Abstract
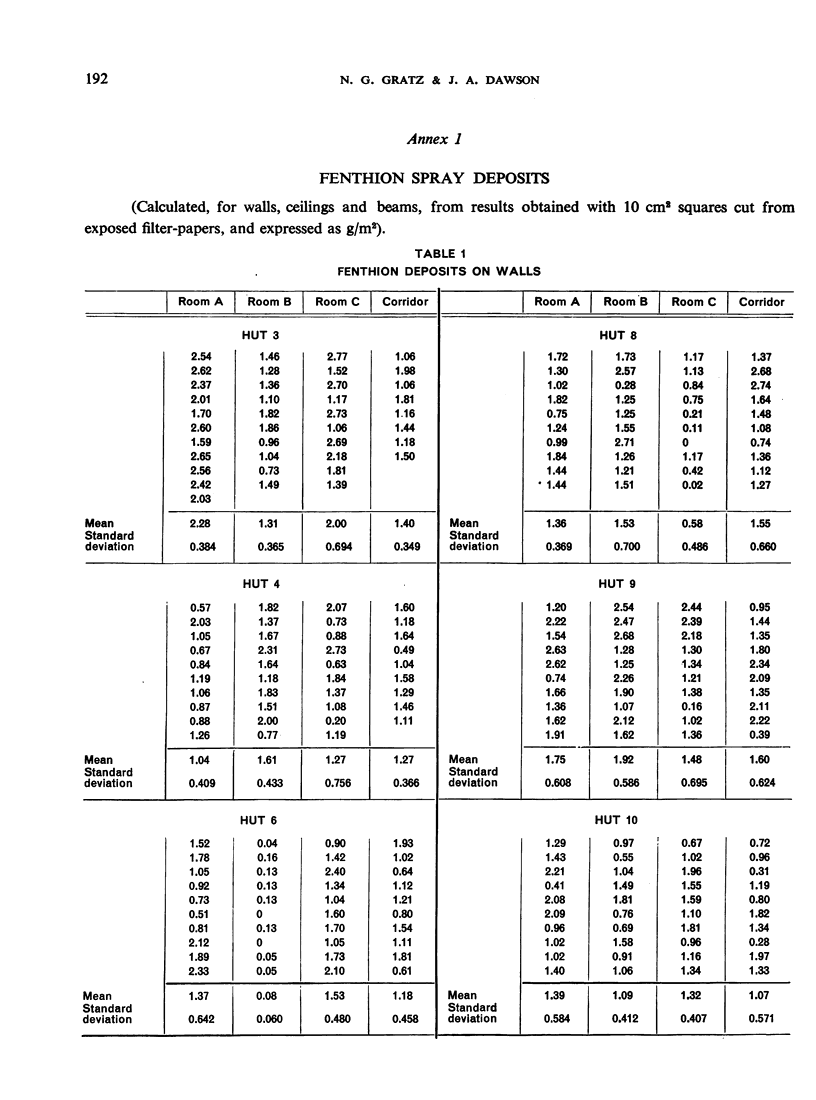
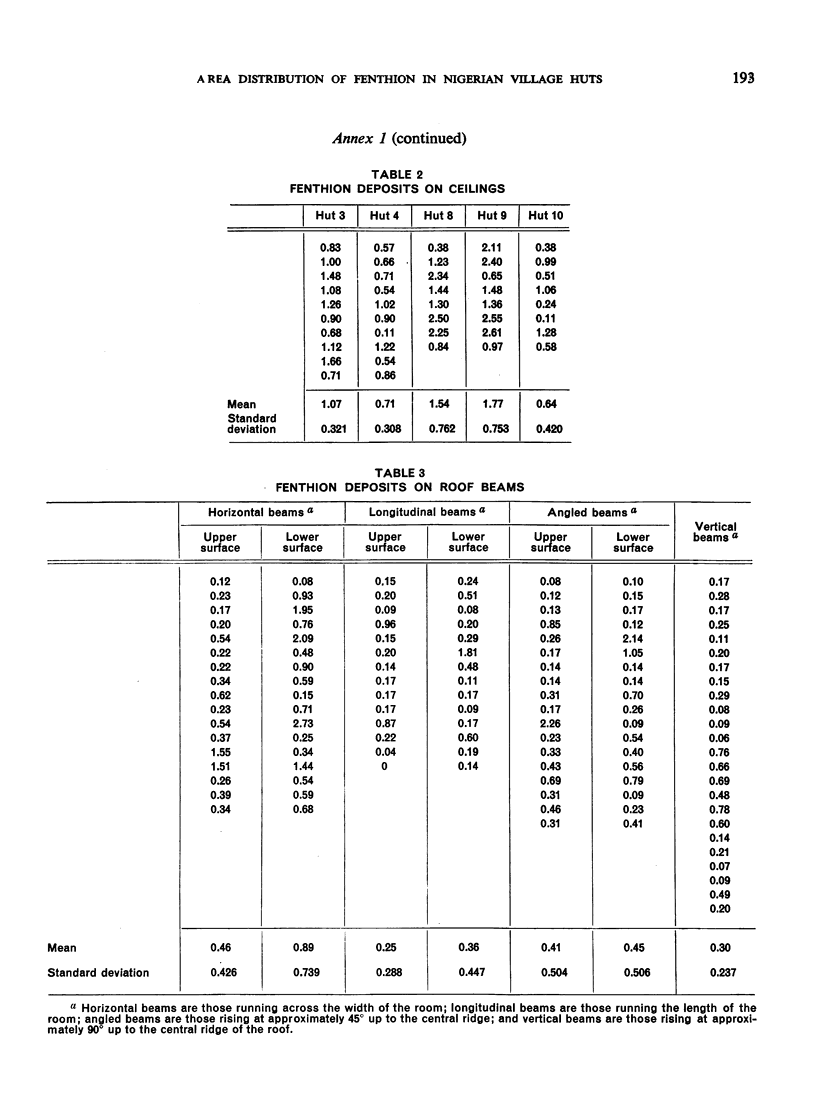
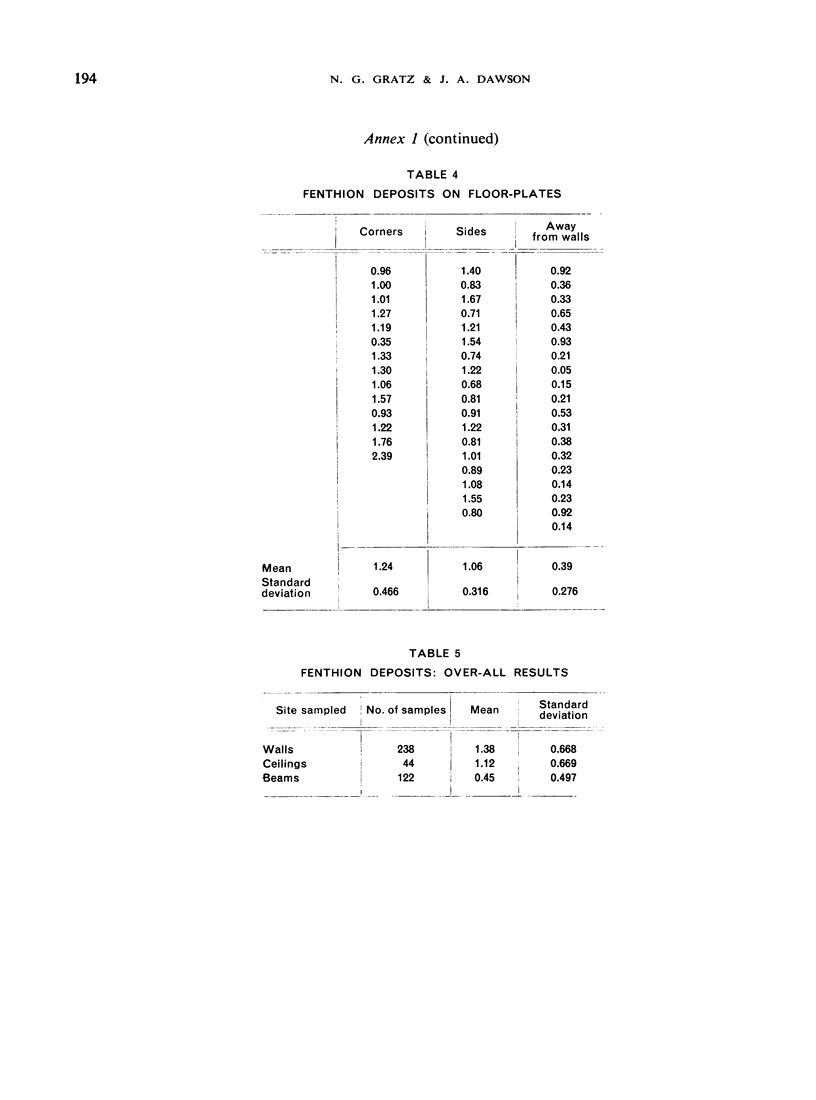
In the course of a village-scale trial of fenthion, carried out in a village near Lagos, Nigeria, 40% fenthion water-dispersible powder was used at a 3.75% concentration. This was applied by Galeazzi “OM” sprayers with constant-pressure assemblies. The target concentration was 1.5 g/m2. Filter-papers were placed on walls, ceilings and roof beams to determine the actual average rate of application, and glass plates were placed on the floors to determine the rate of “bounce-off” from the walls or of “drop-out” from the ceilings. The results of chemical tests show that the rate actually applied came closest to the target concentration on the walls, followed, in that order, by ceilings and roof beams. There were heavy deposits on the floors up to 30 cm away from the walls. The authors analyse the causes for the variations encountered.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNETT G. F., WOODCOCK K. E. The choice of nozzles for spraying buildings with residual insecticides. East Afr Med J. 1956 Feb;33(2):54–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE H. R., WALKER K. C., ELLIOTT J. W., DURHAM W. F. Evaluation of the health hazards involved in house-spraying with DDT. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20(1):1–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]