of lambda Dam vectors and their use in cloning DNA fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:281–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann J. W., Steffen D., Gusella J., Tabin C., Bird S., Cowing D., Weinberg R. A. DNA methylation affecting the expression of murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):144–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.144-157.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Buckler C. E., Sears J. F., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Organization and stability of endogenous xenotropic murine leukemia virus proviral DNA in mouse genomes. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.473-477.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D. R. Molecular cloning of AKR xenotropic murine leukemia virus unintegrated proviral DNA. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Stewart C. L., Harbers K., Löhler J., Simon I., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation and expression of retroviral genomes during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):623–628. doi: 10.1038/298623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Crowther R., Straceski A., Haseltine W. Nucleotide sequence of the Akv env gene. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):519–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.519-529.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R. Infectious murine leukemia virus from DNA of virus-negative AKR mouse embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5539–5543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rowe W. P., Teich N., Hartley J. W. Murine leukemia virus: high-frequency activation in vitro by 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease cleavage (update). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r169–r173. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.235-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J., Horowitz J. M., Risser R. Structure and expression of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia viruses in RF/J mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1461–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J., Risser R. Allelism and linkage studies of murine leukemia virus activation genes in low leukemic strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1233–1238. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J., Risser R. Genetic interactions in induction of endogenous murine leukemia virus from low leukemic mice. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):881–888. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier H., Myers D. D., Huebner R. J. Genetic control by the hr-locus of susceptibility and resistance to leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):759–766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. High-efficiency ligation and recombination of DNA fragments by vertebrate cells. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):606–609. doi: 10.1126/science.6301012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø B. A., Ulrich K. Variants of type-C retroviruses from DBA/2 mice: protein-structural and biological properties. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):454–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Sugahara T. 5-Azacytidine induction of mouse endogenous type C virus and suppression of DNA methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6290–6294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Mapping of alterations in noninfectious proviruses of spleen necrosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):138–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.138-149.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Spontaneous changes in nucleotide sequence in proviruses of spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1230–1234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Rowe W. P., Lilly F. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. II. Apparent identity to a major locus described for resistance to friend murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1234–1241. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rands E., Lowy D. R., Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. Restriction endonuclease mapping of ecotropic murine leukemia viral DNAs: size and sequence heterogeneity of the long terminal repeat. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of Akv-1 and Akv-2 type C viruses of AKR mice. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):690–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.690-694.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Hartley J. W. Studies of genetic transmission of murine leukemia virus by AKR mice. II. Crosses with Fv-1 b strains of mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1286–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Kozak C. A. Germ-line reinsertions of AKR murine leukemia virus genomes in Akv-1 congenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4871–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Harbers K., Chumakov I., Jaenisch R. Endogenous Moloney leukemia virus in nonviremic Mov substrains of mice carries defects in the proviral genome. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Taylor B. A., Weinberg R. A. Continuing germ line integration of AKV proviruses during the breeding of AKR mice and derivative recombinant inbred strains. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.165-175.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Infectivity and methylation of retroviral genomes is correlated with expression in the animal. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson J. A., Laipis P. J., Stein G. S., Stein J. L., Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. Regulation of endogenous type C viruses: evidence for transcriptional control of AKR viral expression. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):529–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]